Abstract: Researchers came upon a singular function of the proteasome, historically referred to as the mobile’s waste processor, in nerve cells. Their findings expose that proteasomes in dorsal root ganglion neurons would possibly act extra like sign messengers, assisting within the differentiation between ache and itch sensations.Through blocking off proteasomes with particular inhibitors in mice, the researchers seen vital adjustments in sensory reaction, highlighting the proteasomes’ function in environmental sensing and neuronal communique. This find out about now not handiest redefines our figuring out of proteasome purposes but in addition opens new avenues for treating sensory problems.Key Information:Proteasomes are historically seen as mobile rubbish disposals however are actually noticed as a very powerful for signaling in sensory neurons.The find out about used a proteasome-blocking drug to reveal that those constructions are crucial for standard sensory purposes, affecting how temporarily mice replied to sensory checks.Researchers recommend that manipulating neuronal membrane proteasomes may doubtlessly modify ache and itch sensations, offering a brand new goal for healing interventions.Supply: Johns Hopkins MedicineThe conventional process of the proteasome, the rubbish disposal of the mobile, is to grind down proteins into smaller bits and recycle a few of the ones bits and portions. That’s nonetheless the case, for probably the most section, however, Johns Hopkins Drugs researchers, learning nerve cells grown within the lab and mice, say that the proteasome’s function would possibly pass way past that.Its further function, say the researchers, would possibly shift from trash sorter to sign messenger in dorsal root ganglion neurons — cells that put across sensory alerts from nerve cells on the subject of the outside to the central worried device. 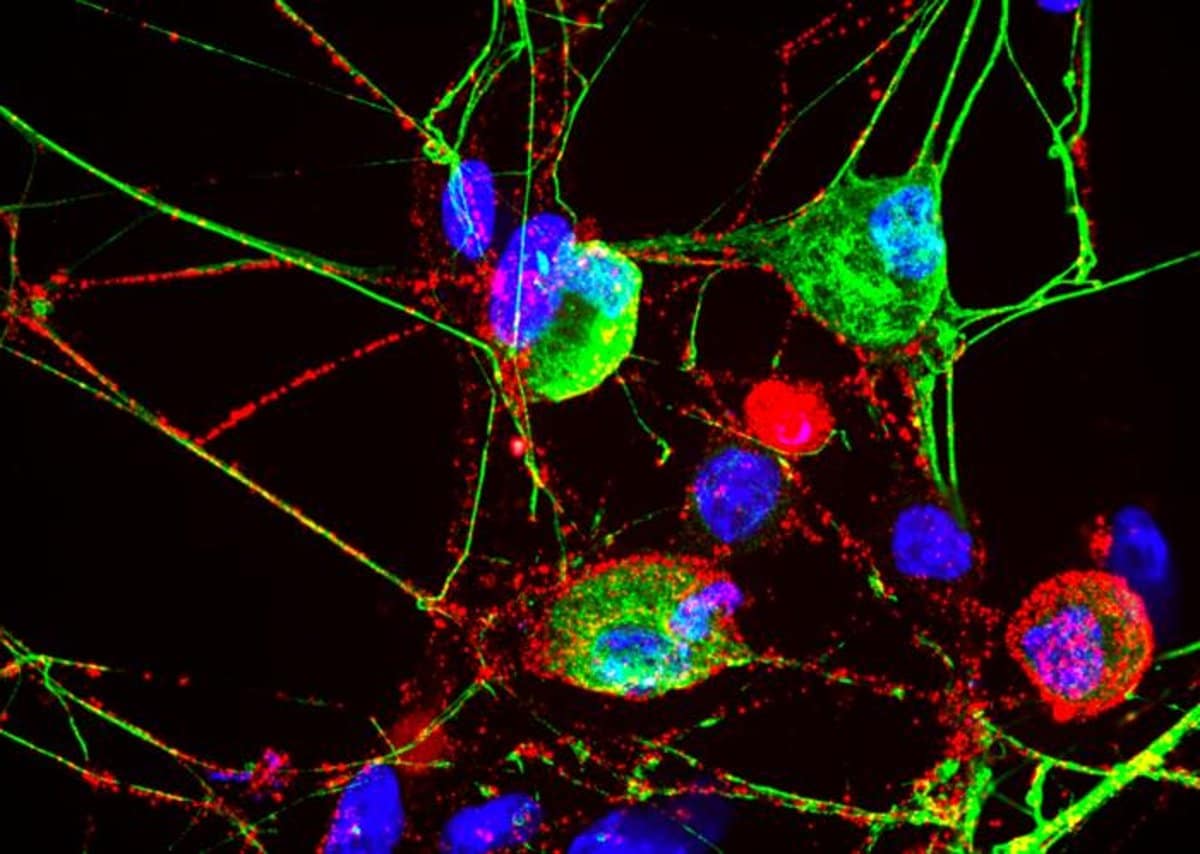 Neuronal membrane proteasomes are classified with a crimson compound and seem in a subset of sensory neurons which are classified with inexperienced compound. Notice, now not all inexperienced classified neurons have the crimson label, which will seem in different distinctive dorsal root ganglion neurons that don’t label with inexperienced. Blue staining is the nuclei of cells within the tradition dish. Credit score: Seth Margolis and Eric Villalón Landeros, Johns Hopkins MedicineResults in their experiments, printed April 12 in Cellular Studies, display that proteasomes would possibly assist the ones specialised neurons sense the encompassing setting, ship alerts to one another and doubtlessly differentiate between sensing ache and itch, a discovering that would assist scientists higher perceive those sensory processes and new goals for treating ache and different sensory issues.“Neurons reside subsequent to one another for a very long time, they usually want techniques to be in contact with every different about what they’re doing and who they’re,” says Seth S. Margolis, Ph.D., affiliate professor of organic chemistry on the Johns Hopkins College Faculty of Drugs.“Proteasomes within the membrane of neurons would possibly assist the cells effective song this messaging procedure.”“Proteasomes are extra difficult than they seem,” says Margolis. He and his colleagues first discovered proteasomes within the plasma membranes of central worried device neurons in mice in 2017, which they dubbed neuronal membrane proteasomes, and feature persisted learning how those particular proteasomes advertise messaging, or crosstalk, amongst neurons.On the time, Margolis’ center of attention used to be at the central worried device, encompassing the mind and spinal wire. However later, he collaborated with neurobiologist Eric Villalón Landeros, Ph.D., postdoctoral fellow in Margolis’ laboratory at Johns Hopkins, whose paintings makes a speciality of the peripheral worried device, the community of neurons operating thru the remainder of the frame, nearer to the outside, taking pictures sensory knowledge from the surroundings.Margolis and Villalón Landeros questioned whether or not proteasomes might be present in peripheral neurons, and if this is the case, what they may do.The usage of mouse antibodies that glom directly to proteasomes, and different strategies, the investigators discovered the proteasomes at the floor of neurons within the spinal wire, dorsal root ganglia, sciatic nerve and peripheral nerves innervating pores and skin.The researchers have been additionally in a position to search out proteasomes in the similar form of peripheral neurons grown in laboratory tradition dishes.To know the proteasome’s serve as in peripheral sensory neurons, the researchers gave mice biotin-epoxomicin, a mobile membrane-impermeable proteasome inhibitor that blocks the serve as of neuronal membrane proteasomes. Then, they carried out vintage sensory checks.The researchers discovered that the mice that were given injections of the proteasome-blocking drug biotin-epoxomicin on one facet of the frame have been between 25% to 50% slower than the opposite facet to answer sensory checks.“This implies that membrane proteasomes are essential for sensation, they usually will have to be facilitating this on the signaling degree,” says Margolis.The researchers used unmarried mobile sequencing generation to decide that membrane proteasomes have been expressed in a subpopulation of neurons interested by itch sensation and identified to be delicate to histamine, an immune device compound that launches an animal’s (together with human’s) reaction to allergens.In laboratory tradition dishes, the researchers stimulated each itch-related and non-itch connected neurons and blocked their membrane proteasomes with biotin-epoxomicin. This led to adjustments to exercise in the entire cells.“Blockading proteasomes turns out to have an activity-modulatory impact throughout the entire cells, regardless of being expressed in a subpopulation, suggesting that proteasomes facilitate a type of go communicate between those cells,” says Margolis.Proteasome blockers, together with one known as Velcade, are recently used to regard positive kinds of most cancers.Villalón Landeros and Margolis plan to proceed operating in combination to decide how neuronal membrane proteasomes serve as in sensory neurons and in sensing ache as opposed to itch.“We wish to see if we will be able to manipulate neuronal membrane proteasomes to have a special consequence on ache and itch sensation,” says Villalón Landeros.Further scientists who contributed to the analysis are Samuel Kho, Taylor Church, Anna Brennan, Fulya Türker, Michael Delannoy and Michael Caterina from Johns Hopkins.Investment: Investment for the analysis used to be equipped by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (F32NS119202, R01 NS110754) and a Merkin Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Regeneration Middle grant.About this sensory neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Vanessa Wasta
Neuronal membrane proteasomes are classified with a crimson compound and seem in a subset of sensory neurons which are classified with inexperienced compound. Notice, now not all inexperienced classified neurons have the crimson label, which will seem in different distinctive dorsal root ganglion neurons that don’t label with inexperienced. Blue staining is the nuclei of cells within the tradition dish. Credit score: Seth Margolis and Eric Villalón Landeros, Johns Hopkins MedicineResults in their experiments, printed April 12 in Cellular Studies, display that proteasomes would possibly assist the ones specialised neurons sense the encompassing setting, ship alerts to one another and doubtlessly differentiate between sensing ache and itch, a discovering that would assist scientists higher perceive those sensory processes and new goals for treating ache and different sensory issues.“Neurons reside subsequent to one another for a very long time, they usually want techniques to be in contact with every different about what they’re doing and who they’re,” says Seth S. Margolis, Ph.D., affiliate professor of organic chemistry on the Johns Hopkins College Faculty of Drugs.“Proteasomes within the membrane of neurons would possibly assist the cells effective song this messaging procedure.”“Proteasomes are extra difficult than they seem,” says Margolis. He and his colleagues first discovered proteasomes within the plasma membranes of central worried device neurons in mice in 2017, which they dubbed neuronal membrane proteasomes, and feature persisted learning how those particular proteasomes advertise messaging, or crosstalk, amongst neurons.On the time, Margolis’ center of attention used to be at the central worried device, encompassing the mind and spinal wire. However later, he collaborated with neurobiologist Eric Villalón Landeros, Ph.D., postdoctoral fellow in Margolis’ laboratory at Johns Hopkins, whose paintings makes a speciality of the peripheral worried device, the community of neurons operating thru the remainder of the frame, nearer to the outside, taking pictures sensory knowledge from the surroundings.Margolis and Villalón Landeros questioned whether or not proteasomes might be present in peripheral neurons, and if this is the case, what they may do.The usage of mouse antibodies that glom directly to proteasomes, and different strategies, the investigators discovered the proteasomes at the floor of neurons within the spinal wire, dorsal root ganglia, sciatic nerve and peripheral nerves innervating pores and skin.The researchers have been additionally in a position to search out proteasomes in the similar form of peripheral neurons grown in laboratory tradition dishes.To know the proteasome’s serve as in peripheral sensory neurons, the researchers gave mice biotin-epoxomicin, a mobile membrane-impermeable proteasome inhibitor that blocks the serve as of neuronal membrane proteasomes. Then, they carried out vintage sensory checks.The researchers discovered that the mice that were given injections of the proteasome-blocking drug biotin-epoxomicin on one facet of the frame have been between 25% to 50% slower than the opposite facet to answer sensory checks.“This implies that membrane proteasomes are essential for sensation, they usually will have to be facilitating this on the signaling degree,” says Margolis.The researchers used unmarried mobile sequencing generation to decide that membrane proteasomes have been expressed in a subpopulation of neurons interested by itch sensation and identified to be delicate to histamine, an immune device compound that launches an animal’s (together with human’s) reaction to allergens.In laboratory tradition dishes, the researchers stimulated each itch-related and non-itch connected neurons and blocked their membrane proteasomes with biotin-epoxomicin. This led to adjustments to exercise in the entire cells.“Blockading proteasomes turns out to have an activity-modulatory impact throughout the entire cells, regardless of being expressed in a subpopulation, suggesting that proteasomes facilitate a type of go communicate between those cells,” says Margolis.Proteasome blockers, together with one known as Velcade, are recently used to regard positive kinds of most cancers.Villalón Landeros and Margolis plan to proceed operating in combination to decide how neuronal membrane proteasomes serve as in sensory neurons and in sensing ache as opposed to itch.“We wish to see if we will be able to manipulate neuronal membrane proteasomes to have a special consequence on ache and itch sensation,” says Villalón Landeros.Further scientists who contributed to the analysis are Samuel Kho, Taylor Church, Anna Brennan, Fulya Türker, Michael Delannoy and Michael Caterina from Johns Hopkins.Investment: Investment for the analysis used to be equipped by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (F32NS119202, R01 NS110754) and a Merkin Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Regeneration Middle grant.About this sensory neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Vanessa Wasta
Supply: Johns Hopkins Drugs
Touch: Vanessa Wasta – Johns Hopkins Drugs
Symbol: The picture is credited to Seth Margolis and Eric Villalón Landeros, Johns Hopkins MedicineOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“The nociceptive exercise of peripheral sensory neurons is modulated by way of the neuronal membrane proteasome” by way of Seth Margolis et al. Cellular ReportsAbstractThe nociceptive exercise of peripheral sensory neurons is modulated by way of the neuronal membrane proteasomeHighlightsThe neuronal membrane proteasome (NMP) is located in peripheral somatosensory neuronsThe NMP selectively localizes to express kinds of somatosensory neuronsThe NMP mediates crosstalk between sensory neurons to modulate sensitivity to stimulationInhibition of the NMP reduces sensitivity to mechanical and painful stimuliSummaryProteasomes are crucial for peripheral worried device (PNS) serve as. Right here, we examine mammalian PNS proteasomes and expose the presence of the neuronal membrane proteasome (NMP).We display that exact inhibition of the NMP on distal nerve fibers innervating the mouse hind paw ends up in relief in mechanical and ache sensitivity.Via investigating PNS NMPs, we reveal their presence at the somata and proximal and distal axons of a subset of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Unmarried-cell RNA sequencing experiments expose that the NMP-expressing DRGs are essentially MrgprA3+ and Cysltr2+.NMP inhibition in DRG cultures ends up in cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous adjustments in Ca2+ signaling brought on by way of KCl depolarization, αβ-meATP, or the pruritogen histamine.Taken in combination, those knowledge improve a style wherein NMPs are expressed on a subset of somatosensory DRGs to modulate signaling between neurons of distinct sensory modalities and point out the NMP as a possible goal for controlling ache.
Proteasomes Might Be Key to Sensory Alerts – Neuroscience Information