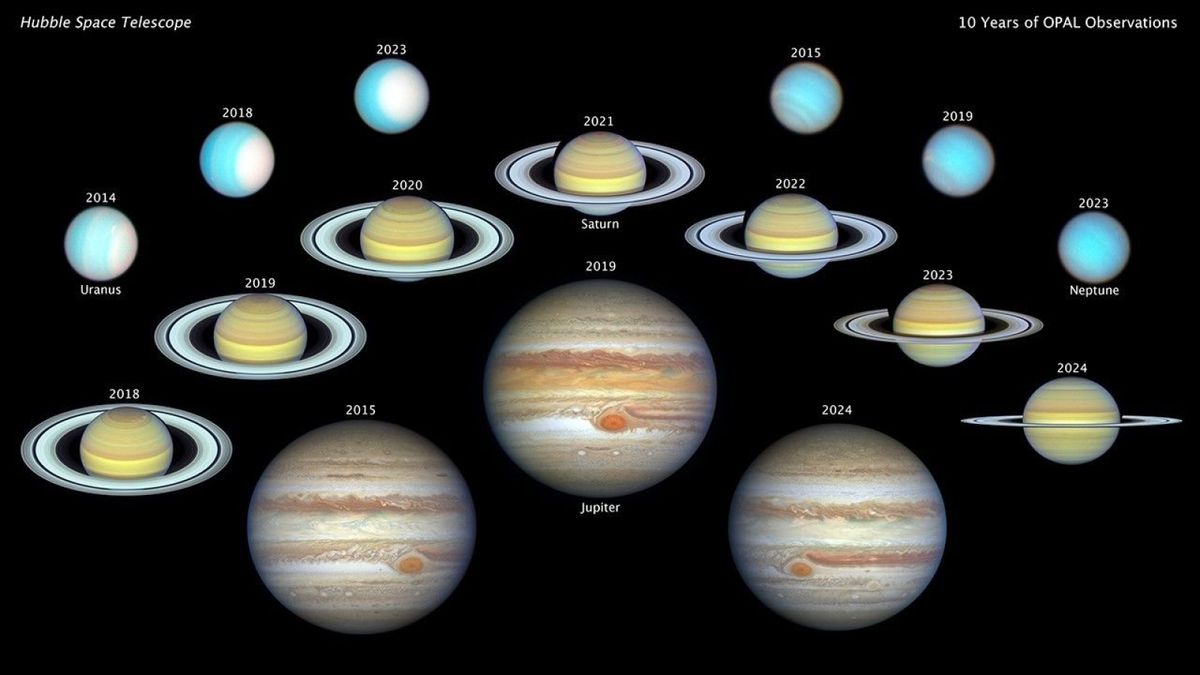
The black hearts of galaxies have had their historical past instructed virtually in complete for the primary time, as astronomers blended X-ray observations with detailed supercomputer fashions to chronicle the expansion of supermassive black holes over 12 billion years of cosmic historical past.In doing so, the scientists have proven that the black gap on the core of our Milky Means galaxy attained its 4 million sun lots slightly overdue in its historical past.Supermassive black holes vary from tens of millions of instances extra huge than our solar to billions of instances extra huge, however their origins are unclear and the way they grew to such huge lots has been a problem for astronomers to know.Now, on the other hand, astronomers Fan Zou and W. Niel Brandt, either one of Penn State College, have led a crew that attached the 2 mechanisms of black-hole enlargement from observations and simulations. The consequences would possibly supply some solutions ultimately.Comparable: NASA telescope spots ‘cosmic fireworks’ and faint echos from the Milky Means’s supermassive black gap”An excessively giant query is how do those supermassive black holes develop so huge?” mentioned Zou whilst presenting their paintings on the 244th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Wisconsin.. “To deal with that, we wish to observe the whole enlargement historical past of those supermassive black holes.”As discussed, black holes develop by the use of two primary mechanisms. One is in the course of the accretion of chilly fuel from their host galaxy. This fuel paperwork an accretion disk across the black gap itself and subject from the disk steadily spirals in opposition to the black gap’s core. The accretion disk can develop so dense that friction between fuel molecules reasons it to warmth as much as tens of millions of levels, radiating X-rays within the procedure. The opposite mechanism happens right through galaxy collisions. When this occurs, no longer simplest do galaxies merge, however their supermassive black holes additionally in the end coalesce and unlock a burst of gravitational waves. Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Monitoring cosmic voids To evaluate how a lot the accretion of fuel contributes to the expansion of supermassive black holes, the learn about crew scoured via greater than two decades’ price of archival knowledge from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Ecu House Company’s XMM-Newton undertaking and the eROSITA X-ray device on board the joint German–Russian Spektr-RG spacecraft. The researchers have been ready to spot X-ray indicators coming from about 8,000 unexpectedly rising supermassive black holes.”When supermassive black holes accrete the encompassing fuel they emit robust X-rays, so by means of detecting them within the X-ray bands we will be able to measure their accretion energy,” mentioned Zou.They then grew to become to the IllustrisTNG cosmological supercomputer simulation to fashion galaxy mergers all through cosmic historical past. From there, the crew blended X-ray knowledge appearing enlargement via accretion with the result of the simulated mergers to achieve an working out of the way and when supermassive black holes grew over the last 12 billion years, from 1.8 billion years after the Large Bang to nowadays.Those simulations “seize the whole large-scale construction [of the universe] but additionally are ready to probe person galaxies,” mentioned Zou.Supermassive black gap tales  At the left, in blue, is an X-ray symbol of an accreting supermassive black gap (proven inset as paintings) composited on an optical symbol of galaxies within the deep universe. At the proper is an IllustrisTNG simulation of galaxies appearing how they evolve at the cosmic internet of subject. (Symbol credit score: F. Zou/Penn State, et al.; Observations: The XMM-SERVS Collaboration; Simulations: The TNG Collaboration; Representation: Nahks TrEhnl/Penn State/Penn State)Zou and Brandt discovered that the X-ray knowledge displays accretion has been the dominant driving force of black-hole enlargement right through all epochs of cosmic historical past. Moreover, the extra huge the galaxy, the quicker the supermassive black gap within grew by means of accretion. Mergers, then again, are much less distinguished drivers of black gap enlargement in line with the simulations, however can nonetheless have some affect.”Accretion dominates the supermassive black-hole enlargement generally and mergers make some notable secondary contributions,” mentioned Zou.Those effects additionally display that supermassive black holes grew extra unexpectedly previous within the universe, with new ones steadily showing. Via about 7 billion years in the past, on the other hand, the full choice of supermassive black holes had develop into roughly settled with few new supermassive black holes forming. Mergers had extra of an have an effect on in later historical past, peaking of their significance to black-hole enlargement about 4 billion years in the past. “We discovered that after the universe reaches about 40% of its age, the whole demography of supermassive black holes is similar to the demography of supermassive black holes that we see within the native universe,” mentioned Zou.The astronomers even particularly modeled our galaxy’s black gap, Sagittarius A*, and concluded that it grew maximum of its subject slightly overdue in cosmic time. This enlargement would were basically via accretion, with the vast majority of the Milky Means’s mergers with different galaxies going down greater than 8 billion to ten billion years in the past. Then again, the Ecu House Company’s Gaia undertaking has just lately discovered proof for a dwarf galaxy that collided with the Milky Means simply 2 billion to three billion years in the past. Dwarf galaxies are concept to include intermediate-mass black holes, measuring tens to loads of hundreds of instances the mass of our solar, and it’s conceivable that one will have merged with Sagittarius A* to spice up our black gap’s mass.For the reason that effects simplest take us again to at least one.8 billion years after the Large Bang, they do not describe how the seeds for supermassive black holes first shaped. This stays a dilemma for cosmologists, specifically because the Hubble House Telescope and the James Webb House Telescope have discovered strangely huge black holes very previous within the historical past of the universe. How they grew to be tens of millions of instances the mass of our solar in lower than one thousand million years is these days unknown.One paper describing the findings was once revealed in March in The Astrophysical Magazine, with a 2d paper ready within the pipeline.
At the left, in blue, is an X-ray symbol of an accreting supermassive black gap (proven inset as paintings) composited on an optical symbol of galaxies within the deep universe. At the proper is an IllustrisTNG simulation of galaxies appearing how they evolve at the cosmic internet of subject. (Symbol credit score: F. Zou/Penn State, et al.; Observations: The XMM-SERVS Collaboration; Simulations: The TNG Collaboration; Representation: Nahks TrEhnl/Penn State/Penn State)Zou and Brandt discovered that the X-ray knowledge displays accretion has been the dominant driving force of black-hole enlargement right through all epochs of cosmic historical past. Moreover, the extra huge the galaxy, the quicker the supermassive black gap within grew by means of accretion. Mergers, then again, are much less distinguished drivers of black gap enlargement in line with the simulations, however can nonetheless have some affect.”Accretion dominates the supermassive black-hole enlargement generally and mergers make some notable secondary contributions,” mentioned Zou.Those effects additionally display that supermassive black holes grew extra unexpectedly previous within the universe, with new ones steadily showing. Via about 7 billion years in the past, on the other hand, the full choice of supermassive black holes had develop into roughly settled with few new supermassive black holes forming. Mergers had extra of an have an effect on in later historical past, peaking of their significance to black-hole enlargement about 4 billion years in the past. “We discovered that after the universe reaches about 40% of its age, the whole demography of supermassive black holes is similar to the demography of supermassive black holes that we see within the native universe,” mentioned Zou.The astronomers even particularly modeled our galaxy’s black gap, Sagittarius A*, and concluded that it grew maximum of its subject slightly overdue in cosmic time. This enlargement would were basically via accretion, with the vast majority of the Milky Means’s mergers with different galaxies going down greater than 8 billion to ten billion years in the past. Then again, the Ecu House Company’s Gaia undertaking has just lately discovered proof for a dwarf galaxy that collided with the Milky Means simply 2 billion to three billion years in the past. Dwarf galaxies are concept to include intermediate-mass black holes, measuring tens to loads of hundreds of instances the mass of our solar, and it’s conceivable that one will have merged with Sagittarius A* to spice up our black gap’s mass.For the reason that effects simplest take us again to at least one.8 billion years after the Large Bang, they do not describe how the seeds for supermassive black holes first shaped. This stays a dilemma for cosmologists, specifically because the Hubble House Telescope and the James Webb House Telescope have discovered strangely huge black holes very previous within the historical past of the universe. How they grew to be tens of millions of instances the mass of our solar in lower than one thousand million years is these days unknown.One paper describing the findings was once revealed in March in The Astrophysical Magazine, with a 2d paper ready within the pipeline.
12 billion years of black gap historical past, printed via X-rays and simulations