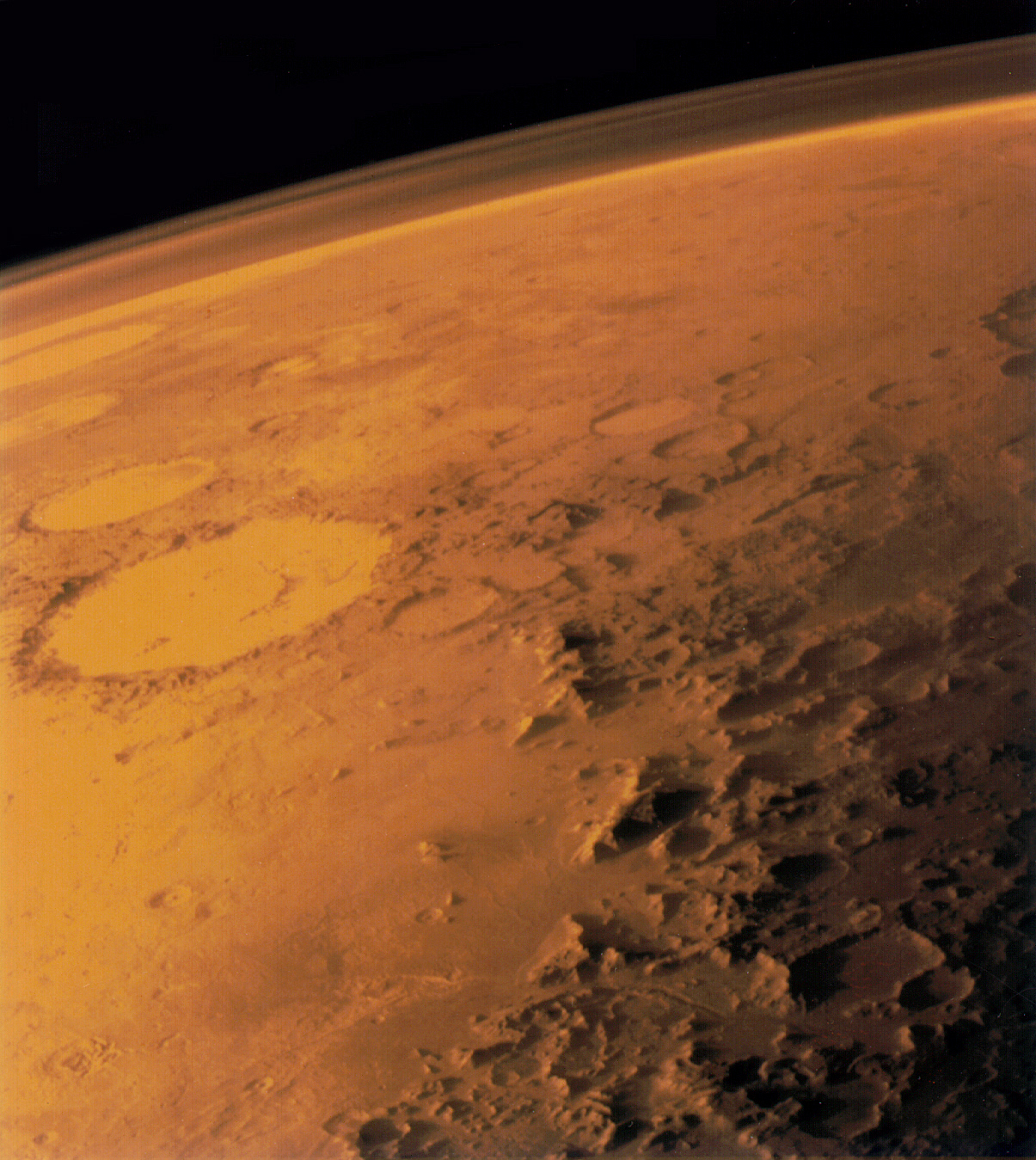
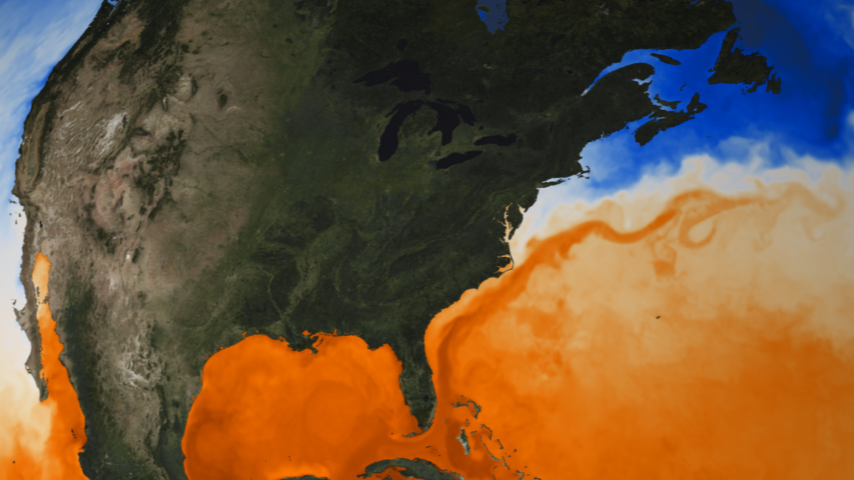
The Gulf Movement is sort of no doubt weakening, a brand new learn about has showed.The go with the flow of heat water in the course of the Florida Straits has slowed through 4% over the last 4 a long time, with grave implications for the arena’s local weather. The sea present begins close to Florida and threads a belt of heat water alongside the U.S. East Coast and Canada earlier than crossing the Atlantic to Europe. The warmth it transports is very important for keeping up temperate prerequisites and regulating sea ranges. However this circulation is slowing down, researchers wrote in a learn about revealed Sept. 25 within the magazine Geophysical Analysis Letters. Comparable: Gulf Movement present may just cave in in 2025, plunging Earth into local weather chaos: ‘We have been in reality bewildered'”That is the most powerful, maximum definitive proof now we have of the weakening of this climatically-relevant ocean present,” lead-author Christopher Piecuch, a bodily oceanographer on the Woods Hollow Oceanographic Establishment in Massachusetts, mentioned in a commentary.The Gulf Movement is only a small part of the thermohaline movement — an international conveyor belt of ocean currents that strikes oxygen, vitamins, carbon and warmth across the planet, whilst additionally serving to to regulate sea ranges and storm process. Starting in Caribbean earlier than flowing out into the Atlantic in the course of the Florida Straits, the Gulf Movement brings hotter southerly waters (that are saltier and denser) northward to chill and sink within the North Atlantic. After losing deep underneath the sea and liberating its warmth into the ambience, the water slowly drifts southward, the place it heats up once more and the cycle repeats.This procedure is necessary for keeping up temperatures and sea ranges around the U.S. East Coast — whose waters are saved as much as 5 toes (1.5 meters) less than water additional offshore through the sweeping movement of the present.As Earth’s local weather warms, a huge inflow of chilly, recent water from melting ice sheets is spilling into oceans, most likely inflicting the Gulf Movement to sluggish and even veer towards outright cave in, in step with scientists. However because of the size and complexity of the device, that is exhausting to turn out.To seek out definitive proof that the circulation is slowing, scientists analyzed information spanning 40 years from 3 separate assets — undersea cables, satellite tv for pc altimetry and observations made on web site — to watch the motions of the present across the Florida Straits.Their statistical research printed that the present had slowed through 4%, with only a 1% probability in their dimension being a fluke led to through random fluctuations.In the beginning look, a 4% shift would possibly look like a miniscule exchange, however “the concern is that is simply the sluggish get started,” Helen Czerski, an oceanographer at College School London (UCL) who was once no longer concerned within the learn about, instructed Are living Science.Comparable: Learn concerning the planet’s engine in an interview with Helen Czerski”It is like the ones early days of COVID. Other people have been like: ‘Oh, there is handiest 60 instances. We do not care about this,'” she added. “There may be handiest 60 instances, yeah, however the previous day there have been 30 and the day earlier than that there have been 15. In case you simply assume per week forward, we now have were given an issue.”To seek out definitive evidence that local weather exchange is the offender, scientists will wish to tease aside the diversities between the herbal variability of the sea programs and the have an effect on made through world heating — a tough process given the slightly few minutes that people were at once measuring the sea flows intimately.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2180769590-fbe7294d24b144ada1d2ac8af0c447d7.jpg)




