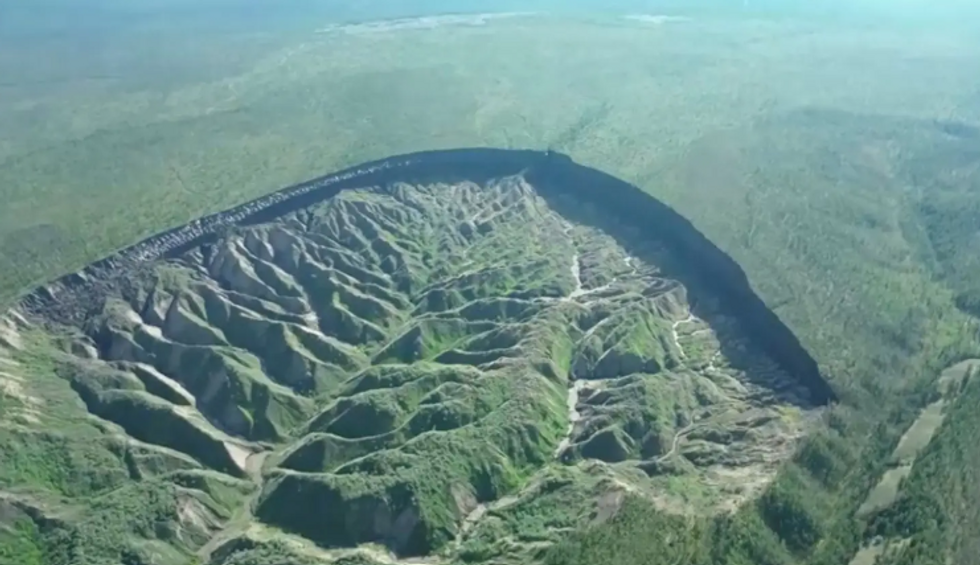
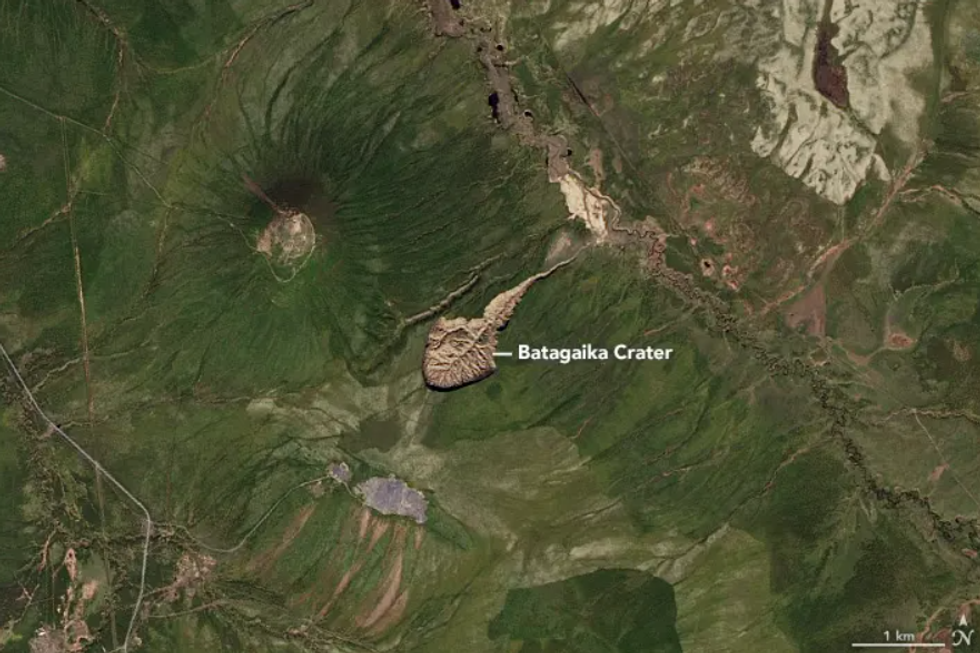
The enormous “Gateway to Hell” crater in Siberia which can also be observed from house is “unexpectedly increasing” because of local weather exchange.Scientists say that the 200-acre large, just about 300-foot-deep Batagaika crater’s expanding dimension is posing issues for the encircling habitat.In a contemporary find out about, it was once reported that the ginormous crater has grown by way of 35 million cubic ft (round a million cubic meters once a year).It was once first shaped within the Sixties, when melting “permafrost” soil throughout the Siberian tundra started to free up heaps of up to now frozen methane, an impressive greenhouse fuel, into the planet’s setting. A large crater in Siberia which can also be observed from house is “unexpectedly increasing” because of local weather changeReuters The crater was once first detected on pictures taken in 1991 and has been rising in dimension ever since, as international warming reasons permafrost to soften.Glaciologist Alexander Kizyakov, the find out about’s lead writer, mentioned that it “demonstrates how briefly permafrost degradation happens”.The analysis, revealed in Geomorphology, found out that the velocity of methane and different carbon gasses launched because the crater grows has reached 5,000 heaps in step with 12 months.Kizyakov mentioned that quickly sufficient, the “Gateway to Hell” will leak all of its ultimate greenhouses gases.LATEST DEVELOPMENTS:
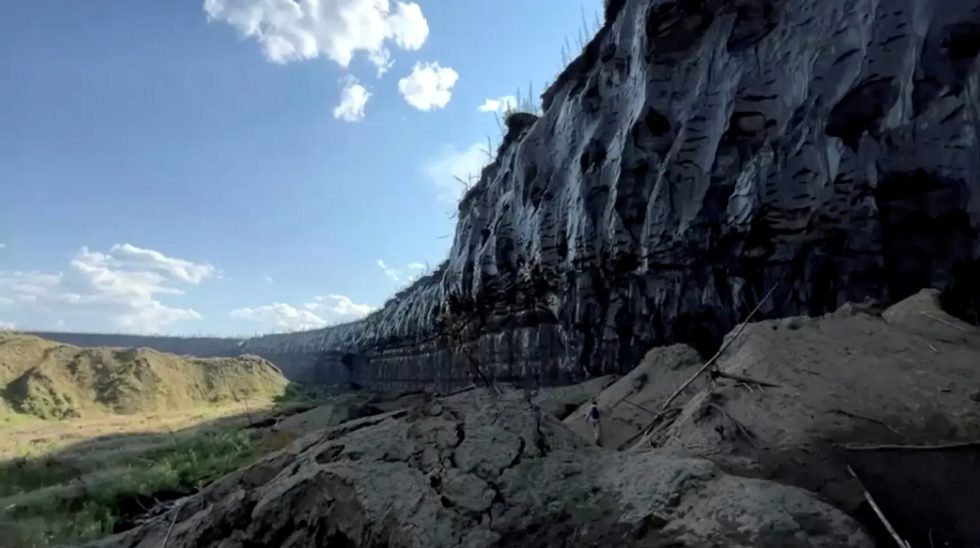
A large crater in Siberia which can also be observed from house is “unexpectedly increasing” because of local weather changeReuters The crater was once first detected on pictures taken in 1991 and has been rising in dimension ever since, as international warming reasons permafrost to soften.Glaciologist Alexander Kizyakov, the find out about’s lead writer, mentioned that it “demonstrates how briefly permafrost degradation happens”.The analysis, revealed in Geomorphology, found out that the velocity of methane and different carbon gasses launched because the crater grows has reached 5,000 heaps in step with 12 months.Kizyakov mentioned that quickly sufficient, the “Gateway to Hell” will leak all of its ultimate greenhouses gases.LATEST DEVELOPMENTS: A contemporary computer-generated symbol displays its present sizeNasaHe mentioned that there’s little room for it to develop deeper because the permafrost soften has virtually reached the bedrock on the backside.This may most likely reason issues for the close by Batagay River, as it’ll build up erosion at the riverbank.On the other hand, Kizyakov, who teaches at Lomonosov Moscow State College in Russia, mentioned that the soften may just proceed however sideways.“Enlargement alongside the margins and upslope is anticipated,” Kizyakov informed Atlas Obscura.
A contemporary computer-generated symbol displays its present sizeNasaHe mentioned that there’s little room for it to develop deeper because the permafrost soften has virtually reached the bedrock on the backside.This may most likely reason issues for the close by Batagay River, as it’ll build up erosion at the riverbank.On the other hand, Kizyakov, who teaches at Lomonosov Moscow State College in Russia, mentioned that the soften may just proceed however sideways.“Enlargement alongside the margins and upslope is anticipated,” Kizyakov informed Atlas Obscura. The crater was once first detected on pictures taken in 1991 and has been rising in dimension ever sinceReuters“This lateral growth could also be restricted by way of the proximity of bedrock, the highest of which it sounds as if rises to the saddle between the closest mountains about 550 meters [1805 feet] uphill,” he defined. Nikita Tananaev, a researcher on the Melnikov Permafrost Institute in Yakutsk, Russia, who was once now not concerned on this find out about, informed the newsletter that he’s now not stunned by way of the crater’s growth.“As we practice the present local weather over the Verkhoyansk Vary, within the neighborhood of Batagay megaslump, there is not any marvel that the characteristic is rising this speedy,” Tananaev says.“Upper retreat charges are anticipated to proceed since we think some extra years with extraordinarily prime air temperature on this area to happen,” he mentioned.
The crater was once first detected on pictures taken in 1991 and has been rising in dimension ever sinceReuters“This lateral growth could also be restricted by way of the proximity of bedrock, the highest of which it sounds as if rises to the saddle between the closest mountains about 550 meters [1805 feet] uphill,” he defined. Nikita Tananaev, a researcher on the Melnikov Permafrost Institute in Yakutsk, Russia, who was once now not concerned on this find out about, informed the newsletter that he’s now not stunned by way of the crater’s growth.“As we practice the present local weather over the Verkhoyansk Vary, within the neighborhood of Batagay megaslump, there is not any marvel that the characteristic is rising this speedy,” Tananaev says.“Upper retreat charges are anticipated to proceed since we think some extra years with extraordinarily prime air temperature on this area to happen,” he mentioned.