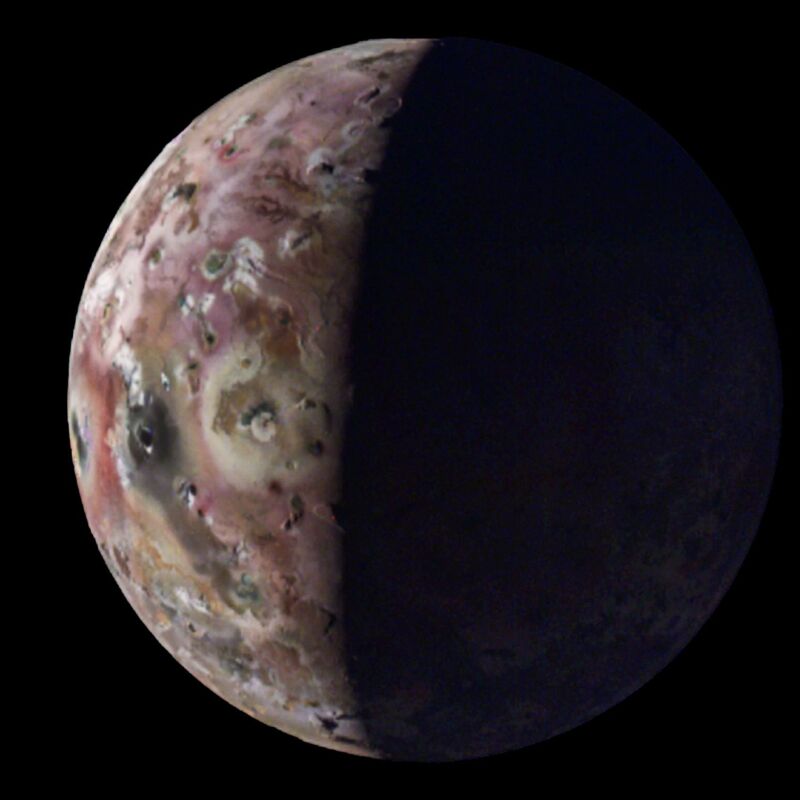
Ever because the Voyager project despatched house pictures of Jupiter’s moon Io spewing subject matter into area, we have step by step constructed up a clearer image of Io’s volcanic job. It slowly become transparent that Io, which is a bit of smaller than Mercury, is essentially the most volcanically energetic frame within the Sun Machine, with all that job pushed by way of the gravitational pressure brought about by way of Jupiter and its 3 different large moons. There’s such a lot volcanism that its floor has been totally made over, and not using a indicators of have an effect on craters.
A couple of extra information about its violence got here to gentle this week, with new pictures being launched of the moon’s options, together with an island in a lake of lava, taken by way of the Juno orbiter. On the identical time, imaging performed the use of an Earth-based telescope has equipped some indications that this volcanism has been reshaping Io from virtually the instant it shaped.
Fiery, glassy lakes
The Juno orbiter’s project is essentially keen on finding out Jupiter, together with the dynamics of its storms and its interior composition. However a lot of its orbital passes have taken it proper previous Io, and this week, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory launched one of the most easiest pictures from those flybys. They come with a shot of Loki Patera, a lake of lava that has an island inside it. Additionally featured: the impossibly sheer slopes of Io’s Steeple Mountain.
Having a look extra intently on the lake, the Juno workforce discovered that one of the most spaces inside it have been extremely easy, elevating the chance that obsidian glass had shaped at the floor the place it had cooled sufficient to solidify. Given the extent of volcanism on Io, this can be extra in style than the Loki Patera.
Commercial
Volcanic ash would additionally create a reasonably easy floor, and could be much more commonplace, however it could have considerably other reflective houses.
How lengthy has this been occurring?
However we would not have to ship {hardware} to Jupiter to be informed one thing about Io. A US-based workforce were given time at the Atacama Massive Millimeter Array (ALMA) and used it to file emissions from atoms in Io’s sparse setting. By means of combining the imaging energy of a lot of smaller telescopes scattered throughout a plateau, ALMA is in a position to spot regional variations within the presence of explicit components in Io’s setting, in addition to determine other isotopes of the ones components.
What can isotopes let us know? Any atoms that extend Io’s higher setting are susceptible to being misplaced to area. And, as a result of their relative atomic weights, heavier isotopes have a better likelihood of being misplaced. So, it is imaginable to match the existing ratio of components within the setting with the anticipated ratio, and we will be able to make inferences concerning the historical past of lack of lighter isotopes. And, because the subject matter is put into the ambience by way of volcanoes within the first position, that tells us one thing concerning the historical past of volcanism.
The analysis workforce keen on two explicit components: sulfur and chlorine. Sulfur has two commonplace non-radioactive isotopes, 32S and 34S, and chlorine, its neighbor at the periodic desk, has 35Cl and 37Cl. There are variations within the ratio of those isotopes all over the our bodies of the Sun Machine, however the ones variations are typically small. And, as a result of we expect we all know what kind of subject matter contributed to the formation of Io, we will be able to focal point at the ratios present in our bodies that experience a an identical foundation.
Chlorine enters the ambience from volcanoes essentially within the type of sodium and potassium salts. Those have an overly quick half-life ahead of they are cut up up by way of publicity to gentle and radiation. The ALMA knowledge indicated each those chemical compounds have been found in localized areas, most probably comparable to energetic volcanic plumes. The knowledge from the chlorine isotopes have been a bit of noisy, so have been in large part used as a sanity test for those received from sulfur isotopes.