The Aurich Lawson worm that went undetected for a decade has left hundreds of macOS and iOS apps susceptible to device distributors. Hackers can have added malicious code that can have compromised the protection of hundreds of thousands or billions of people that put in it, researchers stated Monday. The vulnerability, which used to be established closing October, used to be within the “trunk” server used to control CocoaPods, a repository of open-source Swift and Function-C initiatives that just about 3 million macOS and iOS programs depend on. When builders replace certainly one of their “pods” — CocoaPods is lingo for generic applications — the programs they rely on regularly combine them routinely thru device updates, regularly with none interplay required from customers. Code injection possibility “Many systems can get right of entry to the person’s delicate knowledge: bank card knowledge, scientific historical past, non-public units, and so forth.,” wrote researchers from EVA Data Safety, the corporate that came upon the vulnerability. “Encrypting numbers in those systems can permit attackers to get right of entry to this data for any malicious reason why you’ll be able to call to mind – ransomware, fraud, fraud, company espionage… The 3 threats EVA came upon come from the insecure authentication emails used to authenticate pod producers. The producer posted the cope with of the e-mail hooked up to their pod. When an individual clicks at the hyperlink, the attacker can spoof the hyperlink to indicate to the attacker’s underlying XFH HTTP via figuring out the objective particular person within the HTTP request. EVA researchers discovered that they are able to use pretend XFH to generate the specified URLs. Generally, the e-mail incorporates a sound hyperlink to the CocoaPods.org server equivalent to:
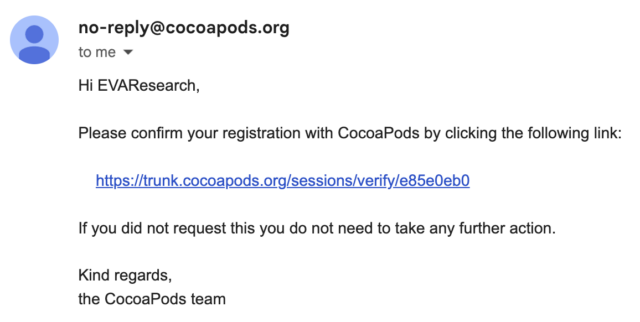 Amplify / How the verification e mail looks as if.EVA Data Safety Researchers can trade the hyperlink to direct to their very own server:
Amplify / How the verification e mail looks as if.EVA Data Safety Researchers can trade the hyperlink to direct to their very own server:
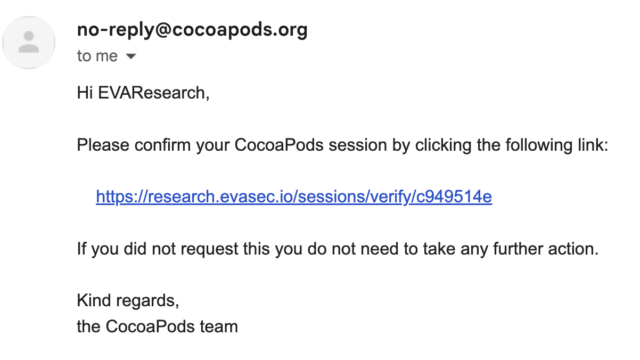 Lengthen / Validate e mail after it’s been changed.EVA Data Safety This vulnerability, which is recognized as CVE-2024-38367, is living within the session_controller elegance of the supply code, which controls the consultation’s authentication URL. This elegance implements the sessions_controller.rb manner, which prioritizes XFH over the preliminary host header. The code for getting access to the browser used to be: POST /api/v1/classes HTTP/1.1 Host: trunk.cococapods.org Content material-Sort: utility/json; charset=utf-8 Obtain: serve as/json; charset=utf-8 Person-Agent: CocoaPods/1.12.1 Settle for-Encoding: gzip, deflate X-Forwarded-Host: analysis.evasec.io Content material-Period: 78 {“e mail”:”analysis@evasec.io”, “Title”:”EVAResearch”, “descript”:null } Any other vulnerability recognized as CVE-2024-38368 allowed attackers to regulate pods that had been deserted via their builders however proceed for use via programs. The device interface that permits producers to recycle their pods has remained lively just about 10 years after it used to be first offered. The researchers discovered that any one who has get right of entry to to an orphaned pot can turn on it to take regulate, with out evidence of possession required. A easy curl request that contained the identify of the pod used to be all that used to be wanted: # Curl request to modify the possession of the orphan that desires to curve -X ‘POST’ -H ‘Host: trunk.cocoapods.org’ -H ‘Content material- Sort: the use of/x-www-form-urlencoded’ –data-binary ‘proprietor[name]=EVA&e mail=analysis@evasec.io’ –data-binary ‘pods[]=[TARGET_UNCLAIMED_POD]&button=SUBMIT’ ‘ A 3rd vulnerability, CVE-2024-38366, allowed attackers to execute code at the major server. The primary server is determined by RFC822 which used to be established in 1982 to ensure registered e mail addresses and notice in the event that they apply the right kind process. A part of this procedure comes to checking the MX report of e mail addresses as established via this RFC822.
Lengthen / Validate e mail after it’s been changed.EVA Data Safety This vulnerability, which is recognized as CVE-2024-38367, is living within the session_controller elegance of the supply code, which controls the consultation’s authentication URL. This elegance implements the sessions_controller.rb manner, which prioritizes XFH over the preliminary host header. The code for getting access to the browser used to be: POST /api/v1/classes HTTP/1.1 Host: trunk.cococapods.org Content material-Sort: utility/json; charset=utf-8 Obtain: serve as/json; charset=utf-8 Person-Agent: CocoaPods/1.12.1 Settle for-Encoding: gzip, deflate X-Forwarded-Host: analysis.evasec.io Content material-Period: 78 {“e mail”:”analysis@evasec.io”, “Title”:”EVAResearch”, “descript”:null } Any other vulnerability recognized as CVE-2024-38368 allowed attackers to regulate pods that had been deserted via their builders however proceed for use via programs. The device interface that permits producers to recycle their pods has remained lively just about 10 years after it used to be first offered. The researchers discovered that any one who has get right of entry to to an orphaned pot can turn on it to take regulate, with out evidence of possession required. A easy curl request that contained the identify of the pod used to be all that used to be wanted: # Curl request to modify the possession of the orphan that desires to curve -X ‘POST’ -H ‘Host: trunk.cocoapods.org’ -H ‘Content material- Sort: the use of/x-www-form-urlencoded’ –data-binary ‘proprietor[name]=EVA&e mail=analysis@evasec.io’ –data-binary ‘pods[]=[TARGET_UNCLAIMED_POD]&button=SUBMIT’ ‘ A 3rd vulnerability, CVE-2024-38366, allowed attackers to execute code at the major server. The primary server is determined by RFC822 which used to be established in 1982 to ensure registered e mail addresses and notice in the event that they apply the right kind process. A part of this procedure comes to checking the MX report of e mail addresses as established via this RFC822.












/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25806981/parker_solar_probe_artist_rendering.jpg)