Kind of 41,000 years in the past, Earth’s magnetic box weakened dramatically because the planet’s poles started to opposite — a herbal however uncommon phenomenon referred to as a geomagnetic tour. Consistent with new analysis from the College of Michigan, this shift uncovered a lot of Earth to damaging sun radiation, forcing early people to conform or perish.
The find out about means that Homo sapiens survived — and in the long run thrived — through growing applied sciences like adapted clothes, sun-blocking ochre, and strategic cave use. Neanderthals, then again, would possibly not have had the similar equipment for survival.
“Within the find out about, we mixed the entire areas the place the magnetic box wouldn’t have been attached, permitting cosmic radiation, or any roughly full of life debris from the solar, to seep all of the manner in to the bottom,” mentioned Agnit Mukhopadhyay, lead writer.
“We discovered that a lot of the ones areas in reality fit lovely intently with early human process from 41,000 years in the past, in particular an build up in using caves and an build up in using prehistoric sunscreen.”
A wandering North Pole and a weakened protect
About 41,000 years in the past, right through the Laschamps tour, Earth’s magnetic box was once best 10% of what it’s these days. With much less coverage, sun debris and cosmic radiation streamed into Earth’s setting, bringing aurora to low latitudes and lengthening UV publicity globally.
With the assistance of a extra complicated three-D reconstruction of Earth’s geospace device, Mukhopadhyay and his workforce simulated how charged sun debris would have penetrated the faint magnetic box. Their fashions counsel that the most powerful affects affected Europe and Northern Africa, which is exactly the place the early Homo sapiens and Neanderthal populations thrived along one some other.
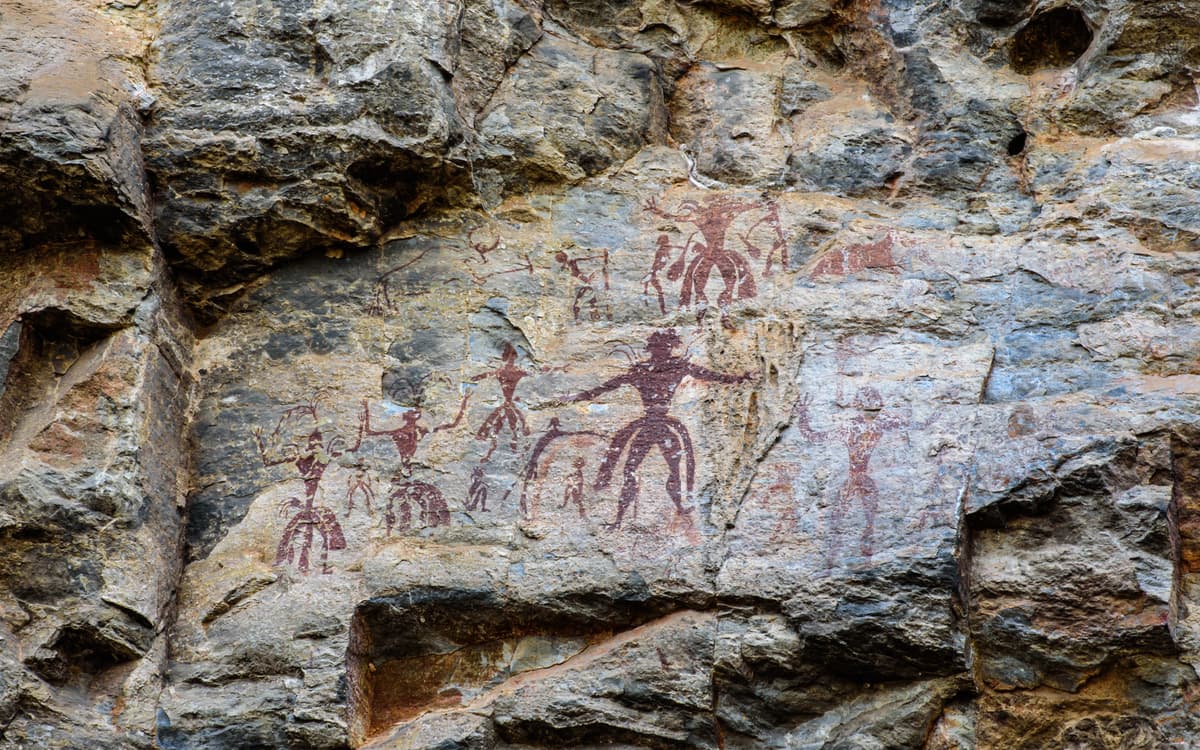
Round this identical time, archaeological proof presentations that Homo sapiens started the usage of ochre extra often — a mineral with herbal sun-blocking homes — and generating adapted clothes with equipment like needles and awls. Those diversifications, the researchers argue, had been extra than simply cultural traits; they will had been crucial to survival.
Those clothes helped take care of heat and enabled complicated mobility, leading to stepped forward searching levels. Keeping up frame temperature whilst protective from environmental stresses was once crucial right through this era.
On the identical time, Neanderthals, who didn’t have such clothes applied sciences and perhaps didn’t use ochre as sunblock, disappeared from Europe kind of 40,000 years in the past.
Implications for these days — and for different worlds
If this sort of magnetic tour took place these days, Mukhopadhyay says, shall we be expecting critical affects: communique blackouts, satellite tv for pc screw ups, and infrastructure disruption.
“I feel it’s necessary to notice that those findings are correlational and (ours is a) meta research, if you’ll,” mentioned Raven Garvey. “However I feel this is a contemporary point of view on those knowledge in gentle of the Laschamps tour.”
The analysis additionally informs the seek for extraterrestrial existence.“Many of us say {that a} planet can’t maintain existence with out a robust magnetic box,” he mentioned.“Having a look at prehistoric Earth, and particularly at occasions like this, is helping us find out about exoplanetary physics from an overly other vantage level. Lifestyles did exist again then. However it was once a bit of bit other than it’s these days.”