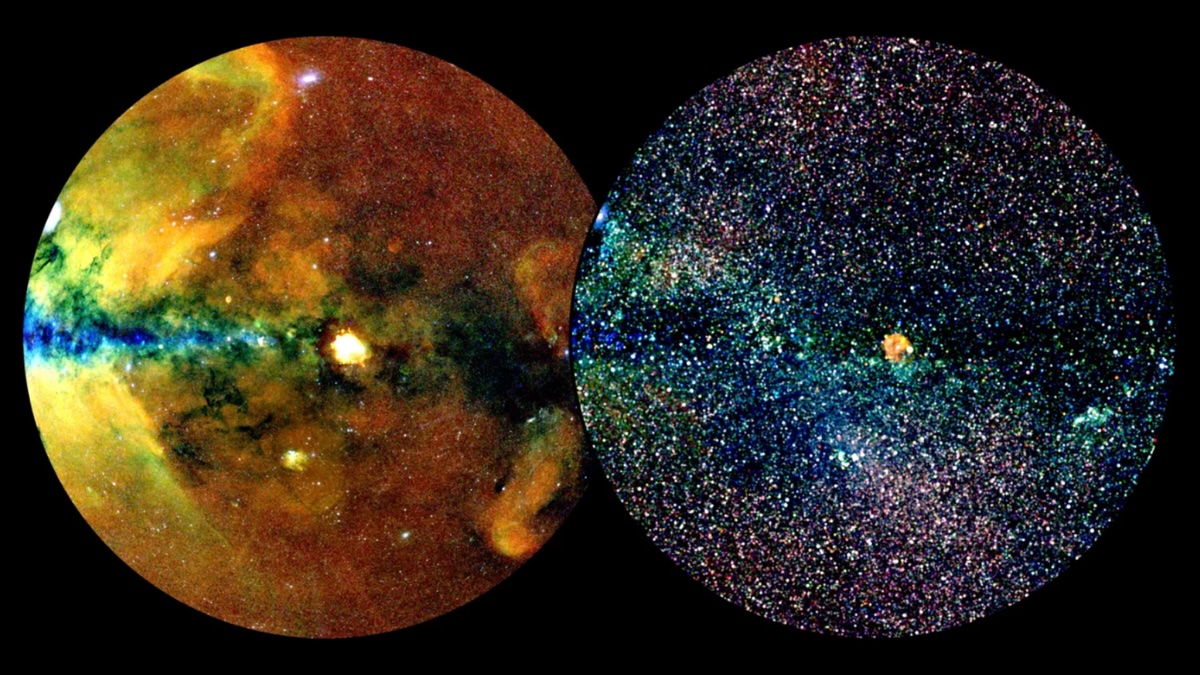
Abstract: Researchers visualized the overall community of blood vessels in wide awake mice, finding rhythmic expansions and contractions that create blood drift waves around the mind’s floor. This find out about unearths new insights into mind blood provide, even though the serve as of those waves stays unclear.The findings would possibly have an effect on how fMRI scans are interpreted, including complexity to our working out of mind job. The waves’ possible position in waste removing suggests implications for neurological dysfunction coverage.Key Information:Blood vessels at the mind’s floor rhythmically enlarge and contract, developing sluggish waves of blood drift.Those waves happen independently of mind job, suggesting new complexities in deciphering fMRI scans.The waves would possibly assist combine fluids round mind cells, doubtlessly assisting in waste removing and coverage towards neurological issues.Supply: NIHResearchers have, for the primary time, visualized the overall community of blood vessels around the cortex of wide awake mice, discovering that blood vessels rhythmically enlarge and contract resulting in “waves” washing around the floor of the mind. Those findings, funded via the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (NIH), toughen the working out of ways the mind receives blood, even though the serve as of the waves stays a thriller.  Particularly, the discovering that those waves of blood drift adjustments happen in large part impartial of mind job suggests a brand new stage of complexity complication that must be regarded as when deciphering the hyperlink between the fMRI knowledge and mind activation. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsA community of elastic and actively pumping vessels wearing oxygenated blood span the skin of the mind prior to getting into the cortex. There, they feed right into a 2d community of capillaries that offer oxygen deeper into the tissue.The usage of physics-based experimental strategies and analyses, the researchers noticed that along with the pulses of blood drift that happen with every heartbeat, there are slower waves of blood drift adjustments that sweep around the mind and happen about as soon as each and every ten seconds.The trade in blood drift that happen with those sluggish waves used to be as much as 20% of all of the mind blood provide. Unusually, this phenomenon used to be best weakly tied to adjustments in mind job.The waves produced visual bulges within the blood vessels, which is able to support in blending the fluid across the mind’s cells. This has implications in how waste merchandise and different fabrics are got rid of from the fluid surrounding mind cells.For the reason that waves of bulging blood vessels transfer in a lot of instructions, the authors surmise that the pulses of dilation and contraction of the blood vessels are much more likely to be keen on blending the fluid round them reasonably than actively transferring it in a given path.Regardless, this blending job may support in taking out misfolded proteins and different parts from the mind into the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds it. This procedure is thought of as crucial protecting mechanism for a lot of neurological issues, akin to Alzheimer’s illness and different similar dementias, and is extra lively all over sleep. Those findings might also impact present approaches to deciphering fMRI scans, which measure adjustments in blood oxygenation inside mind constructions as they’re activated. Particularly, the discovering that those waves of blood drift adjustments happen in large part impartial of mind job suggests a brand new stage of complexity complication that must be regarded as when deciphering the hyperlink between the fMRI knowledge and mind activation. Investment: This analysis used to be funded partially via the NIH’s Mind Analysis Via Advancing Leading edge Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative (U19NS123717, R01NS108472), the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke (R35NS097265), the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being (R01MH111438), and the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Organic Imaging and Bioengineering (U24EB028942, R01EB026936)About this neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Carl Wonders
Particularly, the discovering that those waves of blood drift adjustments happen in large part impartial of mind job suggests a brand new stage of complexity complication that must be regarded as when deciphering the hyperlink between the fMRI knowledge and mind activation. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsA community of elastic and actively pumping vessels wearing oxygenated blood span the skin of the mind prior to getting into the cortex. There, they feed right into a 2d community of capillaries that offer oxygen deeper into the tissue.The usage of physics-based experimental strategies and analyses, the researchers noticed that along with the pulses of blood drift that happen with every heartbeat, there are slower waves of blood drift adjustments that sweep around the mind and happen about as soon as each and every ten seconds.The trade in blood drift that happen with those sluggish waves used to be as much as 20% of all of the mind blood provide. Unusually, this phenomenon used to be best weakly tied to adjustments in mind job.The waves produced visual bulges within the blood vessels, which is able to support in blending the fluid across the mind’s cells. This has implications in how waste merchandise and different fabrics are got rid of from the fluid surrounding mind cells.For the reason that waves of bulging blood vessels transfer in a lot of instructions, the authors surmise that the pulses of dilation and contraction of the blood vessels are much more likely to be keen on blending the fluid round them reasonably than actively transferring it in a given path.Regardless, this blending job may support in taking out misfolded proteins and different parts from the mind into the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds it. This procedure is thought of as crucial protecting mechanism for a lot of neurological issues, akin to Alzheimer’s illness and different similar dementias, and is extra lively all over sleep. Those findings might also impact present approaches to deciphering fMRI scans, which measure adjustments in blood oxygenation inside mind constructions as they’re activated. Particularly, the discovering that those waves of blood drift adjustments happen in large part impartial of mind job suggests a brand new stage of complexity complication that must be regarded as when deciphering the hyperlink between the fMRI knowledge and mind activation. Investment: This analysis used to be funded partially via the NIH’s Mind Analysis Via Advancing Leading edge Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative (U19NS123717, R01NS108472), the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke (R35NS097265), the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being (R01MH111438), and the NIH’s Nationwide Institute of Organic Imaging and Bioengineering (U24EB028942, R01EB026936)About this neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Carl Wonders
Supply: NIH
Touch: Carl Wonders – NIH
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Closed get entry to.
“Lengthy-wavelength touring waves of vasomotion modulate the perfusion of cortex” via Jim Gnadt et al. NeuronAbstractLong-wavelength touring waves of vasomotion modulate the perfusion of cortexHighlightsVaso-oscillations in arteriole diameter modulate the perfusion of blood to cortexModulation all over the resting state exceeds that of stimulus-induced activityVaso-oscillations improve long-wavelength touring waves alongside all arteriolesWaves alongside penetrating arterioles are not likely to translocate interstitial solutesSummaryBrain arterioles are lively, multicellular complexes whose diameters oscillate at ∼ 0.1 Hz. We assess the physiological have an effect on and spatiotemporal dynamics of vaso-oscillations within the wide awake mouse.First, vaso-oscillations in penetrating arterioles, which supply blood from pial arterioles to the capillary mattress, profoundly have an effect on perfusion all through neocortex. The modulation in flux all over resting-state job exceeds that of stimulus-induced job.2nd, the trade in perfusion via arterioles relative to the trade of their diameter is susceptible. This signifies that the capillary mattress dominates the hydrodynamic resistance of mind vasculature.Finally, the part of vaso-oscillations evolves slowly alongside arterioles, with a wavelength that exceeds the span of the cortical mantle and enough variability to ascertain useful cortical spaces as parcels of uniform part.The phase-gradient helps touring waves in both path alongside each pial and penetrating arterioles.This signifies that waves alongside penetrating arterioles can combine, however now not directionally delivery, interstitial fluids.
Blood Glide Waves Wash Throughout Mind Floor – Neuroscience Information










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Apple-News-Image---How-to-Invest-Like-Warren-Buffett-final-9c3f954d6d2d4677af76f5530292de13.jpg)