Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the largest questions of all
Some of the unexpected discoveries in all of astronomical historical past took place just about a complete century in the past: after we came upon that the remote galaxies in our Universe aren’t desk bound, however are mutually receding from one every other. This realization first happened in 1927, and has since been interpreted to imply that the Universe is increasing, with the distance between galaxies, galaxy teams, and galaxy clusters “stretching” to larger and bigger distances as time continues onward. For many of the twentieth century, the primary quest of cosmology used to be to measure two parameters: how briskly the Universe used to be increasing at this time, and the way that growth charge modified and developed through the years.Within the past due Nineteen Nineties and early 2000s, either one of the ones questions had been in any case spoke back with sufficiently just right information. Our Universe used to be increasing at a charge of round 72 km/s/Mpc, with an uncertainty of solely round 10%, and the recession velocity of a far off galaxy wasn’t reducing as we anticipated, however used to be in truth expanding as time is going on. The latter discovery used to be an incredible marvel, and forced us so as to add a brand new species of power — darkish power — to our conception of the Universe. In 2011, the Nobel Prize in physics used to be awarded for precisely that discovery, with Saul Perlmutter, Adam Riess, and Brian Schmidt sharing the accolades.Then again, within the time since then, a brand new puzzle over the increasing Universe has arisen, and it has rapidly turn out to be most likely probably the most confounding conundrum in cosmology as of late: the Hubble rigidity. The ‘raisin bread’ fashion of the increasing Universe, the place relative distances building up as the distance (dough) expands. The farther away any two raisins are from one every other, the higher the seen redshift might be by the point the sunshine is gained. The redshift-distance relation predicted by means of the increasing Universe is borne out in observations, however other strategies of measuring the cosmic growth yield other, incompatible effects.
The ‘raisin bread’ fashion of the increasing Universe, the place relative distances building up as the distance (dough) expands. The farther away any two raisins are from one every other, the higher the seen redshift might be by the point the sunshine is gained. The redshift-distance relation predicted by means of the increasing Universe is borne out in observations, however other strategies of measuring the cosmic growth yield other, incompatible effects.
Credit score: Ben Gibson/Giant Assume; Adobe Inventory
The Hubble rigidity arises from the truth that there are two essentially other categories of way for measuring how briefly the Universe is increasing as of late. You’ll both:
start within sight, by means of measuring stars in our galaxy immediately, then measuring those self same forms of stars in a special galaxy, after which the usage of some belongings or object inside the ones galaxies to increase our succeed in to the remote Universe,
or you’ll start a ways away, in a while after the Giant Bang, with an early relic sign that used to be imprinted onto the Universe, after which measure how that relic sign has developed through the years because the Universe has expanded.
The primary way is referred to as the gap ladder way, and reliably yields a ramification charge of 73 km/s/Mpc, with the most productive (lowest-uncertainty) way offering that price to a precision of about ~1%. The second one way, in the meantime, is referred to as the early relic way, and yields a price of round 67 km/s/Mpc, once more with an uncertainty of simply ~1%.Then again, a contemporary learn about has claimed to discover a price of 68 km/s/Mpc for the growth charge whilst the usage of the gap ladder way; a consequence that looks to “get to the bottom of” the Hubble rigidity by means of bringing the consequences from the 2 more than a few strategies into settlement. I took an in-depth take a look at this factor for myself (and you’ll learn that evaluation right here), concluding that the learn about had some crucial flaws — unquantified systematic mistakes, a pattern variety bias, a small pattern measurement, and so forth. — that it didn’t deal with, and that the Hubble rigidity remained as sturdy as ever.Then again, my skilled talent to guage such issues has its limits; I’m no longer a professional on the subject of observational cosmology, despite the fact that I do know rather a couple of people who find themselves. It used to be with that objective in thoughts that I contacted Nobel Laureate Adam Riess, who agreed to do a question-and-answer with me about precisely this matter. Listed here are the culmination of that alternate.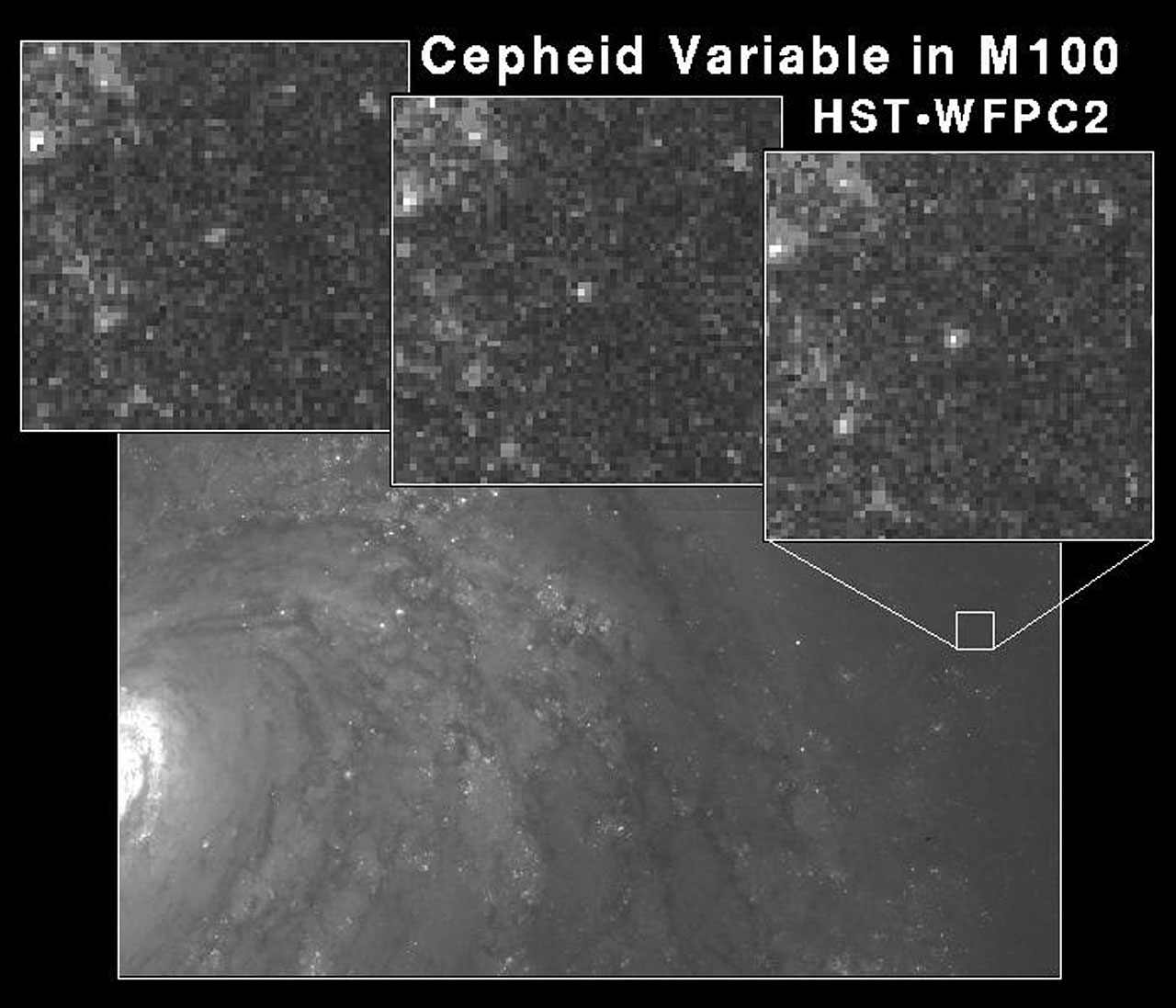 This Hubble Area Telescope symbol of a area within the galaxy M100 displays a category of pulsating superstar known as a Cepheid variable. Even though uncommon, those stars have an intrinsic courting between the era in their variability and their inherent brightness, enabling them for use as extremely dependable distance signs to remote galaxies.
This Hubble Area Telescope symbol of a area within the galaxy M100 displays a category of pulsating superstar known as a Cepheid variable. Even though uncommon, those stars have an intrinsic courting between the era in their variability and their inherent brightness, enabling them for use as extremely dependable distance signs to remote galaxies.
Credit score: Dr. Wendy L. Freedman, Observatories of the Carnegie Establishment of Washington, and NASA/ESA
Ethan Siegel (ES): Again within the past due Nineteen Nineties and the early 2000s, two vital advances took place in observational cosmology. Certainly one of them used to be that, basically the usage of Cepheid variable stars, we had been ready to exactly decide the growth charge of the Universe: 72 km/s/Mpc, with an uncertainty of simply 8 km/s/Mpc on that quantity, which stood in stark distinction to 2 dominant narratives that the Hubble parameter used to be both 50-55 km/s/Mpc or ~100 km/s/Mpc. Are you able to discuss how enormous that discovery used to be, together with what it intended for our figuring out of ways the Universe used to be increasing and what it taught us about our cosmic previous?Adam Riess (AR): The 1990’s actually began the period of “Precision Cosmology.” The Hubble Area Telescope gave us a brand new superpower, the facility to get to the bottom of particular person Cepheid variable stars in galaxies tens of megaparsecs (30-60 million gentle years) away. Cepheids had been then, and nonetheless are, the gold usual of distance measuring equipment. Two groups led efforts to measure the Hubble consistent (the growth charge of the Universe), the usage of Cepheids to build distance ladders between our native group and deep, increasing house.By way of the top of the early 2000s, the uncertainty within the charge at which the Universe expands, the Hubble consistent, have been lower by means of two-thirds: to a good 10%. The brand new consequence used to be towards the center of the prior vary and used to be a just right have compatibility to our creating new image of the Universe. It taught us that we lived in a Universe that used to be certainly older than the oldest stars in it, which would possibly appear evident in hindsight, however used to be no longer transparent on the time.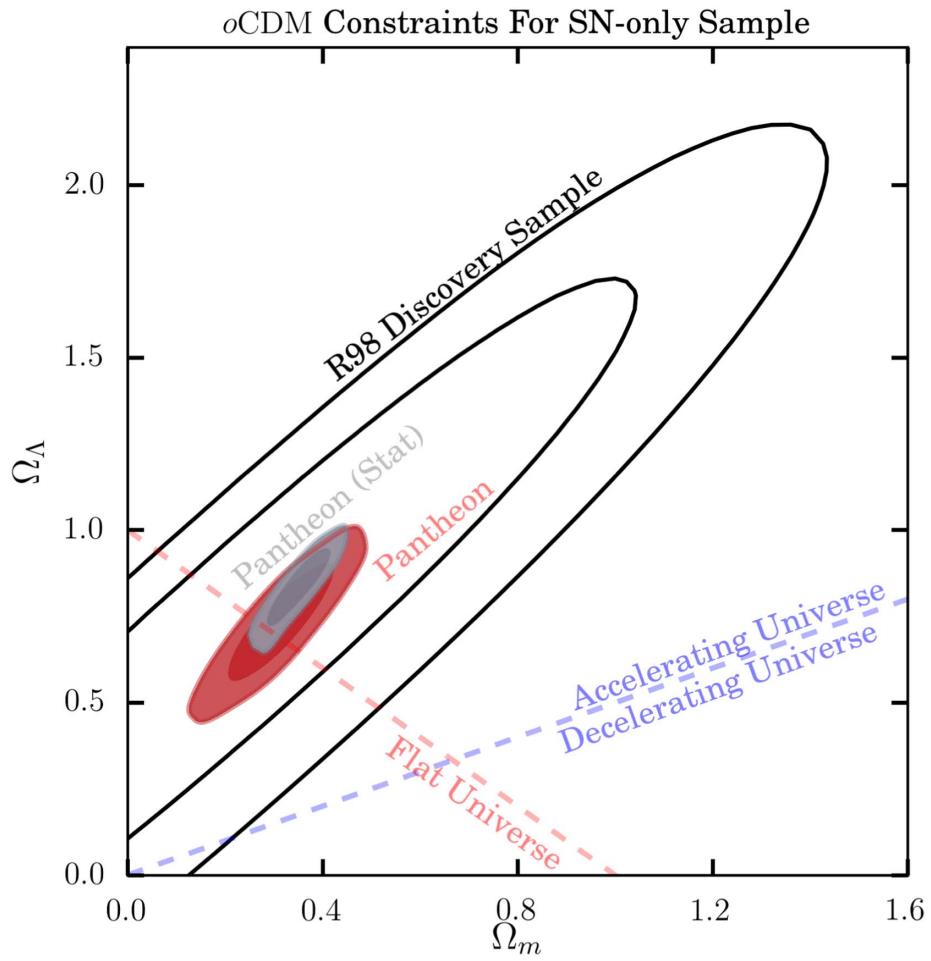 This graph displays the (overwhelming) proof for darkish power’s presence and density, the usage of solely supernova constraints, with out folding in more strains of proof equivalent to large-scale construction or cosmic microwave background information. The unique information from Riess 1998, in black contours (68% and 95% self belief ranges, respectively) are proven along the Pantheon information (in gray and crimson) from two decades later: in 2018.
This graph displays the (overwhelming) proof for darkish power’s presence and density, the usage of solely supernova constraints, with out folding in more strains of proof equivalent to large-scale construction or cosmic microwave background information. The unique information from Riess 1998, in black contours (68% and 95% self belief ranges, respectively) are proven along the Pantheon information (in gray and crimson) from two decades later: in 2018.
Credit score: D.M. Scolnic et al., Astrophysical Magazine, 2018
ES: The opposite used to be that, the usage of remote sort Ia supernovae, we had been ready to decide that the velocity of growth wasn’t proceeding to decelerate as despite the fact that the Universe had been made solely of subject and radiation, however that the growth itself used to be accelerating, indicating the presence of a brand new species of power within the cosmos: darkish power. I do know that it took a few years of collecting information issues sooner than your staff drew the realization that there used to be a brand new species of power provide. What used to be it like behind-the-scenes while you discovered that this information couldn’t be reconciled with a matter-and-radiation-only Universe?AR: Frankly it used to be horrifying. Scientists by means of nature are wary — there are 1,000,000 techniques to get the incorrect reply. However, there are only a few techniques to get it proper. Then you’re doing one thing no person has achieved sooner than, so there’s no reply key at the back of the e-book to test whether or not your reply is true or incorrect. So, while you get a shocking consequence like we did, that most often way you probably did one thing incorrect. Then again, if you’re too cynical and come to a decision the whole thing unexpected is incorrect, you actually can not uncover anything else new. So we spent numerous time double checking our paintings till we knew we had been both proper or incorrect for a fascinating sufficient reason why to post our findings. Following the knowledge quite than your ideals is how unexpected discoveries are made, and it’s wonderful that it has held up for 25 years. This graph displays the 1550 supernovae which might be part of the Pantheon+ research, plotted as a serve as of magnitude as opposed to redshift. The supernova information, for lots of many years now (ever since 1998), has pointed towards a Universe that expands in a selected style that calls for one thing past subject, radiation, and/or spatial curvature: a brand new type of power that drives the growth, referred to as darkish power. The supernovae all fall alongside the road that our usual cosmological fashion predicts, with even the highest-redshift, maximum far-flung sort Ia supernovae adhering to this straightforward relation. Calibrating the relation with out considerable error is of paramount significance.
This graph displays the 1550 supernovae which might be part of the Pantheon+ research, plotted as a serve as of magnitude as opposed to redshift. The supernova information, for lots of many years now (ever since 1998), has pointed towards a Universe that expands in a selected style that calls for one thing past subject, radiation, and/or spatial curvature: a brand new type of power that drives the growth, referred to as darkish power. The supernovae all fall alongside the road that our usual cosmological fashion predicts, with even the highest-redshift, maximum far-flung sort Ia supernovae adhering to this straightforward relation. Calibrating the relation with out considerable error is of paramount significance.
Credit score: D. Brout et al./Pantheon+, Astrophysical Magazine, 2022
ES: Within the time since, many “selection” explanations to darkish power — together with photon oscillations, novel forms of mud, and evolving environments for sort Ia supernovae — were introduced up, however have conflicted with the enhanced, extra complete information. These days, now we have over 1000 sort Ia supernovae came upon at all kinds of distances. Coupled with measurements of the acoustic scale at various distance scales, those information units make an awesome case for darkish power’s presence and abundance: a discovery that you just had been awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for in 2011. In only one era, we’ve long past from no longer understanding that darkish power existed to it being extensively permitted because the dominant type of power in our Universe. What used to be it love to be part of that revolution?AR: Cosmology has at all times addressed large questions, actually the largest. What’s the Universe manufactured from? How did it get started? How lengthy has it been round? How will it finish? Those questions have been round a very long time after I began, so I didn’t suppose that might exchange. So I used to be lucky to witness a in reality modern era in cosmology. Take the invention of darkish power, which seems to make up 70% of our Universe. Best as soon as within the historical past of humankind are we able to actually uncover many of the Universe! This used to be additionally the era when our talent to look the Universe used to be maximum stepped forward, from house telescopes to gravitational wave detectors, it’s been exhilarating to look and be a part of! As a scientist who entered the sector with monumental interest, it’s been and is still my pastime to pursue the solutions to those higher than existence questions.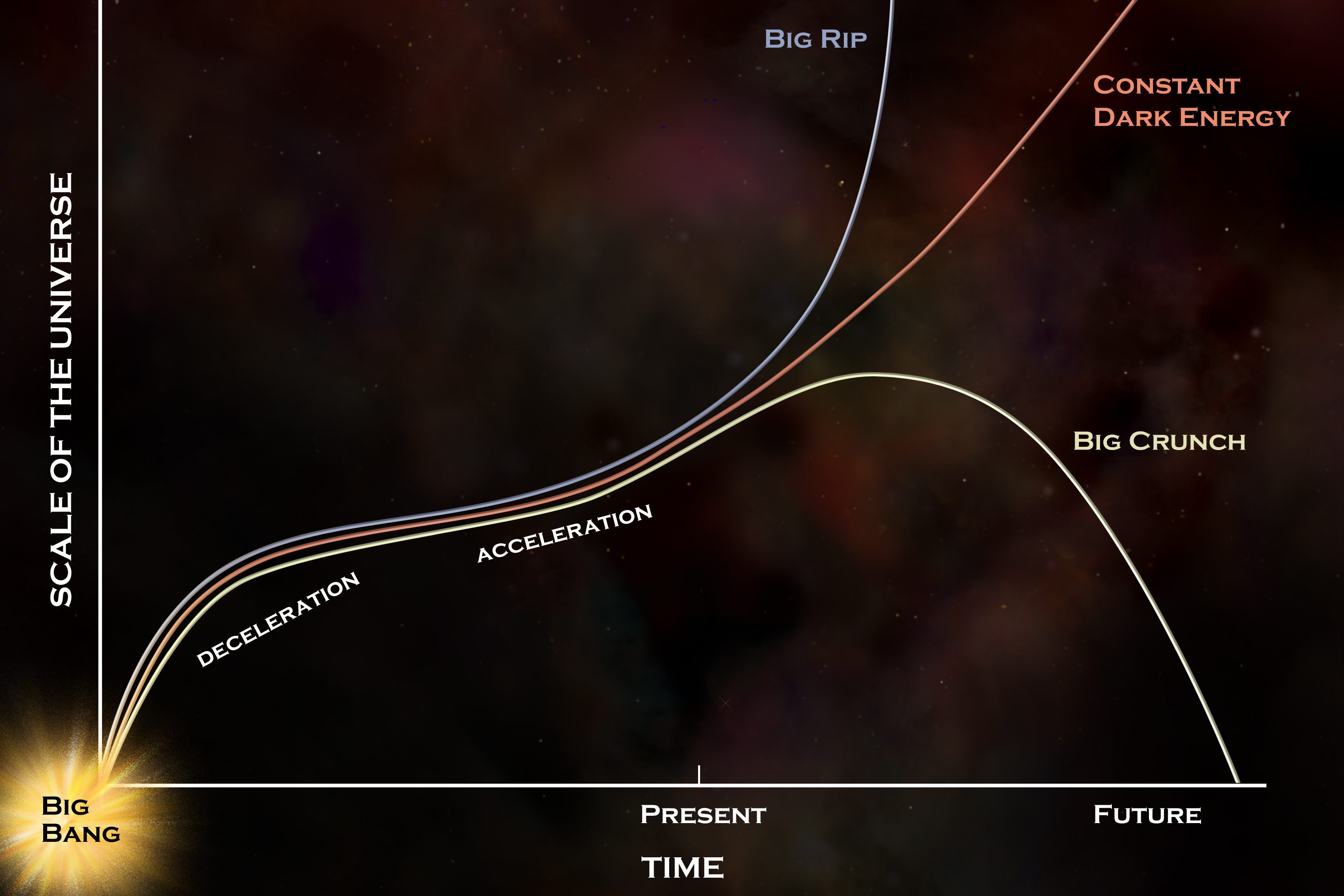 The a ways remote fates of the Universe be offering quite a lot of chances, but when darkish power is in reality a continuing, as the knowledge signifies, it’s going to proceed to observe the crimson curve, resulting in the long-term state of affairs ceaselessly described on Begins With A Bang: of the eventual warmth loss of life of the Universe. If darkish power can fortify, weaken, or opposite signal through the years, alternatively, all bets are off, and selection chances abound.
The a ways remote fates of the Universe be offering quite a lot of chances, but when darkish power is in reality a continuing, as the knowledge signifies, it’s going to proceed to observe the crimson curve, resulting in the long-term state of affairs ceaselessly described on Begins With A Bang: of the eventual warmth loss of life of the Universe. If darkish power can fortify, weaken, or opposite signal through the years, alternatively, all bets are off, and selection chances abound.
Credit score: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss
ES: As is so continuously the case, new discoveries and stepped forward measurements can have equipped solutions to older questions, however have cleared the path for us to invite new, deeper ones. One tantalizing risk that the knowledge now signifies is that darkish power is probably not a cosmological consistent, however in truth is also evolving. Because the co-discoverer of darkish power, what are your ideas at the proof for evolving darkish power, and what wouldn’t it take so that you can persuade your self that darkish power doesn’t possess a continuing power density?AR: Combining all measurements now we have of the cosmic microwave background, supernovae and large-scale buildings hints that darkish power is also fading in energy. It kind of feels slightly like déjà vu as a result of we predict a an identical factor can have took place after the Giant Bang when one of those darkish power inflated the Universe then pale away.Then again, the boldness threshold for this conclusion has no longer but been reached. The excellent news is that we don’t wish to have interaction in an excessive amount of hypothesis because the information which hints this fashion is ready to dramatically fortify within the subsequent couple of years. I will be able to look forward to that. Additionally, new house telescopes are coming on-line — like NASA’s Roman Area Telescope — which can very much fortify our image of darkish power.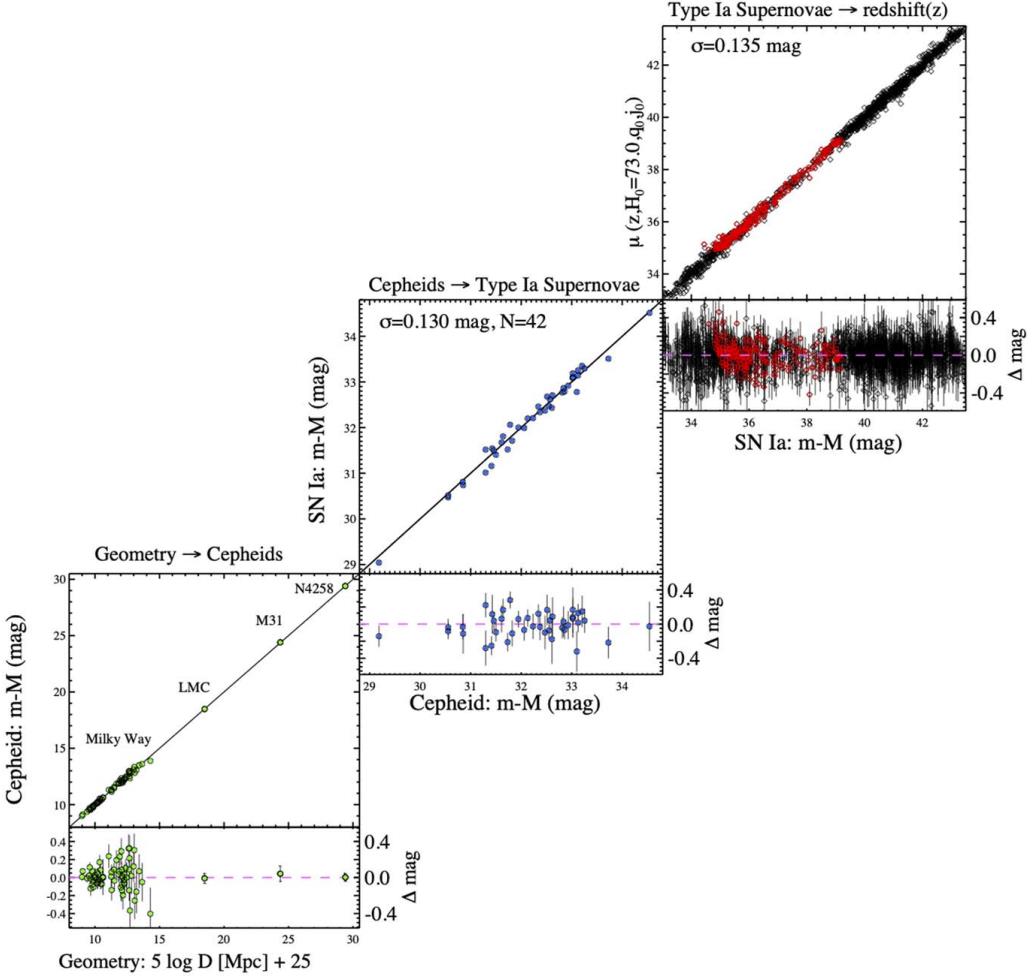 This graphs lays out your entire distance ladder the usage of Cepheids within the Milky Approach and Native Crew (decrease left panel), to galaxies which space each Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae (center panel), to ultra-distant galaxies which might be hosts to sort Ia supernovae (higher proper panel). That is the biggest, maximum complete “whole” distance ladder ever assembled.
This graphs lays out your entire distance ladder the usage of Cepheids within the Milky Approach and Native Crew (decrease left panel), to galaxies which space each Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae (center panel), to ultra-distant galaxies which might be hosts to sort Ia supernovae (higher proper panel). That is the biggest, maximum complete “whole” distance ladder ever assembled.
Credit score: A.G. Riess et al., Astrophysical Magazine Letters, 2022
ES: Some other puzzle that has arisen lately is that two other categories of measurements — with one elegance the usage of the cosmic distance ladder to start out within sight after which regularly leap to larger and bigger distances, and the opposite elegance the usage of baryon-photon oscillations imprinted within the early Universe and following their evolution ahead in time — give very exact, however very other, effects for the growth charge of the Universe as of late. For the “distance ladder” way, that price seems to be round 73 km/s/Mpc, however for the “early relic” way, we get solely 67 km/s/Mpc. Each units of measurements document solely a few ~1% uncertainty on their values, however they range from each and every different by means of about ~9%. What do you suppose this mismatch is telling us concerning the Universe?AR: It’s telling us that there’s something we don’t perceive. We continuously say while you know one thing smartly, you understand it “ahead and backward.” However on this case, after we use our figuring out of the Universe to move ahead or backward in time, we can not make the ends meet. This downside has lasted a decade and is going by means of the identify of the “Hubble rigidity.”No matter is inflicting it, it’s not evident to both scientists like me who make the measurements or to theorists who speculate after which calculate new techniques to glue the start and provide state of the Universe. Some see this as an issue. I believe if we observe the knowledge, it’s a finding out alternative. Those are the forms of puzzles scientists hope for.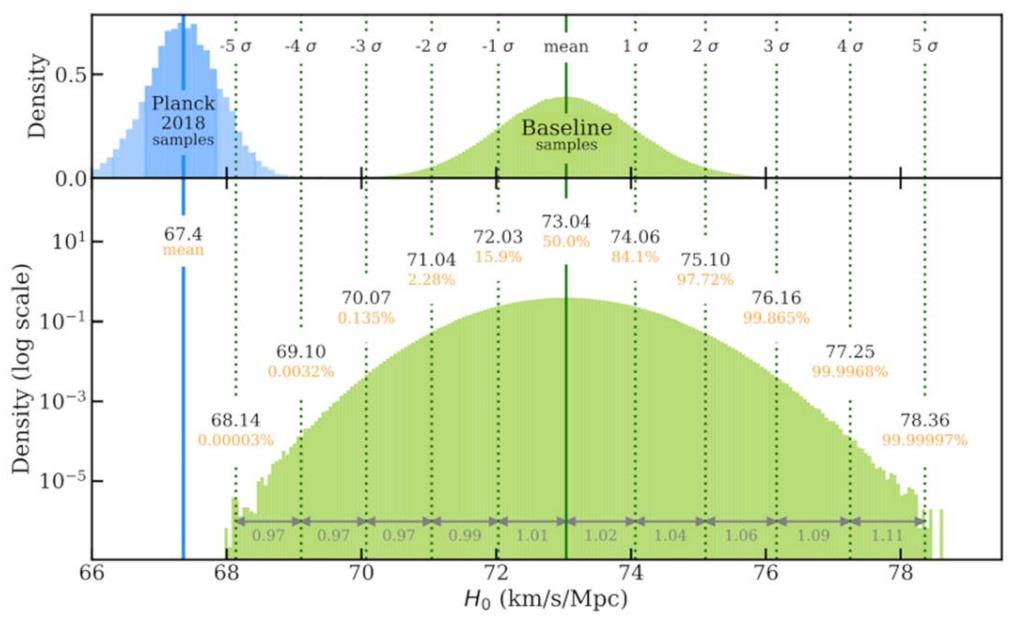 It used to be solely after addressing a huge collection of statistical and systematic problems about Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae, in addition to gathering sufficient galaxies that housed either one of them (there are 42 at this time), that the gap ladder way used to be ready to yield a ramification charge that differed from the early relic (e.g., Planck satellite tv for pc) effects by means of the vaunted five-sigma threshold had to claim a powerful discovery. That threshold used to be crossed in 2022.
It used to be solely after addressing a huge collection of statistical and systematic problems about Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae, in addition to gathering sufficient galaxies that housed either one of them (there are 42 at this time), that the gap ladder way used to be ready to yield a ramification charge that differed from the early relic (e.g., Planck satellite tv for pc) effects by means of the vaunted five-sigma threshold had to claim a powerful discovery. That threshold used to be crossed in 2022.
Credit score: A.G. Riess et al., Astrophysical Magazine Letters, 2022
ES: Many of us through the years — together with me, which I’ll admit — have puzzled whether or not this discrepancy couldn’t simply be the results of having unidentified mistakes in making those distance ladder measurements, together with:
in making parallax measurements of particular forms of stars,
in measuring those self same forms of stars in within sight galaxies,
within the (admittedly small) pattern of galaxies that include each the ones crucial forms of stars and likewise that include sort Ia supernovae,
and in inferring the distances to these within sight galaxies.
Then again, a huge collection of resources of error and uncertainty were stepped forward in recent times. Are you able to let us know concerning the adventure to achieve some degree the place we will in any case claim that this mismatch between other strategies of measuring the increasing Universe (distance ladder vs. early relic) has reached the “gold usual” for statistical importance?AR: Over the past decade, the importance of the discrepancy has grown. It used to be two times the margin of error 10 years in the past when the brand new Planck CMB information first got here out, a threshold we name a “interest.” After a number of extra years of accelerating the pattern of supernova hosts seen with Hubble, it become thrice the margin, what we name a “rigidity,” therefore the identify. Within the closing 5 years the native measurements stepped forward, supported by means of the ESA Gaia undertaking parallaxes (a soar in parallax measurements), every other doubling of the Hubble pattern, extra surveys of remote SNe, new staring at ways, and so forth., in order that as of a few years in the past, the adaptation is greater than 5 occasions the margin of error.That is the edge when scientists say, “This isn’t a fluke, one thing has been discovered!” In parallel, there was a huge effort by means of the group to scrutinize the consequences (as they must), reflect them, and notice if there’s any consensus of a particular downside with the measurements. At this level, the Hubble rigidity may be very transparent and powerful except you’re prepared to discard numerous information, cherry-pick research or samples whilst except others, posit an unknown downside (with out a testable speculation), or invoke a fair more unusual state of affairs, that the Universe is other close to us than in different places. I believe those are all scientifically unhealthy possible choices. I believe the Universe is smarter than we’re, so we’re almost certainly at an advantage believing it.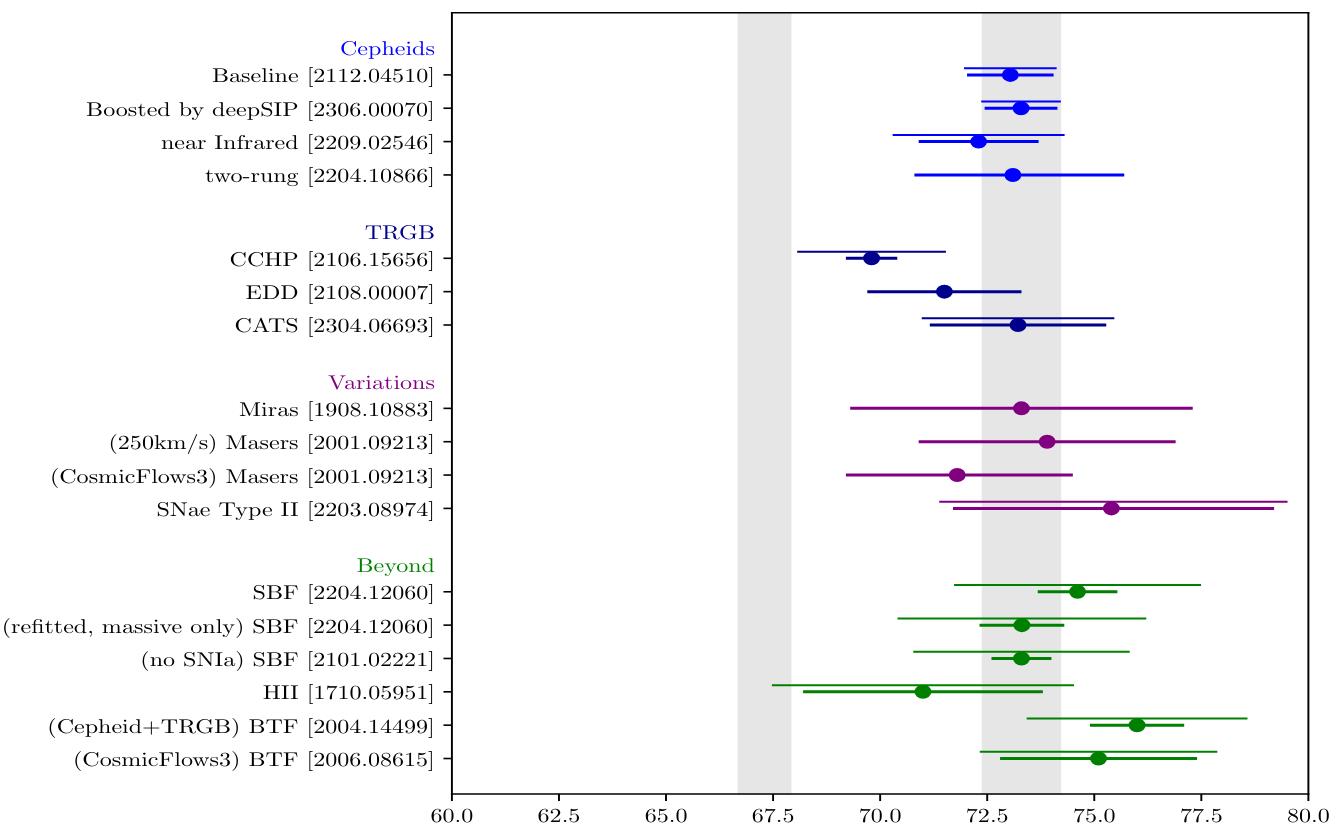 A 2023-era research of the more than a few measurements for the growth charge the usage of distance ladder strategies, depending on which pattern, which research, and which set of signs are used. Notice that the CCHP workforce, the one one to acquire a “low” price of the growth charge, is solely reporting statistical uncertainties, and does no longer quantify their systematic uncertainties at this time. There may be overwhelming consensus settlement that the growth charge is round 73 km/s/Mpc the usage of all kinds of distance ladder strategies.
A 2023-era research of the more than a few measurements for the growth charge the usage of distance ladder strategies, depending on which pattern, which research, and which set of signs are used. Notice that the CCHP workforce, the one one to acquire a “low” price of the growth charge, is solely reporting statistical uncertainties, and does no longer quantify their systematic uncertainties at this time. There may be overwhelming consensus settlement that the growth charge is round 73 km/s/Mpc the usage of all kinds of distance ladder strategies.
Credit score: L. Verde, N. Schoeneberg, and H. Gil-Marin, Annual Evaluations of Astronomy and Astrophysics (permitted), 2023
ES: One not unusual theme that reappears all the way through cosmology debates through the years is the significance of getting more than one unbiased techniques of constructing a crucial dimension or figuring out a parameter of our Universe. For the gap ladder way, there are lots of imaginable techniques to jump from stars inside our galaxy (perfect measured by way of parallax) to stars in within sight galaxies, together with RR Lyrae stars, Cepheid variable stars, or stars in more than a few levels of stellar evolution, equivalent to crimson massive stars or asymptotic massive department stars.In a similar way, whether or not you employ sort Ia supernovae (together with whether or not you employ the Pantheon+ or Carnegie samples), surface-brightness fluctuations, or different homes of a galaxy must all result in the similar effects. Many, together with you, have again and again proven, together with on your most up-to-date paper, that each one of those strategies result in the similar puzzle: a ramification charge of 73 km/s/Mpc, which stays inconsistent with the early relic way that yields 67 km/s/Mpc. What does the truth that all of those strains of proof level to the similar conclusion counsel, on your thoughts?AR: It is extremely useful to have more than one techniques to make the most important dimension. Then again, I might quite have a few superb ones than many unhealthy ones. Fifty years in the past the issue used to be that we had many deficient ones in order that one may just see anything else they sought after within the information, a scenario we name “confirming your priors.” The location is best as of late as the knowledge has sharpened and we will take a look at it piece by means of piece, quite than taking all of it or not anything.Richard Feynman used to advise — make higher measurements of the hints and they are going to both cross away (a fluke) or turn out to be more potent to expose one thing attention-grabbing. The truth that the proof has regularly grown suggests we’re seeing one thing attention-grabbing this is at the sky quite than any evident error or unhealthy dimension. It’s a great time to be curious.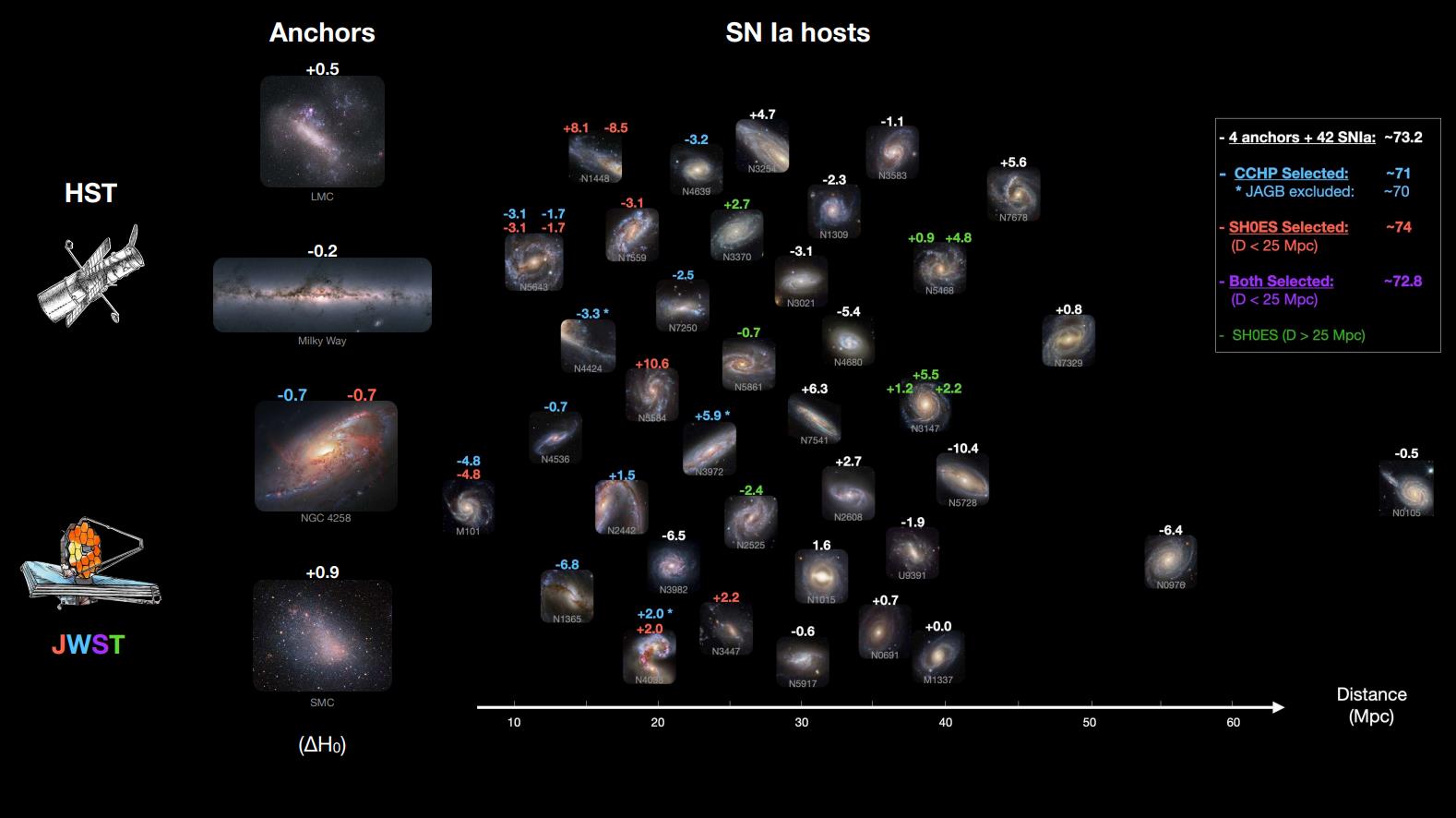 This graphic displays which galaxies which might be used as anchors and include each sort Ia supernovae and Cepheids were imaged by means of Hubble and JWST, respectively. You’ll see the exchange in each and every galaxy’s contribution to the price of the growth charge as of late, H0, by means of together with or except each and every galaxy throughout the complete pattern.
This graphic displays which galaxies which might be used as anchors and include each sort Ia supernovae and Cepheids were imaged by means of Hubble and JWST, respectively. You’ll see the exchange in each and every galaxy’s contribution to the price of the growth charge as of late, H0, by means of together with or except each and every galaxy throughout the complete pattern.
Credit score: A.G. Riess et al., Astrophysical Magazine submitted, arXiv:2408.11770, 2024
ES: A up to date workforce, referred to as CCHP (for Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program), has been an outlier on this regard for a number of years, claiming decrease effects for the growth charge (of between 68 and 70 km/s/Mpc) the usage of massive stars and smaller numbers of galaxies than the bigger Cepheid research. Then again, this workforce has additionally been accused of underestimating (or no longer estimating in any respect) their resources of uncertainty, and their way additionally suffers from a small pattern measurement, the place their effects are the usage of not up to one-fourth of the knowledge this is to be had from Cepheid research. Are you able to give an explanation for why the CCHP’s effects range from all different research, and why you’re skeptical in their claims for an extremely low growth charge?AR: Should you take a look at fresh opinions of the Hubble consistent you’ll see dozens of research starting from 70 to 75 km/s/Mpc. We predict fluctuations so we generally take the imply or median as a perfect estimate. Should you do a typical research with usual error propagation of the entire set of knowledge, you get an excessively sturdy case for rigidity. That conclusion has been extensively replicated and examined. Then again, you’ll prohibit your research to subsets of the entire information you choose which might cut back the price of the Hubble consistent, building up its uncertainty, or each, and loosen up the strain.Then again, I’ve no longer noticed empirical justification or broad make stronger for except information — normally in statistical science except information ends up in bias and I don’t suppose that could be a professional direction to move. I’ve additionally noticed the, uh, quite unconventional error research you consult with. In the end, that stuff gets taken care of, however I believe we wish to watch out to keep away from affirmation bias — like giving higher consideration to the bottom dimension as it’s nearer to what’s anticipated from the early relic direction. That received’t train us a lot. At this level we wish to seek for a lovely the reason why the entire exact native measurements are upper than the early relic direction. There should be a reason why and we must be searching for it.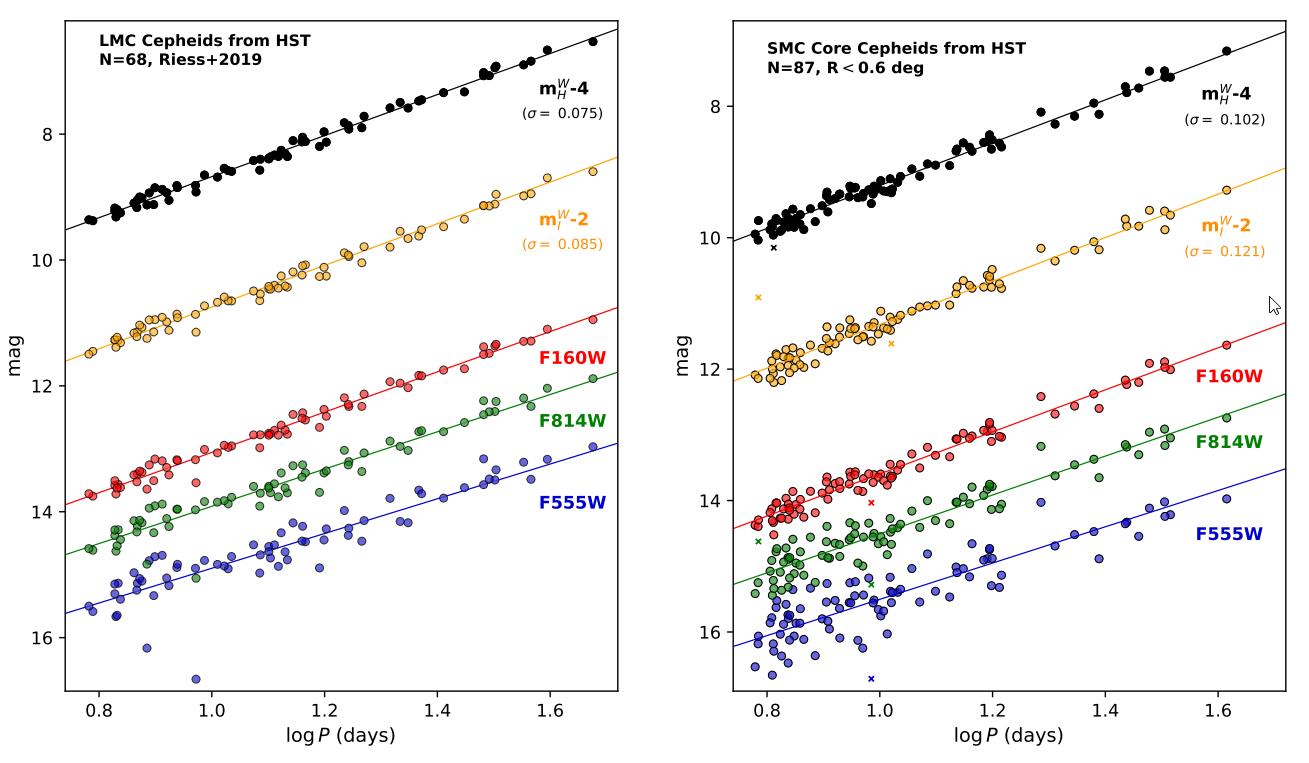 This graph of astronomical magnitude (y-axis) as opposed to Cepheid era (x-axis) for Cepheid variable stars within the Huge (left) and Small (proper) Magellanic Clouds. The celebs are proven in two Weisenheit indices (best) and 3 Hubble filters (backside) for each and every one. As soon as outliers (small x symbols) are excluded, the period-luminosity family members (cast strains) are derived.
This graph of astronomical magnitude (y-axis) as opposed to Cepheid era (x-axis) for Cepheid variable stars within the Huge (left) and Small (proper) Magellanic Clouds. The celebs are proven in two Weisenheit indices (best) and 3 Hubble filters (backside) for each and every one. As soon as outliers (small x symbols) are excluded, the period-luminosity family members (cast strains) are derived.
Credit score: L. Breuval et al., Astrophysical Magazine submitted/arXiv:2404.08038, 2024
ES: One of the crucial key options of each Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae is that they’ve been what we name “standardized,” the place we will measure simply observable homes (like brightening-faintening occasions or the fall-off time from height brightness) after which use that data to deduce how intrinsically brilliant that object is. If you understand how intrinsically brilliant a gentle bulb is after which measure how brilliant apparently on your eyes, you’ll know its distance. Then again, for those who didn’t know the intrinsic brightness, you’d must reckon with mistakes and uncertainties out of your lack of understanding of the items you’re staring at. Are ways that depend on both stars on the tip of the crimson massive department or stars at the asymptotic massive department much less standardized than Cepheids, and if this is the case, what questions wish to be spoke back sooner than we will believe the distances we infer from the usage of the ones strategies?AR: The nice step forward by means of Henrietta Leavitt a century in the past used to be to acknowledge that the era of variation of Cepheid brightnesses tightly correlated with their luminosities. So after we see a brilliant, yellow superstar exchange brightness frequently over weeks or months, we mechanically understand it’s a Cepheid superstar and we all know its luminosity to about 3% according to superstar (as demonstrated within the Milky Approach or Magellanic Clouds). This takes many observations through the years, however the praise is to grasp the suitable form of superstar and it’s luminosity you’re looking at which makes them nice standardized candles.Cepheids also are a number of the maximum luminous stars, so we will see them farthest to achieve probably the most sort Ia supernova hosts. Some possible choices are “usual populations” — stars in a singular area of colour and brightness house which tells you they’re at a an identical evolutionary state and thus have a an identical luminosity. In apply, usual populations is also a mixture of the objective inhabitants and contaminants.For the top of the crimson massive department inhabitants, the primary contaminant is asymptotic massive department stars which will also be fainter or brighter than the top, leading to a fuzzy tip. Suave algorithms can nonetheless extract the top. Carbon-rich asymptotic massive department stars are every other promising usual inhabitants, however the luminosity of the inhabitants varies with the radial homes of a galaxy (most probably metallicity and age) in order that it’s difficult to check them, apples to apples, between galaxies. Even at fastened radius, the inhabitants has a breadth [ES note: which indicates a larger uncertainty] time and again that of Cepheids.I believe long run paintings will focal point on keeping apart the “wheat from the chaff” in those populations via variability research to lead them to sharper and extra constant between galaxies. Mockingly, that can lead them to dearer to look at like Cepheid variables, however it will be price it.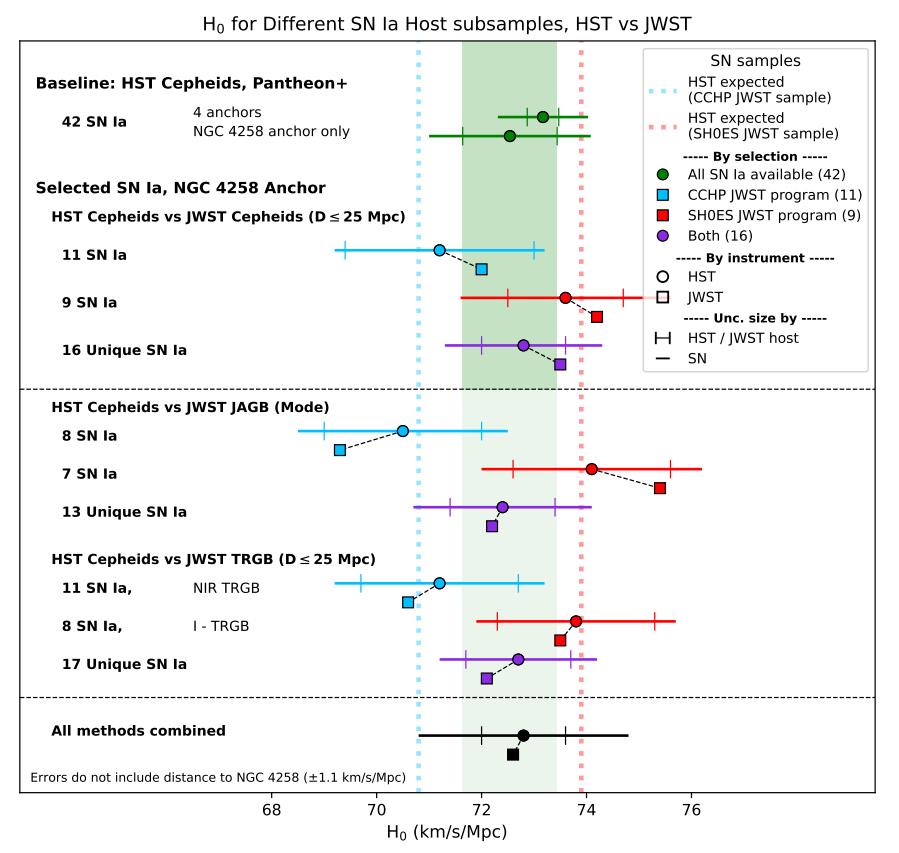 This graph displays how more than a few variety possible choices for the pattern used on your distance ladder affects each the common values (information issues) and the uncertainties (measurement of the mistake bar strains) for various galaxies. Some have JWST information and a few have solely Hubble information; some have Cepheids and a few have asymptotic massive department stars; some had been decided on by means of the CCHP staff and a few had been decided on by means of the SH0ES staff, and so forth. The smallest uncertainties come from research that use the entire suite of knowledge.
This graph displays how more than a few variety possible choices for the pattern used on your distance ladder affects each the common values (information issues) and the uncertainties (measurement of the mistake bar strains) for various galaxies. Some have JWST information and a few have solely Hubble information; some have Cepheids and a few have asymptotic massive department stars; some had been decided on by means of the CCHP staff and a few had been decided on by means of the SH0ES staff, and so forth. The smallest uncertainties come from research that use the entire suite of knowledge.
Credit score: A.G. Riess et al., Astrophysical Magazine submitted, arXiv:2408.11770, 2024
ES: One interesting level from your most up-to-date paper is if a staff (e.g. the SH0ES staff) limited themselves to the small pattern of galaxies used within the CCHP learn about, they’d additionally arrive at a low price for the growth charge of the Universe: someplace round 69 km/s/Mpc. Does this let us know anything else concerning the reliability of asymptotic massive department stars, and does this let us know anything else concerning the significance of no longer solely having extra galaxies to incorporate on your pattern, however galaxies that seem at various distances (together with higher distances) in any type of distance ladder research?AR: The problem is that sort Ia supernovae aren’t completely usual, so even once we calibrate one, we predict it to over or below estimate the common by means of in most cases 15%. This immediately interprets right into a misestimate of the Hubble consistent. So we wish to calibrate numerous them to “beat down” the uncertainty via averaging. By way of 2022, Hubble had calibrated 42 galaxies containing each Cepheids and sort Ia supernovae, which took nearly two decades to assemble. As a result of JWST is new, the samples of supernovae it has calibrated are nonetheless small, simply 7-10, which can produce huge fluctuations in estimating the Hubble consistent.The excellent news is that Hubble has already calibrated a lot of these similar supernovae, so we will expect the scale and route of each and every small pattern distinction. On the subject of the CCHP JWST pattern, Hubble anticipated a price of about 70 km/s/Mpc, which is similar to what they discovered with JWST. Then again, as we confirmed in a brand new paper, a bigger JWST pattern is produced by means of combining JWST systems (ours, CCHP, others) which reduces the fluctuations, the so-called “reversion to the imply.”The mixed pattern is just about each and every SN Ia measured by means of Hubble, 16 of 17, inside 25 Mpc, and the result’s 72.6 km/s/Mpc (the place Hubble will get 72.8 km/s/Mpc for a similar set). So, up to now, Hubble and JWST and the more than a few distance strategies are in just right accord. Whilst I’m as prepared as any person to discover a technique to the strain, I don’t really feel we must level to a downward fluctuation because of a small pattern, particularly a apparently predictable fluctuation, as proof of any exchange within the standing of the Hubble rigidity. It’s vital to at all times evaluate apples to apples, even if the apples are stars.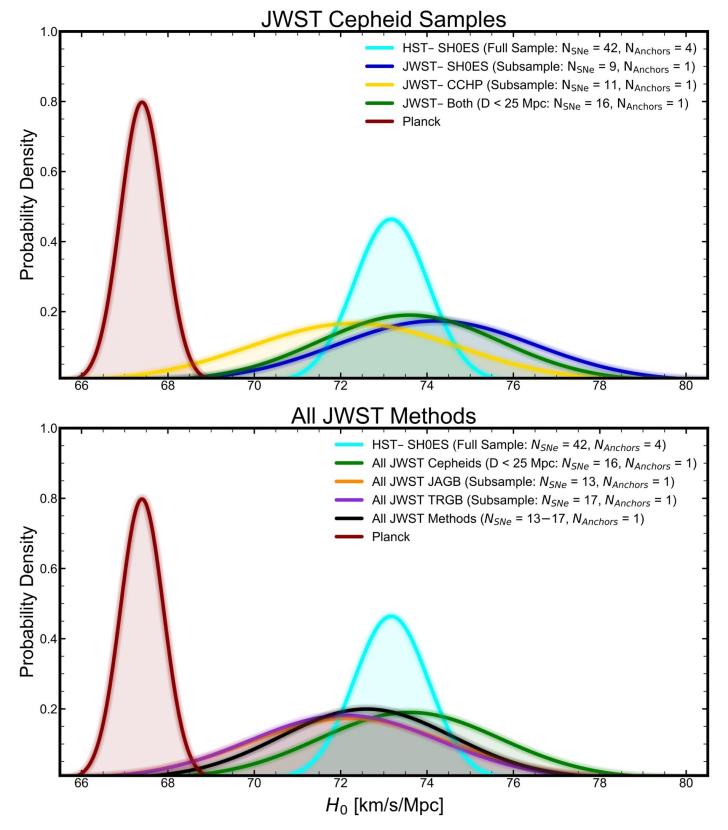 This graph displays a comparability between the price of H0, or the growth charge as of late, as derived from Hubble house telescope Cepheids and anchors in addition to different subsamples of JWST Cepheids (or different forms of stars) and anchors. A comparability to Planck, which makes use of the early relic way as an alternative of the gap ladder way, may be proven.
This graph displays a comparability between the price of H0, or the growth charge as of late, as derived from Hubble house telescope Cepheids and anchors in addition to different subsamples of JWST Cepheids (or different forms of stars) and anchors. A comparability to Planck, which makes use of the early relic way as an alternative of the gap ladder way, may be proven.
Credit score: A.G. Riess et al., Astrophysical Magazine submitted, arXiv:2408.11770, 2024
ES: In the end, as a “bonus query” for you, I believe it’s vital to focus on the position of the junior researchers who’re making extremely vital contributions to this burgeoning sub-field of observational cosmology, inside a number of other collaborations. Are there any other folks whose contributions you’d like to focus on, as a way to make the wider group acutely aware of how this can be a number of a perfect many researchers from around the globe coming in combination to try to resolve one of the vital biggest cosmic mysteries of recent occasions?AR: I want to recognize the paintings of such a lot of who sped up development on those research. Before everything are those that spent years or even many years to carry JWST to fruition. Additionally my collaborators at the SH0ES Workforce, and to focus on probably the most junior participants, Siyang Li, Gagandeep Anand, Louise Breuval, and Yukei Murakami, in addition to my colleagues at the CCHP Workforce, the Hubble Area Telescope staff, and throughout the cosmology group. The adventure continues…Ethan Siegel recognizes Adam Riess for his treasured time and perception in taking part on this interview.
Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the largest questions of all