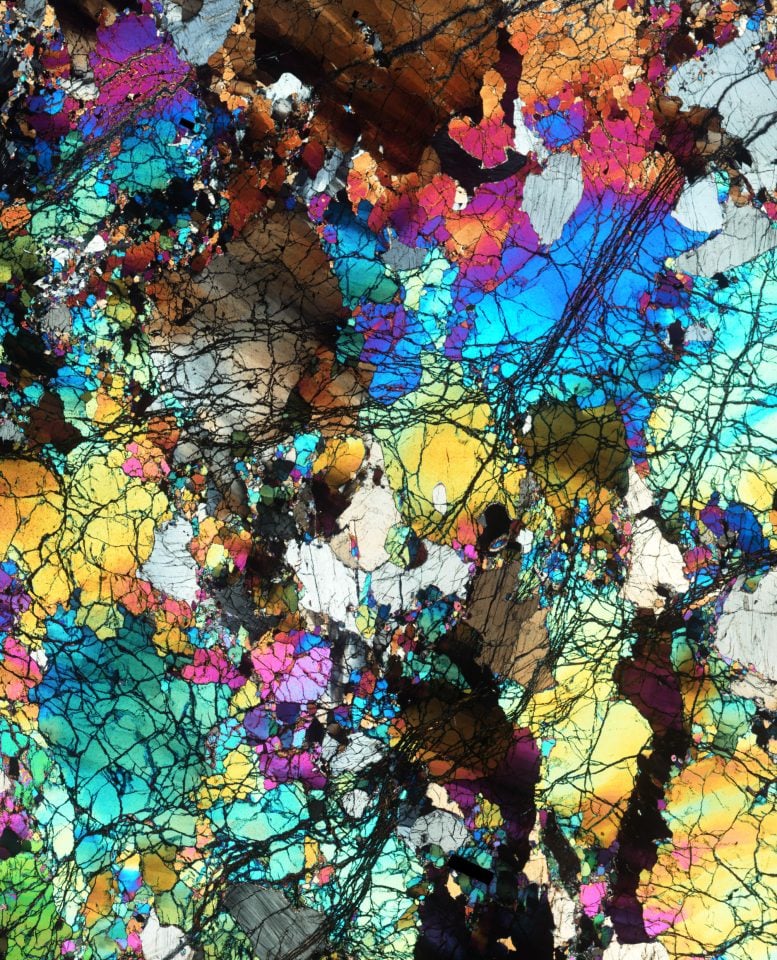
 A skinny slice of the traditional rocks amassed from Gakkel Ridge close to the North Pole, photographed below a microscope and noticed below cross-polarized gentle. Box width ~ 14mm. Inspecting rocks in skinny phase is helping geologists establish and symbolize minerals inside a rock. The analyses expose details about the rock’s mineral composition, texture and historical past, comparable to the way it shaped and any next adjustments it has gone through. Researchers use the id and chemical composition of the minerals in those historical rocks from Earth’s mantle to resolve the stipulations below which those rocks melted. Credit score: E. Cottrell, SmithsonianSmithsonian scientists behavior new analysis on historical ‘time tablet’ rocks, courting again a minimum of 2.5 billion years.Researchers on the Smithsonian’s Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past have carried out a brand new research of rocks believed to be a minimum of 2.5 billion years outdated, losing gentle at the chemical historical past of Earth’s mantle, the layer underneath the planet’s crust. Their findings fortify our figuring out of Earth’s earliest geologic processes and give a contribution to a long-standing clinical debate in regards to the planet’s geologic historical past. Significantly, the find out about supplies proof that the oxidation state of maximum of Earth’s mantle has remained strong over geological time, difficult earlier assertions via different researchers about main transitions.“This find out about tells us extra about how this particular position during which we are living got here to be the best way it’s, with its distinctive floor and inner that experience allowed lifestyles and liquid water to exist,” stated Elizabeth Cottrell, chair of the museum’s division of mineral sciences, curator of the Nationwide Rock Assortment and co-author of the find out about. “It’s a part of our tale as people as a result of our origins all hint again to how Earth shaped and the way it has advanced.”The find out about, revealed within the magazine Nature, focused on a gaggle of rocks amassed from the seafloor that possessed extraordinary geochemical houses. Specifically, the rocks display proof of getting melted to an excessive level with very low ranges of oxidation; oxidation is when an atom or molecule loses a number of electrons in a chemical response. With the assistance of further analyses and modeling, the researchers used the original houses of those rocks to turn that they most likely date again to a minimum of 2.5 billion years in the past all through the Archean Eon. Additional, the findings display that the Earth’s mantle has general retained a strong oxidation state since those rocks shaped, against this to what different geologists have prior to now theorized.
A skinny slice of the traditional rocks amassed from Gakkel Ridge close to the North Pole, photographed below a microscope and noticed below cross-polarized gentle. Box width ~ 14mm. Inspecting rocks in skinny phase is helping geologists establish and symbolize minerals inside a rock. The analyses expose details about the rock’s mineral composition, texture and historical past, comparable to the way it shaped and any next adjustments it has gone through. Researchers use the id and chemical composition of the minerals in those historical rocks from Earth’s mantle to resolve the stipulations below which those rocks melted. Credit score: E. Cottrell, SmithsonianSmithsonian scientists behavior new analysis on historical ‘time tablet’ rocks, courting again a minimum of 2.5 billion years.Researchers on the Smithsonian’s Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past have carried out a brand new research of rocks believed to be a minimum of 2.5 billion years outdated, losing gentle at the chemical historical past of Earth’s mantle, the layer underneath the planet’s crust. Their findings fortify our figuring out of Earth’s earliest geologic processes and give a contribution to a long-standing clinical debate in regards to the planet’s geologic historical past. Significantly, the find out about supplies proof that the oxidation state of maximum of Earth’s mantle has remained strong over geological time, difficult earlier assertions via different researchers about main transitions.“This find out about tells us extra about how this particular position during which we are living got here to be the best way it’s, with its distinctive floor and inner that experience allowed lifestyles and liquid water to exist,” stated Elizabeth Cottrell, chair of the museum’s division of mineral sciences, curator of the Nationwide Rock Assortment and co-author of the find out about. “It’s a part of our tale as people as a result of our origins all hint again to how Earth shaped and the way it has advanced.”The find out about, revealed within the magazine Nature, focused on a gaggle of rocks amassed from the seafloor that possessed extraordinary geochemical houses. Specifically, the rocks display proof of getting melted to an excessive level with very low ranges of oxidation; oxidation is when an atom or molecule loses a number of electrons in a chemical response. With the assistance of further analyses and modeling, the researchers used the original houses of those rocks to turn that they most likely date again to a minimum of 2.5 billion years in the past all through the Archean Eon. Additional, the findings display that the Earth’s mantle has general retained a strong oxidation state since those rocks shaped, against this to what different geologists have prior to now theorized.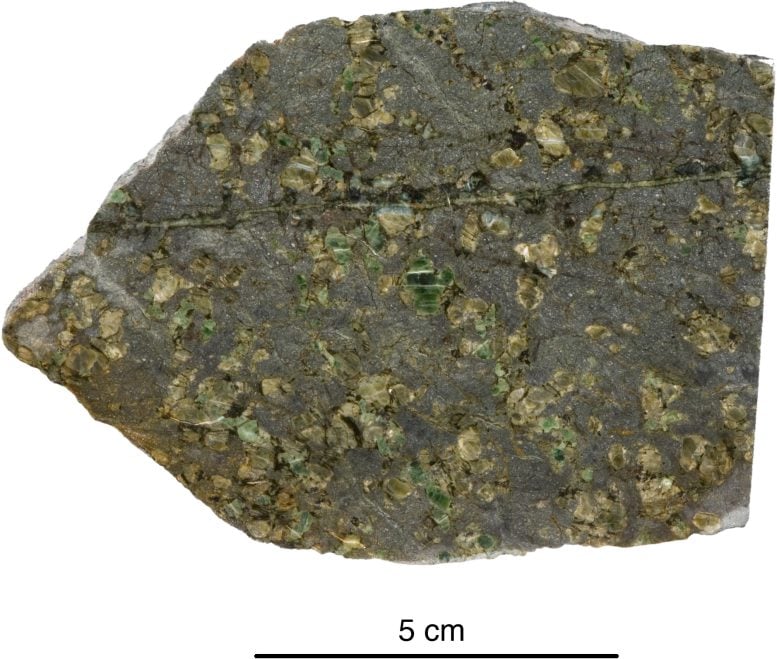 An historical rock dredged from the seafloor and studied via the analysis crew. Credit score: Tom Kleindinst“The traditional rocks we studied are 10,000 instances much less oxidized than standard trendy mantle rocks, and we provide proof that it is because they melted deep within the Earth all through the Archean, when the mantle used to be a lot warmer than it’s these days,” Cottrell stated. “Different researchers have attempted to provide an explanation for the upper oxidation ranges noticed in rocks from these days’s mantle via suggesting that an oxidation tournament or trade has taken position between the Archean and these days. Our proof means that the variation in oxidation ranges can merely be defined via the truth that Earth’s mantle has cooled over billions of years and is now not scorching sufficient to supply rocks with such low oxidation ranges.”Geological Proof and Find out about MethodologyThe analysis crew—together with lead find out about writer Suzanne Birner who finished a pre-doctoral fellowship on the Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past and is now an assistant professor at Berea Faculty in Kentucky—started their investigation to grasp the connection between Earth’s forged mantle and trendy seafloor volcanic rocks. The researchers began via learning a gaggle of rocks that had been dredged from the seafloor at two oceanic ridges the place tectonic plates are spreading aside and the mantle is churning as much as the outside and generating new crust.The 2 puts the studied rocks had been amassed from, the Gakkel Ridge close to the North Pole and the Southwest Indian Ridge between Africa and Antarctica, are two of the slowest-spreading tectonic plate limitations on the earth. The sluggish tempo of the spreading at those ocean ridges implies that they’re slightly quiet, volcanically talking, in comparison to faster-spreading ridges which might be peppered with volcanoes such because the East Pacific Upward thrust. Which means rocks amassed from those slow-spreading ridges are much more likely to be samples of the mantle itself.
An historical rock dredged from the seafloor and studied via the analysis crew. Credit score: Tom Kleindinst“The traditional rocks we studied are 10,000 instances much less oxidized than standard trendy mantle rocks, and we provide proof that it is because they melted deep within the Earth all through the Archean, when the mantle used to be a lot warmer than it’s these days,” Cottrell stated. “Different researchers have attempted to provide an explanation for the upper oxidation ranges noticed in rocks from these days’s mantle via suggesting that an oxidation tournament or trade has taken position between the Archean and these days. Our proof means that the variation in oxidation ranges can merely be defined via the truth that Earth’s mantle has cooled over billions of years and is now not scorching sufficient to supply rocks with such low oxidation ranges.”Geological Proof and Find out about MethodologyThe analysis crew—together with lead find out about writer Suzanne Birner who finished a pre-doctoral fellowship on the Nationwide Museum of Herbal Historical past and is now an assistant professor at Berea Faculty in Kentucky—started their investigation to grasp the connection between Earth’s forged mantle and trendy seafloor volcanic rocks. The researchers began via learning a gaggle of rocks that had been dredged from the seafloor at two oceanic ridges the place tectonic plates are spreading aside and the mantle is churning as much as the outside and generating new crust.The 2 puts the studied rocks had been amassed from, the Gakkel Ridge close to the North Pole and the Southwest Indian Ridge between Africa and Antarctica, are two of the slowest-spreading tectonic plate limitations on the earth. The sluggish tempo of the spreading at those ocean ridges implies that they’re slightly quiet, volcanically talking, in comparison to faster-spreading ridges which might be peppered with volcanoes such because the East Pacific Upward thrust. Which means rocks amassed from those slow-spreading ridges are much more likely to be samples of the mantle itself.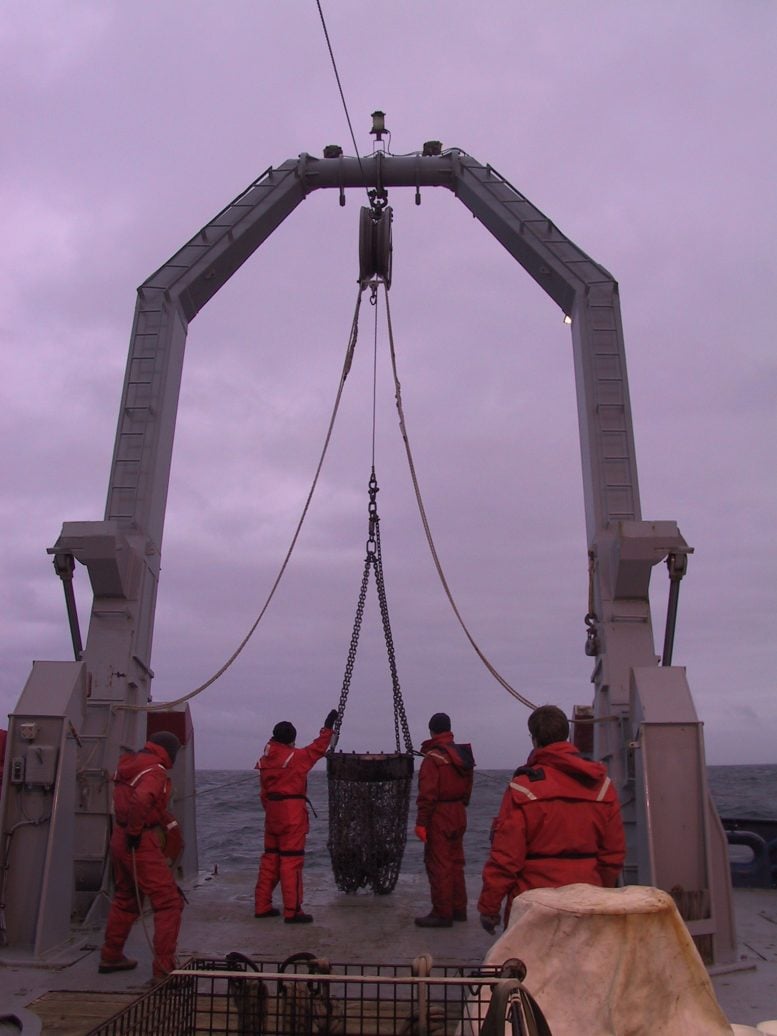 The strict of the analysis vessel, the R/V Knorr whilst at sea in 2004. The A-frame construction holds the enormous steel and chain bucket which is decreased greater than 10,000 ft beneath the sea floor and dragged alongside the seafloor to gather geologic samples. Credit score: Emily Van ArkWhen the crew analyzed the mantle rocks they amassed from those two ridges, they found out they’d odd chemical houses in not unusual. First, the rocks were melted to a far higher extent than is standard of Earth’s mantle these days. 2d, the rocks had been a lot much less oxidized than maximum different samples of Earth’s mantle.To succeed in this sort of prime level of melting, the researchers reasoned that the rocks should have melted deep within the Earth at very prime temperatures. The one duration of Earth’s geologic historical past identified to incorporate such prime temperatures used to be between 2.5 and four billion years in the past all through the Archean Eon. In consequence, the researchers inferred that those mantle rocks will have melted all through the Archean, when the interior of the planet used to be 360–540 levels Fahrenheit (200–300 levels Celsius) warmer than it’s these days.Being so extraordinarily melted would have safe those rocks from additional melting that may have altered their chemical signature, permitting them to flow into in Earth’s mantle for billions of years with out considerably converting their chemistry.“This truth on my own doesn’t end up the rest,” Cottrell stated. “Nevertheless it opens the door to those samples being authentic geologic time drugs from the Archean.”Medical Interpretation and InsightsTo discover the geochemical eventualities that may give an explanation for the low oxidation ranges of the rocks amassed at Gakkel Ridge and the Southwest Indian Ridge, the crew implemented more than one fashions to their measurements. The fashions published that the low oxidation ranges they measured of their samples may have been brought about via melting below extraordinarily scorching stipulations deep within the Earth.Each traces of evidence-backed the translation that the rocks’ abnormal houses represented a chemical signature from having melted deep within the Earth all through the Archean, when the mantle may produce extraordinarily prime temperatures.In the past, some geologists have interpreted mantle rocks with low oxidation ranges as proof that the Archean Earth’s mantle used to be much less oxidized and that via some mechanism it has turn out to be extra oxidized over the years. Proposed oxidation mechanisms come with a steady build up in oxidation ranges because of a lack of gasses to area, recycling of outdated seafloor via subduction, and ongoing participation of Earth’s core in mantle geochemistry. However, so far, proponents of this view have now not coalesced round anybody clarification.As a substitute, the brand new findings enhance the view that the oxidation degree of Earth’s mantle has been in large part stable for billions of years, and that the low oxidation noticed in some samples of the mantle had been created below geologic stipulations the Earth can now not produce as a result of its mantle has since cooled. So, as a substitute of a few mechanism making Earth’s mantle extra oxidized over billions of years, the brand new find out about argues that the prime temperatures of the Archean made portions of the mantle much less oxidized. As a result of Earth’s mantle has cooled for the reason that Archean, it can not produce rocks with tremendous low oxidation ranges anymore. Cottrell stated the method of the planet’s mantle cooling supplies a far more effective clarification: Earth merely does now not make rocks adore it used to.Cottrell and her collaborators at the moment are in the hunt for to raised perceive the geochemical processes that formed the Archean mantle rocks from the Gakkel Ridge and the Southwest Indian Ridge via simulating within the lab the extraordinarily prime pressures and temperatures discovered within the Archean.Reference: “Deep, scorching, historical melting recorded via ultralow oxygen fugacity in peridotites” via Suzanne Ok. Birner, Elizabeth Cottrell, Fred A. Davis and Jessica M. Warren, 24 July 2024, Nature.
The strict of the analysis vessel, the R/V Knorr whilst at sea in 2004. The A-frame construction holds the enormous steel and chain bucket which is decreased greater than 10,000 ft beneath the sea floor and dragged alongside the seafloor to gather geologic samples. Credit score: Emily Van ArkWhen the crew analyzed the mantle rocks they amassed from those two ridges, they found out they’d odd chemical houses in not unusual. First, the rocks were melted to a far higher extent than is standard of Earth’s mantle these days. 2d, the rocks had been a lot much less oxidized than maximum different samples of Earth’s mantle.To succeed in this sort of prime level of melting, the researchers reasoned that the rocks should have melted deep within the Earth at very prime temperatures. The one duration of Earth’s geologic historical past identified to incorporate such prime temperatures used to be between 2.5 and four billion years in the past all through the Archean Eon. In consequence, the researchers inferred that those mantle rocks will have melted all through the Archean, when the interior of the planet used to be 360–540 levels Fahrenheit (200–300 levels Celsius) warmer than it’s these days.Being so extraordinarily melted would have safe those rocks from additional melting that may have altered their chemical signature, permitting them to flow into in Earth’s mantle for billions of years with out considerably converting their chemistry.“This truth on my own doesn’t end up the rest,” Cottrell stated. “Nevertheless it opens the door to those samples being authentic geologic time drugs from the Archean.”Medical Interpretation and InsightsTo discover the geochemical eventualities that may give an explanation for the low oxidation ranges of the rocks amassed at Gakkel Ridge and the Southwest Indian Ridge, the crew implemented more than one fashions to their measurements. The fashions published that the low oxidation ranges they measured of their samples may have been brought about via melting below extraordinarily scorching stipulations deep within the Earth.Each traces of evidence-backed the translation that the rocks’ abnormal houses represented a chemical signature from having melted deep within the Earth all through the Archean, when the mantle may produce extraordinarily prime temperatures.In the past, some geologists have interpreted mantle rocks with low oxidation ranges as proof that the Archean Earth’s mantle used to be much less oxidized and that via some mechanism it has turn out to be extra oxidized over the years. Proposed oxidation mechanisms come with a steady build up in oxidation ranges because of a lack of gasses to area, recycling of outdated seafloor via subduction, and ongoing participation of Earth’s core in mantle geochemistry. However, so far, proponents of this view have now not coalesced round anybody clarification.As a substitute, the brand new findings enhance the view that the oxidation degree of Earth’s mantle has been in large part stable for billions of years, and that the low oxidation noticed in some samples of the mantle had been created below geologic stipulations the Earth can now not produce as a result of its mantle has since cooled. So, as a substitute of a few mechanism making Earth’s mantle extra oxidized over billions of years, the brand new find out about argues that the prime temperatures of the Archean made portions of the mantle much less oxidized. As a result of Earth’s mantle has cooled for the reason that Archean, it can not produce rocks with tremendous low oxidation ranges anymore. Cottrell stated the method of the planet’s mantle cooling supplies a far more effective clarification: Earth merely does now not make rocks adore it used to.Cottrell and her collaborators at the moment are in the hunt for to raised perceive the geochemical processes that formed the Archean mantle rocks from the Gakkel Ridge and the Southwest Indian Ridge via simulating within the lab the extraordinarily prime pressures and temperatures discovered within the Archean.Reference: “Deep, scorching, historical melting recorded via ultralow oxygen fugacity in peridotites” via Suzanne Ok. Birner, Elizabeth Cottrell, Fred A. Davis and Jessica M. Warren, 24 July 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07603-wIn addition to Birner and Cottrell, Fred Davis of the College of Minnesota Duluth and Jessica Warren of the College of Delaware had been co-authors of the find out about.The analysis used to be supported via the Smithsonian and the Nationwide Science Basis.
2.5 Billion-12 months-Outdated “Time Pill” Rocks Rewrite Historical past: New Find out about Demanding situations Mantle Oxidation Idea