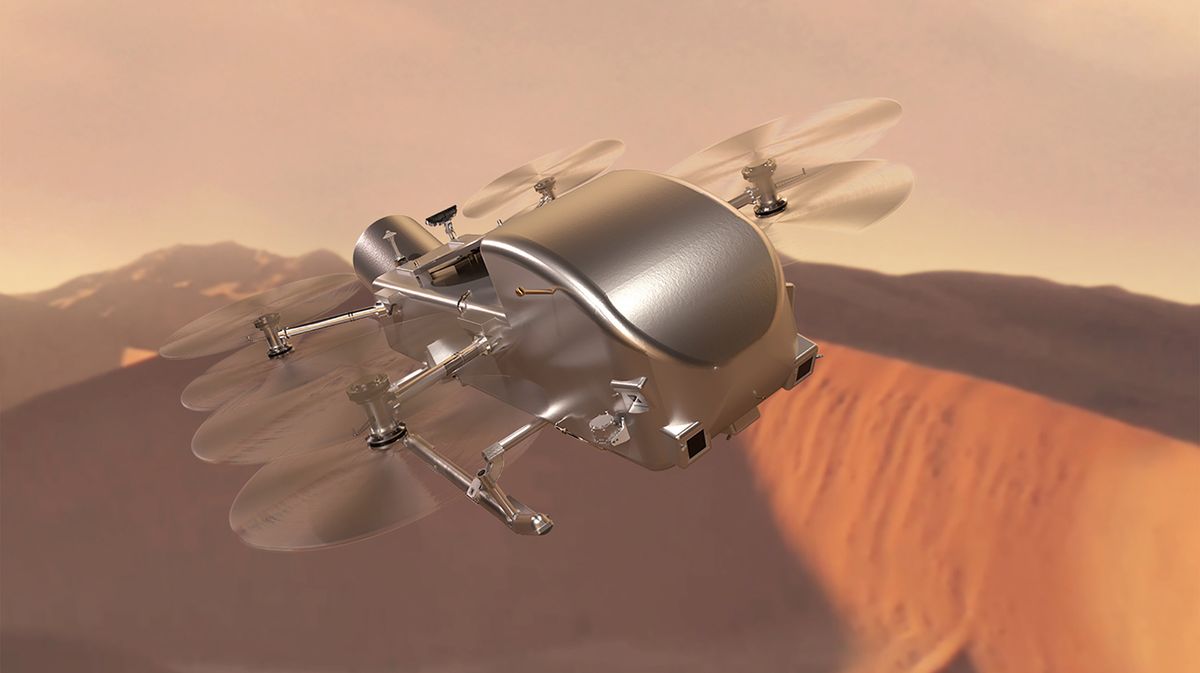
NASA’s behind schedule Dragonfly drone challenge to Saturn’s biggest moon Titan is heading in the right direction to release in July 2028, the distance company showed overdue Tuesday (April 16).The extremely expected choice greenlights the challenge crew to continue to ultimate challenge design and checking out in preparation for the revised release date.The auto-sized Dragonfly, which is being constructed through the Johns Hopkins Carried out Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, will achieve Titan in 2034. For the following 2.5 years, the nuclear-powered drone is anticipated to accomplish one hop each Titan day — 16 days to us Earthlings — trying to find prebiotic chemical processes at quite a lot of pre-selected places at the frigid moon, which is understood to comprise biological fabrics. Similar: Nuclear-powered Dragonfly challenge to Saturn moon Titan behind schedule till 2028, NASA saysAs the one satellite tv for pc in our sun gadget identified to be blanketed through a dense setting and host liquid seas on its floor, Titan has lengthy planetary scientists, who assume the moon resembles the primordial, methane-rich Earth and may just be offering clues to the genesis of lifestyles. Rivers of hydrocarbons, blended with the presence of probably life-supporting biological subject matter, spice up the case for Titan’s habitability, which Dragonfly will assist examine.Whilst the Dragonfly challenge handed a chain of impartial technical opinions early remaining 12 months and was once heading in the right direction for its unique release date of 2027, NASA had postponed surroundings the general release date because of uncertainty in what quantity of money can be to be had for challenge building this 12 months and the following. The proposed 2025 finances request for NASA, launched through the Biden Management in early March, allocates $2.73 billion for robot planetary exploration that comes with the Dragonfly challenge, whose overall lifecycle prices will now be $3.35 billion, NASA stated in a remark.That ultimate ticket is considerably upper than the to start with proposed value for Dragonfly, whose building was once capped at $1 billion when it was once first chosen in 2019 because the fourth challenge in NASA’s New Frontiers program. The distance company stated the challenge’s finances larger on account of design iterations, supply-chain problems because of the COVID-19 pandemic and further price range for a heavy-lift release car that may make amends for the behind schedule arrival at Titan through shortening the spacecraft’s cruise section.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Over a decade ahead of Dragonfly in fact flies on Titan, a number of of the drone’s elements, together with its keep an eye on and navigation methods, were examined on Earth. In July 2022, challenge engineers flew a drone similar to Dragonfly over California’s Imperial Dunes, which resemble Titan’s organic-rich dunes, and in wind tunnels at NASA’s Langley Analysis Middle in Virginia. NASA’s reliable affirmation on Tuesday permits the challenge to continue to ultimate design phases.”Dragonfly is a impressive science challenge with huge neighborhood passion, and we’re excited to take the following steps in this challenge,” Nicky Fox, affiliate administrator of NASA’s Science Project Directorate, stated within the remark. “Exploring Titan will push the bounds of what we will do with rotorcraft out of doors of Earth.”
NASA greenlights 2028 release for epic Dragonfly challenge to Saturn’s large moon Titan