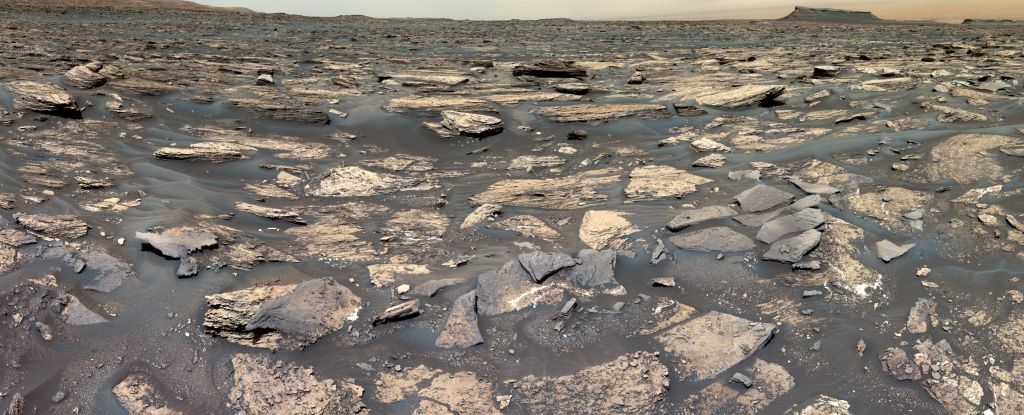
Rocks scrutinized via the Interest rover in an historic, long-dried lakebed on Mars have published prerequisites more likely to had been liveable, billions of years in the past.There, in rocks at the Gale Crater, Interest has discovered a shocking quantity of manganese oxide – a mineral this is regularly present in lakes on Earth because of the extremely oxidating prerequisites therein, which reasons manganese crystals to shape within the presence of oxygen.
Its discovery on Mars in such nice amounts means that most likely an identical prerequisites persevered within the Gale Crater, when it used to be full of water in eons previous.
“On Earth, these kind of deposits occur at all times as a result of the top oxygen in our surroundings produced via photosynthetic lifestyles, and from microbes that lend a hand catalyze the ones manganese oxidation reactions,” explains geochemist Patrick Gasda of Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory.
“On Mars, we wouldn’t have proof for lifestyles, and the mechanism to provide oxygen in Mars’s historic surroundings is unclear, so how the manganese oxide used to be shaped and concentrated this is actually puzzling. Those findings level to greater processes going on within the Martian surroundings or floor water and display that extra paintings must be finished to know oxidation on Mars.”
Manganese oxide is commonplace and plentiful right here on Earth, and intricately interested by organic processes as well. It’s an crucial mineral for a number of human organic processes, however just about all lifestyles on Earth calls for manganese for some explanation why or every other.
There are even micro organism that depend at the oxidation states of manganese for power, and their presence can boost up the oxidation procedure.
There is not a large number of oxygen floating round on Mars now, and we now have without a doubt discovered no proof of dwelling micro organism, so precisely how the manganese got here to be putting round there in sedimentary rocks on coastline deposits in amounts related to an Earth-like setting is not transparent.
Gasda and his colleagues made a cautious learn about of the manganese as analyzed via Interest’s ChemCam, which makes use of a laser to vaporize minerals after which analyzes the sunshine to resolve their composition. Then, the researchers explored other mechanisms for the precipitation of manganese within the Gale Crater lake: precipitation from lakewater, or from groundwater via porous sands.
All mechanisms require the presence of extremely oxidizing prerequisites, and after working throughout the choices, the researchers concluded that the in all probability situation would had been the precipitation of manganese oxides alongside a lakeshore within the presence of an oxygen-rich surroundings.
That is additional proof, they are saying, of a long-lived and liveable lake setting within the historic Gale Crater on Mars, since it may well take 1000’s of years for manganese oxide to shape, relying on oxygen ranges.
The place that oxygen got here from is every other query that continues to be unanswered, even supposing it is conceivable that meteorite affects early in Mars’s historical past can have launched oxygen from floor ice deposits.
Nonetheless, the findings be offering a tantalizing prospect for on the lookout for lines of historic lifestyles at the purple planet. Microbe-mediated oxidation will have left biosignatures and organics within the manganese-bearing rocks. Perseverance, which is recently exploring a dried-up delta setting, may search for those in its travels, the researchers say.
“The Gale lake setting, as published via those historic rocks, provides us a window right into a liveable setting that appears unusually very similar to puts on Earth lately,” says planetary scientist Nina Lanza of Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory.
“Manganese minerals are commonplace within the shallow, oxic waters discovered on lake shores on Earth, and it is exceptional to search out such recognizable options on historic Mars.”The crew’s analysis has been revealed within the Magazine of Geophysical Analysis: Planets.
Interest Detects 'Liveable' Earth-Like Previous on Mars, However How Did Oxygen Get There?