Deciphering the previous generally is a tough trade. We are depending on items of rock, tens of millions of years previous, and seeking to figure out what specific, unknown, and most likely long-extinct organism made it a definite means.It isn’t unparalleled for scientists to get historic fossils perplexed or combined up (with effects which might be on occasion hilarious looking back). However a brand new paper has printed a case of flawed identification this is for sure unexpected.The fossil pictured above, and one different adore it, have been came upon in Colombia, a long time in the past, and labeled as a plant named Sphenophyllum colombianum. Now, scientists have made up our minds that the fossils aren’t any plant in any respect, however impressions of the interior of the shells of child turtles.They have got nicknamed the fossil they studied ‘Turtwig’, after the Pokémon that is a part turtle, section plant.”We went to the fossil assortment on the Universidad Nacional de Colombia in Bogotá and began having a look on the crops, and once we photographed them, we idea, ‘that is bizarre’,” says paleobotanist Fabiany Herrera of the Box Museum.”While you take a look at it intimately, the strains observed at the fossils do not appear to be the veins of a plant – I used to be sure that it used to be perhaps bone.”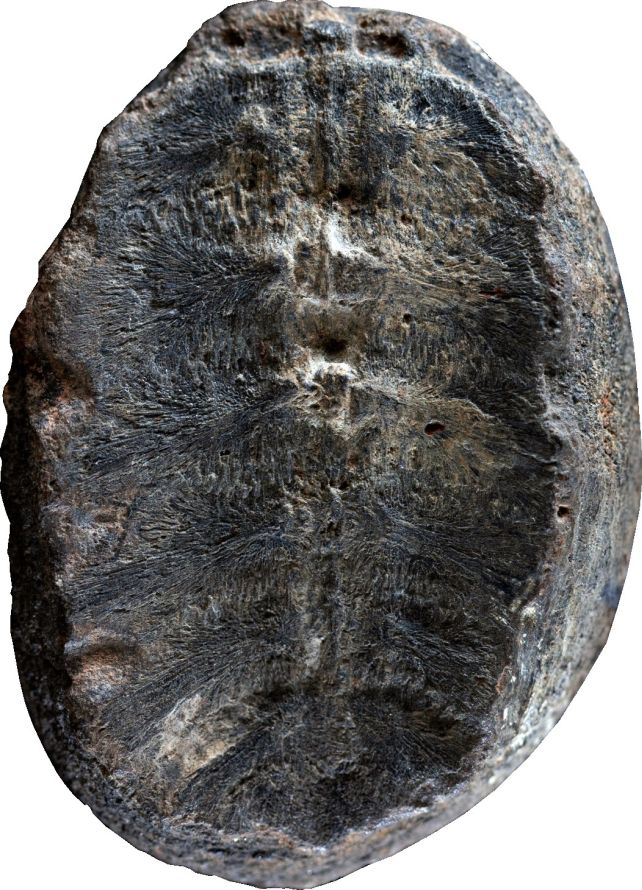 The Turtwig fossil shaped from the interior of the shell of a toddler turtle. (Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro)The fossils have at all times been a little bit bit hinky. They have been came upon through a clergyman named Padre Gustavo Huertas, who accrued rocks and fossils between the Fifties and the Nineteen Seventies, in a area close to town of Villa de Levya. The 2 fossils, dated again to the early Cretaceous between 132 and 113 million years in the past, have been a part of that assortment.Huertas, who printed numerous papers describing new Cretaceous plant species in accordance with the fossils he discovered, printed a guide in 2003, during which he described a species named Sphenophyllum colombianum, in accordance with the 2 fossils.Even then, the declare raised an eyebrow or two: Sphenophyllum used to be idea to have died out over 100 million years prior, and had now not been observed in that a part of the arena earlier than.Those discrepancies stuck the eye of paleobotanist Héctor Palma-Castro of the Nationwide College of Colombia, so he and his colleagues got down to examine the fossils in larger element.After they discovered that the specimens have been nearer to bone than leaf, they reached out to paleontologist Edwin-Alberto Cadena of Del Rosario College, who’s skilled with historic turtle identity.”They despatched me the pictures, and I stated, ‘This for sure looks as if a carapace’ – the bony higher shell of a turtle,” Cadena says. “I stated, ‘Neatly, that is outstanding, as a result of this isn’t just a turtle, however it is also a hatchling specimen, it is very, very small’.”
The Turtwig fossil shaped from the interior of the shell of a toddler turtle. (Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro)The fossils have at all times been a little bit bit hinky. They have been came upon through a clergyman named Padre Gustavo Huertas, who accrued rocks and fossils between the Fifties and the Nineteen Seventies, in a area close to town of Villa de Levya. The 2 fossils, dated again to the early Cretaceous between 132 and 113 million years in the past, have been a part of that assortment.Huertas, who printed numerous papers describing new Cretaceous plant species in accordance with the fossils he discovered, printed a guide in 2003, during which he described a species named Sphenophyllum colombianum, in accordance with the 2 fossils.Even then, the declare raised an eyebrow or two: Sphenophyllum used to be idea to have died out over 100 million years prior, and had now not been observed in that a part of the arena earlier than.Those discrepancies stuck the eye of paleobotanist Héctor Palma-Castro of the Nationwide College of Colombia, so he and his colleagues got down to examine the fossils in larger element.After they discovered that the specimens have been nearer to bone than leaf, they reached out to paleontologist Edwin-Alberto Cadena of Del Rosario College, who’s skilled with historic turtle identity.”They despatched me the pictures, and I stated, ‘This for sure looks as if a carapace’ – the bony higher shell of a turtle,” Cadena says. “I stated, ‘Neatly, that is outstanding, as a result of this isn’t just a turtle, however it is also a hatchling specimen, it is very, very small’.”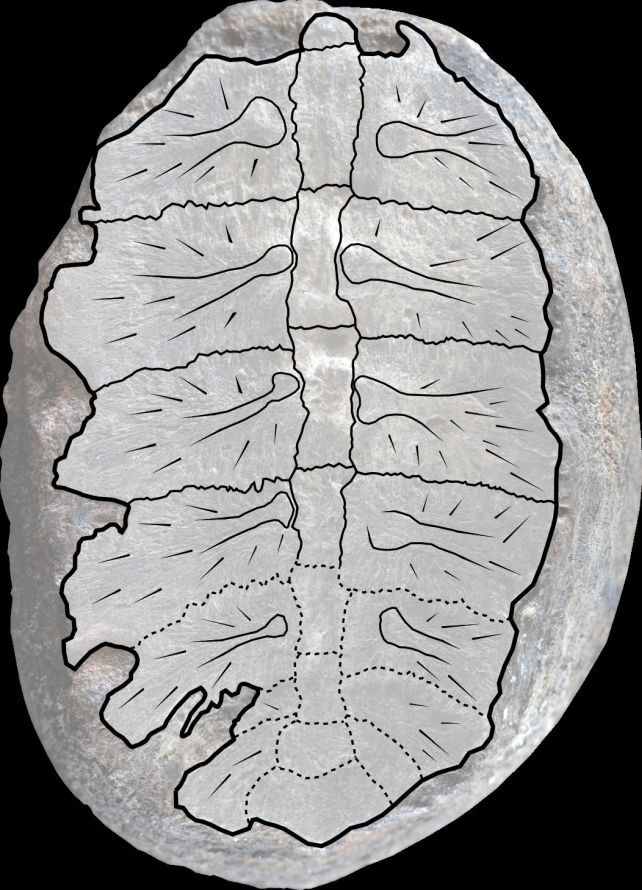 The fossil overlaid with a drawing that demonstrates the positions of the vertebrae and ribs. ((Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro; drawing through Edwin-Alberto Cadena and Diego Cómbita-Romero)However the fossil used to be additionally lacking the standard marks which might be discovered at the out of doors of a turtle’s shell. This turns out to have contributed to its misidentification.Fairly, the marks at the fossil constitute the turtle’s vertebrae and ribs, which make up a part of the shell. They very carefully resemble the midrib and veins of a leaf – it is simple to look how Huertas may just assume that is what it used to be.Those bones knit in combination because the turtle grows, so the researchers have been in a position to resolve how previous the turtle used to be when it died. It used to be now not a hatchling, however nonetheless a juvenile, not up to a yr previous, they discovered, and a member of the Panchelonioidea clade of marine turtles.As a result of juvenile turtles are so fragile, it is uncommon to search out their stays. The researchers imagine that Turtwig is most probably associated with Cretaceous sea turtles that might develop as much as 4.5 meters (15 toes) in duration, and may just constitute the most important clue concerning the mysterious lifestyles cycle of those historic beasts.And, the researchers say, it demonstrates – as such a lot of of those discoveries do – the price and significance of revisiting fossil collections in museums, and making use of new wisdom to previous bones.”We resolved a small paleobotanical thriller, however extra importantly, this be taught presentations the want to re-study historic collections in Colombia,” Herrera says.”The Early Cretaceous is a crucial time in land plant evolution, in particular for flowering crops and gymnosperms. Our long run process is to find the forests that grew on this a part of the arena.”The analysis has been printed in Palaeontologia Electronica.
The fossil overlaid with a drawing that demonstrates the positions of the vertebrae and ribs. ((Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro; drawing through Edwin-Alberto Cadena and Diego Cómbita-Romero)However the fossil used to be additionally lacking the standard marks which might be discovered at the out of doors of a turtle’s shell. This turns out to have contributed to its misidentification.Fairly, the marks at the fossil constitute the turtle’s vertebrae and ribs, which make up a part of the shell. They very carefully resemble the midrib and veins of a leaf – it is simple to look how Huertas may just assume that is what it used to be.Those bones knit in combination because the turtle grows, so the researchers have been in a position to resolve how previous the turtle used to be when it died. It used to be now not a hatchling, however nonetheless a juvenile, not up to a yr previous, they discovered, and a member of the Panchelonioidea clade of marine turtles.As a result of juvenile turtles are so fragile, it is uncommon to search out their stays. The researchers imagine that Turtwig is most probably associated with Cretaceous sea turtles that might develop as much as 4.5 meters (15 toes) in duration, and may just constitute the most important clue concerning the mysterious lifestyles cycle of those historic beasts.And, the researchers say, it demonstrates – as such a lot of of those discoveries do – the price and significance of revisiting fossil collections in museums, and making use of new wisdom to previous bones.”We resolved a small paleobotanical thriller, however extra importantly, this be taught presentations the want to re-study historic collections in Colombia,” Herrera says.”The Early Cretaceous is a crucial time in land plant evolution, in particular for flowering crops and gymnosperms. Our long run process is to find the forests that grew on this a part of the arena.”The analysis has been printed in Palaeontologia Electronica.
132-Million-12 months-Outdated Thriller Fossil’s True Identification Is In the end Published














