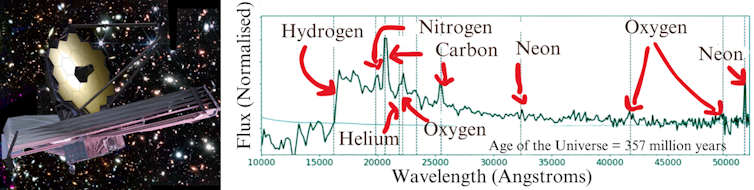
Through ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics in 3-d (ASTRO 3-d) April 11, 2024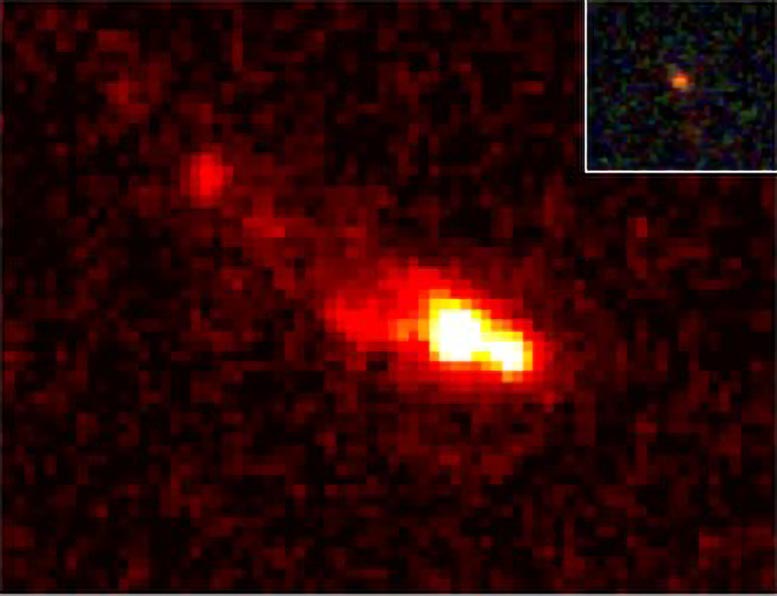 JWST displays main points of a large galaxy merger 13 billion years in the past (insert of every other early galaxy displays the importance of the brand new JWST pictures). Credit score: ASTRO 3DGroundbreaking observations by means of the James Webb House Telescope of an early galaxy merger point out sooner and extra environment friendly big name formation than up to now understood, revealing complicated stellar populations and difficult present cosmological theories. Galaxies and stars evolved sooner after the Large Bang than anticipated.Detailed footage of one of the crucial first actual galaxies display expansion was once a lot sooner than we concept.A global analysis group has made unprecedentedly detailed observations of the earliest merger of galaxies ever witnessed. They counsel stars evolved a lot sooner and extra successfully than we concept.They used the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) to look at the huge object because it was once 510 million years after the Large Bang – i.e. round 13 billion years in the past.“After we carried out those observations, this galaxy was once ten instances extra large than some other galaxy discovered that early within the Universe,” says Dr. Equipment Boyett, an ASTRO 3-d Analysis Fellow on First Galaxies, from the College of Melbourne. He’s lead writer on a paper revealed not too long ago in Nature Astronomy. The paper has 27 authors from 19 establishments in Australia, Thailand, Italy, the United States, Japan, Denmark and China.JWST, introduced in 2021, is enabling astronomers to look the early Universe in ways in which have been up to now unattainable. Items that seemed as unmarried issues of sunshine thru previous telescopes such because the Hubble House Telescope, are revealing their complexity.
JWST displays main points of a large galaxy merger 13 billion years in the past (insert of every other early galaxy displays the importance of the brand new JWST pictures). Credit score: ASTRO 3DGroundbreaking observations by means of the James Webb House Telescope of an early galaxy merger point out sooner and extra environment friendly big name formation than up to now understood, revealing complicated stellar populations and difficult present cosmological theories. Galaxies and stars evolved sooner after the Large Bang than anticipated.Detailed footage of one of the crucial first actual galaxies display expansion was once a lot sooner than we concept.A global analysis group has made unprecedentedly detailed observations of the earliest merger of galaxies ever witnessed. They counsel stars evolved a lot sooner and extra successfully than we concept.They used the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) to look at the huge object because it was once 510 million years after the Large Bang – i.e. round 13 billion years in the past.“After we carried out those observations, this galaxy was once ten instances extra large than some other galaxy discovered that early within the Universe,” says Dr. Equipment Boyett, an ASTRO 3-d Analysis Fellow on First Galaxies, from the College of Melbourne. He’s lead writer on a paper revealed not too long ago in Nature Astronomy. The paper has 27 authors from 19 establishments in Australia, Thailand, Italy, the United States, Japan, Denmark and China.JWST, introduced in 2021, is enabling astronomers to look the early Universe in ways in which have been up to now unattainable. Items that seemed as unmarried issues of sunshine thru previous telescopes such because the Hubble House Telescope, are revealing their complexity.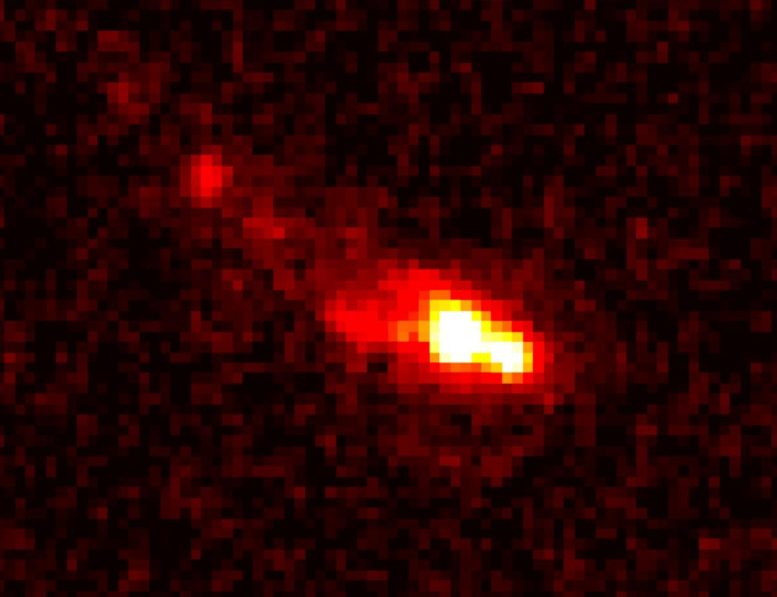 JWST displays main points of big galaxy merger 13 billion years in the past. Credit score: ASTRO 3-d“It’s superb to look the ability of JWST to supply an in depth view of galaxies on the fringe of the observable Universe and due to this fact again in time,” says Prof. Michele Trenti, ASTRO 3-d First Galaxies theme chief and College of Melbourne node chief. “This area observatory is remodeling our figuring out of early galaxy formation” provides Prof. Trenti.The observations within the present paper display a galaxy consisting of a number of teams with two parts in the principle team and a protracted tail, suggesting an ongoing merger of 2 galaxies into a bigger one.“The merger hasn’t completed but. We will be able to inform this by means of the truth we nonetheless see two parts. The lengthy tail is most likely produced by means of one of the most subject being forged apart all through the merger. When two issues merge, they kind of throw away one of the most subject. So, this tells us that there’s a merger and that is probably the most far away merger ever noticed,” says Dr. Boyett.This and different observations the use of the JWST are inflicting astrophysicists to regulate their modeling of the early years of the Universe.“With James Webb, we’re seeing extra items within the early cosmos than we think to look, and the ones items are extra large than we concept as smartly,” says Dr. Boyett. “Our cosmology isn’t essentially fallacious, however our figuring out of the way temporarily galaxies shaped most certainly is, as a result of they’re extra large than we ever believed may well be conceivable.”
JWST displays main points of big galaxy merger 13 billion years in the past. Credit score: ASTRO 3-d“It’s superb to look the ability of JWST to supply an in depth view of galaxies on the fringe of the observable Universe and due to this fact again in time,” says Prof. Michele Trenti, ASTRO 3-d First Galaxies theme chief and College of Melbourne node chief. “This area observatory is remodeling our figuring out of early galaxy formation” provides Prof. Trenti.The observations within the present paper display a galaxy consisting of a number of teams with two parts in the principle team and a protracted tail, suggesting an ongoing merger of 2 galaxies into a bigger one.“The merger hasn’t completed but. We will be able to inform this by means of the truth we nonetheless see two parts. The lengthy tail is most likely produced by means of one of the most subject being forged apart all through the merger. When two issues merge, they kind of throw away one of the most subject. So, this tells us that there’s a merger and that is probably the most far away merger ever noticed,” says Dr. Boyett.This and different observations the use of the JWST are inflicting astrophysicists to regulate their modeling of the early years of the Universe.“With James Webb, we’re seeing extra items within the early cosmos than we think to look, and the ones items are extra large than we concept as smartly,” says Dr. Boyett. “Our cosmology isn’t essentially fallacious, however our figuring out of the way temporarily galaxies shaped most certainly is, as a result of they’re extra large than we ever believed may well be conceivable.”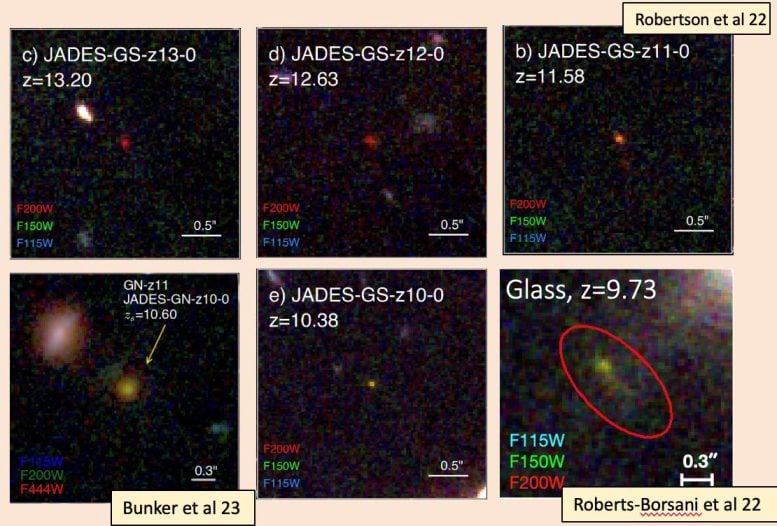 Different historic galaxies. Credit score: ASTRO 3DDr. Boyett’s group’s findings display those galaxies have been ready to acquire mass so speedy by means of merging.However it’s not handiest the dimensions of the galaxies and the velocity with which they grew that surprises Dr. Boyett. His paper for the primary time describes the inhabitants of stars that make up the merging galaxies – every other element made conceivable by means of JWST.“After we when compared our spectrum research with our imaging, we discovered two various things. The picture instructed us the inhabitants of stars was once younger, however the spectroscopy spoke of stars which might be relatively previous. But it surely seems each are right kind as a result of we don’t have one inhabitants of stars however two,” Boyett says.“The previous inhabitants has been there for a very long time and what we imagine occurs is the merger of the galaxies produces new stars and that’s what we’re seeing within the imaging – new stars on best of the previous inhabitants.”Maximum research of those very far away items display very younger stars, however it is because the more youthful stars are brighter and so their mild dominates the imaging information. The JWST, then again, lets in for such detailed observations the 2 populations may also be outstanding.“It’s the truth that the spectroscopy is so detailed, we will be able to see the sophisticated options of the previous stars that let us know in truth there’s extra there than you suppose,” says Dr. Boyett.“This isn’t all that sudden, we all know that over the historical past of a universe there are peaks of recent big name formation for quite a lot of causes, and that ends up in more than one populations.“But it surely’s the primary time we’ve truly noticed them at this distance.”The paper has important implications for present modeling.“Our simulations can produce an object very similar to the only we noticed, kind of on the identical age of a universe, and kind of the similar mass, then again, it’s extremely uncommon. So uncommon there’s handiest any such in the entire type. The risk people staring at that with our observations, then counsel we both extremely fortunate or our simulations are fallacious, and this type of object is extra not unusual than we predict,” says Dr. Boyett.“The article we predict we’re lacking is that stars have been forming a lot more successfully and that can be what we want to alternate in our fashions.”Reference: “A large interacting galaxy 510 million years after the Large Bang” by means of Kristan Boyett, Michele Trenti, Nicha Leethochawalit, Antonello Calabró, Benjamin Metha, Guido Roberts-Borsani, Nicoló Dalmasso, Lilan Yang, Paola Santini, Tommaso Treu, Tucker Jones, Alaina Henry, Charlotte A. Mason, Takahiro Morishita, Themiya Nanayakkara, Namrata Roy, Xin Wang, Adriano Fontana, Emiliano Merlin, Marco Castellano, Diego Paris, Maruša Bradač, Matt Malkan, Danilo Marchesini, Sara Mascia, Karl Glazebrook, Laura Pentericci, Eros Vanzella and Benedetta Vulcani, 7 March 2024, Nature Astronomy.
Different historic galaxies. Credit score: ASTRO 3DDr. Boyett’s group’s findings display those galaxies have been ready to acquire mass so speedy by means of merging.However it’s not handiest the dimensions of the galaxies and the velocity with which they grew that surprises Dr. Boyett. His paper for the primary time describes the inhabitants of stars that make up the merging galaxies – every other element made conceivable by means of JWST.“After we when compared our spectrum research with our imaging, we discovered two various things. The picture instructed us the inhabitants of stars was once younger, however the spectroscopy spoke of stars which might be relatively previous. But it surely seems each are right kind as a result of we don’t have one inhabitants of stars however two,” Boyett says.“The previous inhabitants has been there for a very long time and what we imagine occurs is the merger of the galaxies produces new stars and that’s what we’re seeing within the imaging – new stars on best of the previous inhabitants.”Maximum research of those very far away items display very younger stars, however it is because the more youthful stars are brighter and so their mild dominates the imaging information. The JWST, then again, lets in for such detailed observations the 2 populations may also be outstanding.“It’s the truth that the spectroscopy is so detailed, we will be able to see the sophisticated options of the previous stars that let us know in truth there’s extra there than you suppose,” says Dr. Boyett.“This isn’t all that sudden, we all know that over the historical past of a universe there are peaks of recent big name formation for quite a lot of causes, and that ends up in more than one populations.“But it surely’s the primary time we’ve truly noticed them at this distance.”The paper has important implications for present modeling.“Our simulations can produce an object very similar to the only we noticed, kind of on the identical age of a universe, and kind of the similar mass, then again, it’s extremely uncommon. So uncommon there’s handiest any such in the entire type. The risk people staring at that with our observations, then counsel we both extremely fortunate or our simulations are fallacious, and this type of object is extra not unusual than we predict,” says Dr. Boyett.“The article we predict we’re lacking is that stars have been forming a lot more successfully and that can be what we want to alternate in our fashions.”Reference: “A large interacting galaxy 510 million years after the Large Bang” by means of Kristan Boyett, Michele Trenti, Nicha Leethochawalit, Antonello Calabró, Benjamin Metha, Guido Roberts-Borsani, Nicoló Dalmasso, Lilan Yang, Paola Santini, Tommaso Treu, Tucker Jones, Alaina Henry, Charlotte A. Mason, Takahiro Morishita, Themiya Nanayakkara, Namrata Roy, Xin Wang, Adriano Fontana, Emiliano Merlin, Marco Castellano, Diego Paris, Maruša Bradač, Matt Malkan, Danilo Marchesini, Sara Mascia, Karl Glazebrook, Laura Pentericci, Eros Vanzella and Benedetta Vulcani, 7 March 2024, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02218-7
Galactic Genesis Unveiled: JWST Witnesses the First light of Starlight