Just about twenty years in the past, astronomers seen a large cloud of excellent mud debris round a tender big name situated simply 63 light-years clear of Earth. In contemporary observations from the Webb Area Telescope, on the other hand, the mud cloud had mysteriously vanished. Now, a brand new paper suggests the mud cloud can have been led to by way of a violent tournament that pulverized huge celestial our bodies and unfold their stays around the Beta Pictoris big name gadget.Sonos First Ever Headphones Are Too Pricey For What They OfferUsing new information from Webb, a gaggle of scientists noticed vital adjustments within the power signatures emitted by way of mud grains discovered round Beta Pictoris, with debris that had long past utterly lacking. By means of evaluating the Webb information to older observations captured by way of the Spitzer Area Telescope in 2004 and 2005, the scientists recommend {that a} cataclysmic collision between huge asteroids happened about twenty years in the past, which broke aside the celestial our bodies into tremendous mud debris smaller than powdered sugar. The mud most likely cooled off because it moved clear of the big name, which is why it not emits the similar thermal options first seen by way of Spitzer. The brand new findings had been offered Monday all over the once a year Assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin.Christine Chen, an astronomer on the Area Telescope Science Institute and Johns Hopkins College, first seen Beta Pictoris in 2004 the usage of the Spitzer Area Telescope. The younger big name gadget is house to the primary particles disk ever imaged round some other big name, and is notable for being close to and brilliant. When Chen used to be given 12 hours of observations with Webb, she sought after to return and take a look at the similar big name gadget, Beta Pictoris, that had intrigued her for all the ones years. This time, on the other hand, the big name gadget didn’t glance all that acquainted. “I used to be like, ‘oh my gosh, the options are long past,’” Chen advised Gizmodo. “Is that this actual? And whether it is, then what took place?”
Throughout the Webb observations, Chen, who lead the brand new find out about, and her workforce all in favour of warmth emitted by way of crystalline silicates—minerals often discovered round younger stars—and located no strains of the debris prior to now noticed in 2004 and 2005.“On every occasion astronomers take a look at the sky and so they see one thing, we at all times suppose that the entirety is in secure state, that it’s no longer converting,” Chen stated. “The explanation why we predict this is as a result of if you happen to take into consideration the specific quick that you simply’re taking a look at, that’s very quick in comparison to how outdated those items are, so we simply assume that the possibilities that you simply catch anything else attention-grabbing are very small.”That it appears used to be no longer the case for Beta Pictoris, a celebrity gadget this is believed to be between 20 to 26 million years outdated. That’s somewhat younger in comparison to our personal sun gadget, which is kind of 4.6 billion years outdated. Throughout their early years, big name techniques are extra unpredictable as terrestrial planets are nonetheless forming via massive asteroid collisions.Due to this fact, the adjustments seen in Beta Pictoris had been quite vital. The mud cloud used to be 100,000 occasions higher than the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs, in line with the astronomers. This implies that the collision that can have led to this large cloud to shape most likely concerned an asteroid the scale of Vesta, the second one maximum large frame in the primary asteroid belt that stretches throughout 329 miles (530 kilometers) in diameter.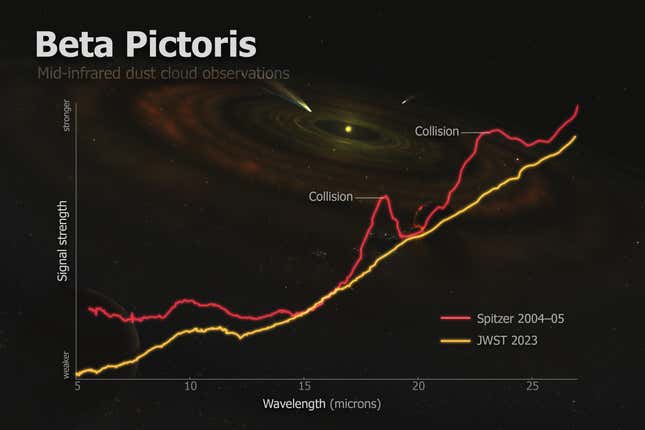 An indication of the variation within the information gathered by way of Spitzer and Webb twenty years aside.Representation: ROBERTO MOLAR CANDANOSA/JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY, WITH BETA PICTORIS CONCEPT ART BY LYNETTE COOK/NASAThe mud used to be then dispersed outward by way of radiation from the big name, and the mud close to the big name heated up and emitted thermal radiation that used to be known by way of Spitzer’s tools. Webb’s new observations printed that the mud had disappeared and had no longer been changed, pointing to a violent collision.
An indication of the variation within the information gathered by way of Spitzer and Webb twenty years aside.Representation: ROBERTO MOLAR CANDANOSA/JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY, WITH BETA PICTORIS CONCEPT ART BY LYNETTE COOK/NASAThe mud used to be then dispersed outward by way of radiation from the big name, and the mud close to the big name heated up and emitted thermal radiation that used to be known by way of Spitzer’s tools. Webb’s new observations printed that the mud had disappeared and had no longer been changed, pointing to a violent collision.
“We predict that massive collisions like this should have took place in our sun gadget when it used to be of a an identical age as a part of the terrestrial planet formation procedure,” Chen stated. “We will take a look at outdated terrestrial surfaces of the Moon, Mars, and Mercury and so they all have craters on them, which tells us that affects had been a lot more widespread when our sun gadget used to be younger.”Throughout the contemporary observations of Beta Pictoris, scientists can probe whether or not the formation procedure that formed our sun gadget is uncommon or extra widespread during the universe, and the way those early collisions have an effect on the habitability of a given big name gadget.“If this massive collision occurs and there’s a mud cloud that’s propagating outward from the big name,” Chen stated. “You should believe that there’s some chance that this mud cloud, because it traveled to the planetary gadget, additionally encountered the planets and it will have rained down mud onto their planetary setting.”Extra: Past the Planets: The Quirky Underdogs of the Sun Device
Astronomers Spot Cataclysmic Collision of Massive Asteroids in Close by Big name Device