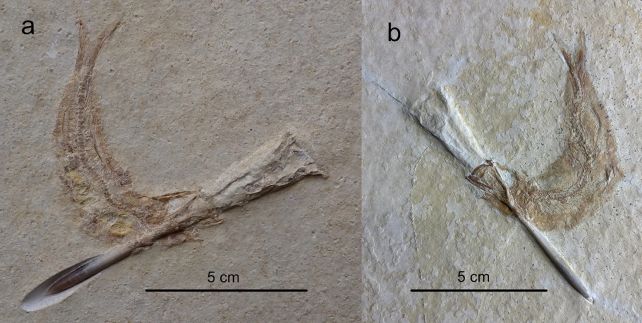
A fossil found out close to Gulgong in New South Wales, Australia, has introduced researchers an in depth glance into themelanosomes lifetime of a freshwater fish that lived 15 million years in the past. The newly known species, Ferruaspis brocksi, now not most effective preserved its abdomen contents and visual colour patterns, but additionally contains strains of a parasite, offering an extraordinary snapshot of Australia’s Miocene ecosystems.
A Fossil That Rewrites Freshwater Fish Historical past
The learn about, led by way of Dr. Matthew McCurry from the Australian Museum and UNSW Sydney, marks the primary identified fossil of a freshwater smelt in Australia. Belonging to the order Osmeriformes—which contains species just like the Australian Grayling and Australian Smelt—the fossil supplies uncommon evolutionary knowledge for this staff.
“The invention of the 15 million-year-old freshwater fish fossil provides us an extraordinary alternative to know Australia’s historical ecosystems and the evolution of its fish species, in particular the Osmeriformes staff all over the Miocene epoch, 11-15 million years in the past.”


Credit score: Salthy Dingo
Within The Abdomen Of Ferruaspis Brocksi
Probably the most outstanding options of the fossil is its preserved abdomen contents. Researchers discovered stays of invertebrates, essentially small phantom midge larvae, indicating the fish’s nutrition.Much more strangely, a parasite—a juvenile freshwater mussel referred to as a glochidium—used to be discovered connected to the fish’s tail.
“One of the most fossils even presentations a parasite connected to the tail of the fish. It’s a juvenile freshwater mussel known as a glochidium. Those juvenile mussels connect themselves to the gills or tails of fish to affix rides up and down streams,” Dr. McCurry defined.
Colour Preserved Via Melanosomes
The fossil additionally supplies a unprecedented glimpse into the exterior look of extinct aquatic vertebrates. The usage of high-resolution microscopy, researchers known melanosomes, pigment-producing constructions that helped reconstruct the fish’s colour trend.
“The fish used to be darker on its dorsal floor, lighter in colour on its abdominal and had two lateral stripes working alongside its facet,” mentioned Dr. Michael Frese from the College of Canberra and CSIRO.
This marks the primary identified use of melanosomes to decide shade in a fossilized fish, one way in the past used basically in research of feathered dinosaurs.
A Tribute Embedded In Stone
The species identify Ferruaspis brocksi displays each its composition and a tribute to a key contributor. “‘Ferru’ comes from the Latin phrase ‘ferrum,’ which means iron,” the crew defined, referencing the iron-rich rocks on the web page.
The second one a part of the identify, brocksi, honors Professor Jochen J. Brocks of the Australian Nationwide College, who performed a an important function in fossil exploration at McGraths Flat.
“Accumulating fossils at McGrath Flat is a spotlight for me annually. Splitting the rust-red slabs of rock is like opening an historical e book, revealing the creatures that inhabited an Australian oxbow lake some 15 million years in the past,” Brocks mentioned.
Mcgraths Flat: A Window Into Historical Australia
McGraths Flat, situated within the Central Tablelands of NSW, is assessed as a Lagerstätte—a fossil web page identified for outstanding preservation. Fossils from this web page date again 11 to 16 million years and display that the world used to be as soon as a temperate rainforest wealthy in biodiversity.
The continuing analysis at McGraths Flat, to begin with funded in 2017 by way of a descendant of famed palaeontologist Robert Etheridge, continues to yield insights into Australia’s historical fauna.