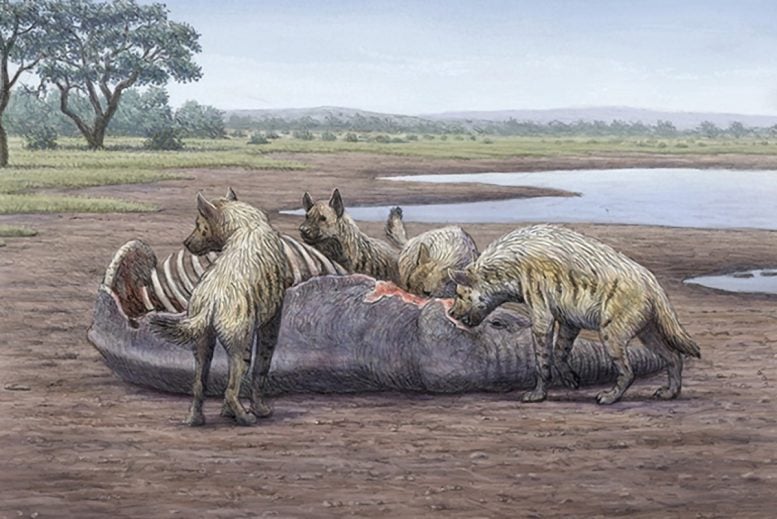
Analysis from the College of Malaga finds that the Orce archaeological web site functioned as a herbal entice for massive mammals right through the Early Pleistocene, marking a vital web site for human job and survival methods in Western Europe. Credit score: Dibujo Mauricio Antón Hienas+Mamut-ColorLocated at Fuente Nueva-3, this Early Pleistocene archaeological web site hosts one of the oldest lines of human habitation in Western Europe.Researchers on the College of Malaga have printed, in an exceptional method, that the Early Pleistocene archaeological web site of Orce, frequently known as the ‘elephant graveyard’ because of the abundance of stays from the extinct elephant species Mammuthus meridionalis, in reality hid a herbal entice within the type of quicksand.The web site of Fuente Nueva 3 (FN3), situated within the northeastern margin of the Guadix-Baza Melancholy (Granada), is likely one of the deposits of Orce that incorporates one of the earliest proof of human presence in Western Europe –consisting of lithic assemblages, this is, stones carved through our ancestors– this is dated to 1,000,000 400 thousand years in the past.Likewise, this archaeological web site preserves manuports –unmodified stones used as percussion equipment to fracture bones and get admission to the marrow and, in all probability, extensively utilized as throwing guns to scare away hyenas– and ample fossils of enormous mammals, a few of which maintain anthropogenic marks associated with skinning, butchering, and marrow processing. And likewise bones with enamel marks led to through scavenging carnivores.The result of this pioneering analysis have not too long ago been revealed in Iberian Magazine of Geology.Two archaeological levelsAccording to this find out about, co-led through Complete Professor of Paleontology on the UMA Paul Palmqvist and Professor of Stratigraphy and Paleontology on the UMA María Patrocinio Espigares, the fertile layers of this web site have two other archaeological ranges: decrease (LAL) and higher (UAL). Each ranges maintain ample skeletal stays and lithic equipment. Then again, whilst the primary one presentations a prime density of manuports, which implies that hominin job used to be extra intense at this stage, the second preserves many stays of megaherbivores, in particular, the extinct elephants Mammuthus meridionalis, which issues to a better involvement of the enormous hyenas.
Analysis from the College of Malaga finds that the Orce archaeological web site functioned as a herbal entice for massive mammals right through the Early Pleistocene, marking a vital web site for human job and survival methods in Western Europe. Credit score: Dibujo Mauricio Antón Hienas+Mamut-ColorLocated at Fuente Nueva-3, this Early Pleistocene archaeological web site hosts one of the oldest lines of human habitation in Western Europe.Researchers on the College of Malaga have printed, in an exceptional method, that the Early Pleistocene archaeological web site of Orce, frequently known as the ‘elephant graveyard’ because of the abundance of stays from the extinct elephant species Mammuthus meridionalis, in reality hid a herbal entice within the type of quicksand.The web site of Fuente Nueva 3 (FN3), situated within the northeastern margin of the Guadix-Baza Melancholy (Granada), is likely one of the deposits of Orce that incorporates one of the earliest proof of human presence in Western Europe –consisting of lithic assemblages, this is, stones carved through our ancestors– this is dated to 1,000,000 400 thousand years in the past.Likewise, this archaeological web site preserves manuports –unmodified stones used as percussion equipment to fracture bones and get admission to the marrow and, in all probability, extensively utilized as throwing guns to scare away hyenas– and ample fossils of enormous mammals, a few of which maintain anthropogenic marks associated with skinning, butchering, and marrow processing. And likewise bones with enamel marks led to through scavenging carnivores.The result of this pioneering analysis have not too long ago been revealed in Iberian Magazine of Geology.Two archaeological levelsAccording to this find out about, co-led through Complete Professor of Paleontology on the UMA Paul Palmqvist and Professor of Stratigraphy and Paleontology on the UMA María Patrocinio Espigares, the fertile layers of this web site have two other archaeological ranges: decrease (LAL) and higher (UAL). Each ranges maintain ample skeletal stays and lithic equipment. Then again, whilst the primary one presentations a prime density of manuports, which implies that hominin job used to be extra intense at this stage, the second preserves many stays of megaherbivores, in particular, the extinct elephants Mammuthus meridionalis, which issues to a better involvement of the enormous hyenas. This find out about has been co-led through Complete Professor of Paleontology on the UMA Paul Palmqvist and Professor of Stratigraphy and Paleontology on the UMA María Patrocinio EspigaresThus, those scientists have analyzed the statistical variations within the composition of the faunal assemblages preserved in those two ranges and the sedimentology, particularly the particle dimension within the fertile layers of each ranges. The latter is a key facet within the analysis, because it presentations a predominance of silts and clays in layers 2-3 of the decrease stage, and superb and really superb sands in layer 5 of the higher stage.“Those superb sand sediments, deposited just about the paleolake that used to be within the area, would additionally include rather saline water, a combination that explains that they might have labored as quicksand, the place better animals have been trapped,” mentioned the UMA scientists.Meals for scavengersTherefore, mavens indicate that the latter stage could also be interpreted as a herbal quicksand entice during which megaherbivores have been trapped because of the increased weight in their limbs, and their half-sunken carcasses attracted the scavengers, each hyenas and people, which ate up those and left their lithic assemblages and coprolites –fossilized excrement of hyenas– as proof in their presence.The brand new discovering came upon through UMA researchers represents a “essential milestone to achieve extra wisdom in regards to the subsistence methods of our ancestors, the primary Europeans, and their pageant with the huge carrion hyenas for get admission to to those meat assets, since it’s the first time a herbal entice with those traits has been described in a fossil deposit of particular hobby to human evolution.”Sporting out extra detailed research differentiating the higher and decrease archaeological ranges, in addition to characterizing different essential websites within the Orce area, corresponding to Barranco León, which additionally contributes proof of human presence, are the following steps deliberate through this medical group of the UMA, during which researchers from the Complutense College of Madrid and Tarragona additionally take part.Greater than a decade of UMA analysis in OrceThe College of Malaga has been researching the web site of Fuente Nueva 3 for a number of many years. The primary e-newsletter of the UMA that highlighted the importance of this position, in 2013, described a partial elephant skeleton surrounded partially through flint flakes and coprolites, testifying to the contest between those two super-scavengers for the carcass assets.Reference: “The past due Early Pleistocene web site of Fuente Nueva-3 (Guadix-Baza Melancholy, SE Spain): a hyena latrine evolved on a quicksand entice for megaherbivores?” through Paul Palmqvist, Isidoro Campaña, Alejandro Granados, Bienvenido Martínez-Navarro, Alejandro Pérez-Ramos, Guillermo Rodríguez-Gómez, Antonio Guerra-Merchán, Sergio Ros-Montoya, María Dolores Rodríguez-Ruiz, José Manuel García-Aguilar, Víctor Hernández and M. Patrocinio Espigares, 26 Might 2024, Magazine of Iberian Geology.
This find out about has been co-led through Complete Professor of Paleontology on the UMA Paul Palmqvist and Professor of Stratigraphy and Paleontology on the UMA María Patrocinio EspigaresThus, those scientists have analyzed the statistical variations within the composition of the faunal assemblages preserved in those two ranges and the sedimentology, particularly the particle dimension within the fertile layers of each ranges. The latter is a key facet within the analysis, because it presentations a predominance of silts and clays in layers 2-3 of the decrease stage, and superb and really superb sands in layer 5 of the higher stage.“Those superb sand sediments, deposited just about the paleolake that used to be within the area, would additionally include rather saline water, a combination that explains that they might have labored as quicksand, the place better animals have been trapped,” mentioned the UMA scientists.Meals for scavengersTherefore, mavens indicate that the latter stage could also be interpreted as a herbal quicksand entice during which megaherbivores have been trapped because of the increased weight in their limbs, and their half-sunken carcasses attracted the scavengers, each hyenas and people, which ate up those and left their lithic assemblages and coprolites –fossilized excrement of hyenas– as proof in their presence.The brand new discovering came upon through UMA researchers represents a “essential milestone to achieve extra wisdom in regards to the subsistence methods of our ancestors, the primary Europeans, and their pageant with the huge carrion hyenas for get admission to to those meat assets, since it’s the first time a herbal entice with those traits has been described in a fossil deposit of particular hobby to human evolution.”Sporting out extra detailed research differentiating the higher and decrease archaeological ranges, in addition to characterizing different essential websites within the Orce area, corresponding to Barranco León, which additionally contributes proof of human presence, are the following steps deliberate through this medical group of the UMA, during which researchers from the Complutense College of Madrid and Tarragona additionally take part.Greater than a decade of UMA analysis in OrceThe College of Malaga has been researching the web site of Fuente Nueva 3 for a number of many years. The primary e-newsletter of the UMA that highlighted the importance of this position, in 2013, described a partial elephant skeleton surrounded partially through flint flakes and coprolites, testifying to the contest between those two super-scavengers for the carcass assets.Reference: “The past due Early Pleistocene web site of Fuente Nueva-3 (Guadix-Baza Melancholy, SE Spain): a hyena latrine evolved on a quicksand entice for megaherbivores?” through Paul Palmqvist, Isidoro Campaña, Alejandro Granados, Bienvenido Martínez-Navarro, Alejandro Pérez-Ramos, Guillermo Rodríguez-Gómez, Antonio Guerra-Merchán, Sergio Ros-Montoya, María Dolores Rodríguez-Ruiz, José Manuel García-Aguilar, Víctor Hernández and M. Patrocinio Espigares, 26 Might 2024, Magazine of Iberian Geology.
DOI: 10.1007/s41513-024-00241-1
1.4 Million-Yr-Previous Human Job Unearthed at Orce’s Quicksand Entice