A number of rocks scattered on an historical coastline on Mars would possibly point out that the Crimson Planet used to be as soon as way more Earth-like than scientists in the past idea.The rocks, came upon by means of NASA’s Interest rover, are strangely wealthy in manganese oxide — a chemical that provides to rising proof that the once-habitable Mars could have sported Earth-like oxygen ranges and life-friendly prerequisites early in its historical past, scientists say.NASA calls manganese on Earth “an unsung hero within the evolution of existence.” Scientists know from our planet’s geological historical past that manganese used to be plentiful in rocks and within the oceans ahead of the earliest life-forms emerged more or less 4 billion years in the past and that it prepared the ground for oxygen that almost all existence now depends upon. The one identified techniques to supply manganese oxide, then again, contain both plentiful oxygen or microbial existence. However there is not sturdy proof for the previous on Mars, and none for the latter, leaving scientists confused by means of how the chemical shaped within the newfound rocks.Similar: Loads of black ‘spiders’ noticed in mysterious ‘Inca Town’ on Mars in new satellite tv for pc photosForming rocks wealthy in manganese oxide “is straightforward to do on Earth as a result of microbes and as a result of oxygen — which [also forms] as a result of microbes — so all of it issues again towards existence,” lead find out about writer Patrick Gasda, a analysis scientist at Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory in New Mexico, advised Are living Science. “We in fact don’t have any proof of existence on Mars, so if we are looking to shape oxygen in an absolutely abiotic machine, our present working out of Mars does not provide an explanation for that.”The Interest rover got here around the closely eroded rocks whilst trekking throughout the heart of Gale crater, a 96-mile-wide (154 kilometers) historical lake mattress that the rover has been exploring since 2012. The rover’s ChemCam device “sniffed” the manganese oxide throughout the rocks by means of vaporizing tiny bits with a laser after which inspecting the ensuing cloud of plasma. The compound constitutes just about part of the rocks’ chemical make-up, consistent with the brand new find out about, which used to be printed remaining week within the magazine JGR Planets.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered immediately for your inbox.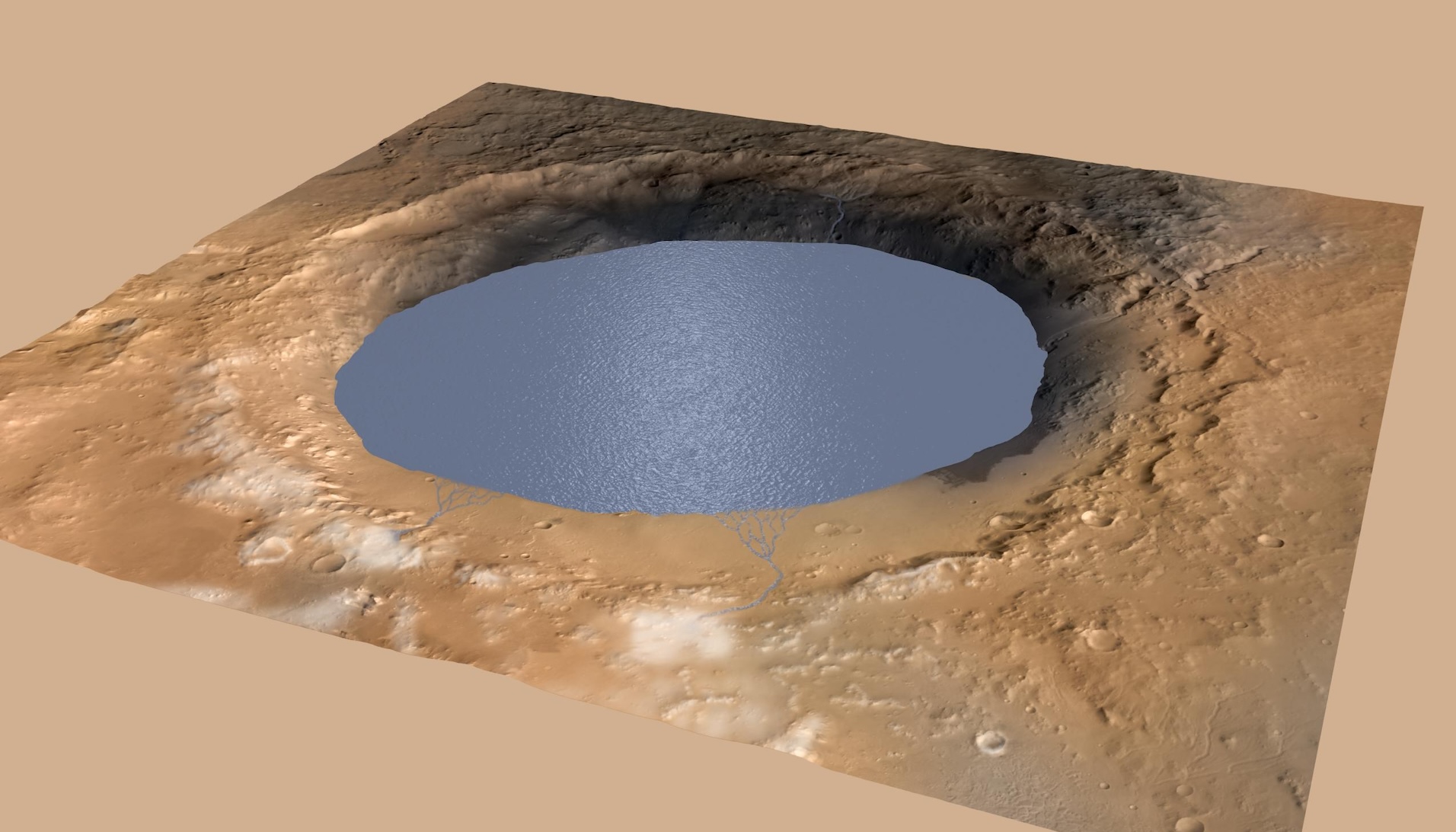 A simulated view of Gale Crater stuffed with water, as it will have seemed hundreds of thousands of years in the past. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)On the web site the place Interest discovered the brand new rocks, the rover recorded 10 to fifteen meters (33 to 49 ft) of elevation trade. Even supposing that is tiny in comparison with the masses of meters Interest has climbed through the years, it’s “pointing us towards one thing particular happening in that position,” Gasda advised Are living Science. The rock texture the place the brand new sandstones had been discovered seems to have transitioned from “curved” to “flat-lined” — a transformation Gasda and his colleagues are deciphering as a river channel opening out right into a lake. “That implies we are on the shore of the lake or close to the shore of the lake,” Gasda stated. He famous that this interpretation is unsure because of restricted information, as a result of Interest drove previous the area simply as soon as. “That made the translation in reality difficult, however that is our best possible speculation,” he added. If the speculation is proper, the rocks could have been dumped within the area when the river water bogged down because it entered the lake, very similar to manganese-oxide-rich rocks which were discovered at the shores of shallow lakes on Earth.The newfound rocks are “every other line of proof for liquid water on Mars prior to now, which is recommended for existence,” Manasvi Lingam, an astrobiologist on the Florida Institute of Generation who used to be no longer affiliated with the brand new analysis, advised Are living Science. “This paintings supplies proof in want of habitability.”Alternatively, no longer everybody consents that the newfound rocks point out an oxygen-rich Mars. In line with Jeffrey Catalano, a professor of Earth, environmental and planetary sciences at Washington College in St. Louis, who used to be no longer concerned within the find out about, the presence of oxidized rocks may just assist scientists perceive whether or not Mars, like Earth, went via “a punctuated transition” from a lower-oxygen length and a higher-oxygen length. “The affect of manganese oxides on our working out of this sort of transition, then again, had been overstated, right here and in prior paintings,” he advised Are living Science.Catalano used to be a part of a 2022 find out about that discovered manganese oxide may just simply shape underneath Mars-like prerequisites with out atmospheric oxygen. That analysis, which used to be in line with lab experiments, confirmed that parts corresponding to chlorine and bromine, that have been plentiful on early Mars, transformed manganese dissolved in water into manganese oxide minerals. This discovering introduced an alternative choice to oxygen that would provide an explanation for rocks just like the newfound ones on Mars.”There are a number of existence kinds even on Earth that don’t require oxygen to live on,” Kaushik Mitra, a geochemist on the College of Texas at San Antonio who led that find out about, stated in a remark in 2022. “I do not believe of it as a ‘setback’ to habitability — handiest that there have been almost definitely no oxygen-based lifeforms.”
A simulated view of Gale Crater stuffed with water, as it will have seemed hundreds of thousands of years in the past. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)On the web site the place Interest discovered the brand new rocks, the rover recorded 10 to fifteen meters (33 to 49 ft) of elevation trade. Even supposing that is tiny in comparison with the masses of meters Interest has climbed through the years, it’s “pointing us towards one thing particular happening in that position,” Gasda advised Are living Science. The rock texture the place the brand new sandstones had been discovered seems to have transitioned from “curved” to “flat-lined” — a transformation Gasda and his colleagues are deciphering as a river channel opening out right into a lake. “That implies we are on the shore of the lake or close to the shore of the lake,” Gasda stated. He famous that this interpretation is unsure because of restricted information, as a result of Interest drove previous the area simply as soon as. “That made the translation in reality difficult, however that is our best possible speculation,” he added. If the speculation is proper, the rocks could have been dumped within the area when the river water bogged down because it entered the lake, very similar to manganese-oxide-rich rocks which were discovered at the shores of shallow lakes on Earth.The newfound rocks are “every other line of proof for liquid water on Mars prior to now, which is recommended for existence,” Manasvi Lingam, an astrobiologist on the Florida Institute of Generation who used to be no longer affiliated with the brand new analysis, advised Are living Science. “This paintings supplies proof in want of habitability.”Alternatively, no longer everybody consents that the newfound rocks point out an oxygen-rich Mars. In line with Jeffrey Catalano, a professor of Earth, environmental and planetary sciences at Washington College in St. Louis, who used to be no longer concerned within the find out about, the presence of oxidized rocks may just assist scientists perceive whether or not Mars, like Earth, went via “a punctuated transition” from a lower-oxygen length and a higher-oxygen length. “The affect of manganese oxides on our working out of this sort of transition, then again, had been overstated, right here and in prior paintings,” he advised Are living Science.Catalano used to be a part of a 2022 find out about that discovered manganese oxide may just simply shape underneath Mars-like prerequisites with out atmospheric oxygen. That analysis, which used to be in line with lab experiments, confirmed that parts corresponding to chlorine and bromine, that have been plentiful on early Mars, transformed manganese dissolved in water into manganese oxide minerals. This discovering introduced an alternative choice to oxygen that would provide an explanation for rocks just like the newfound ones on Mars.”There are a number of existence kinds even on Earth that don’t require oxygen to live on,” Kaushik Mitra, a geochemist on the College of Texas at San Antonio who led that find out about, stated in a remark in 2022. “I do not believe of it as a ‘setback’ to habitability — handiest that there have been almost definitely no oxygen-based lifeforms.”






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BTCUSDChart-c26e5881ebc34f33910ad841d6c8862c.gif)