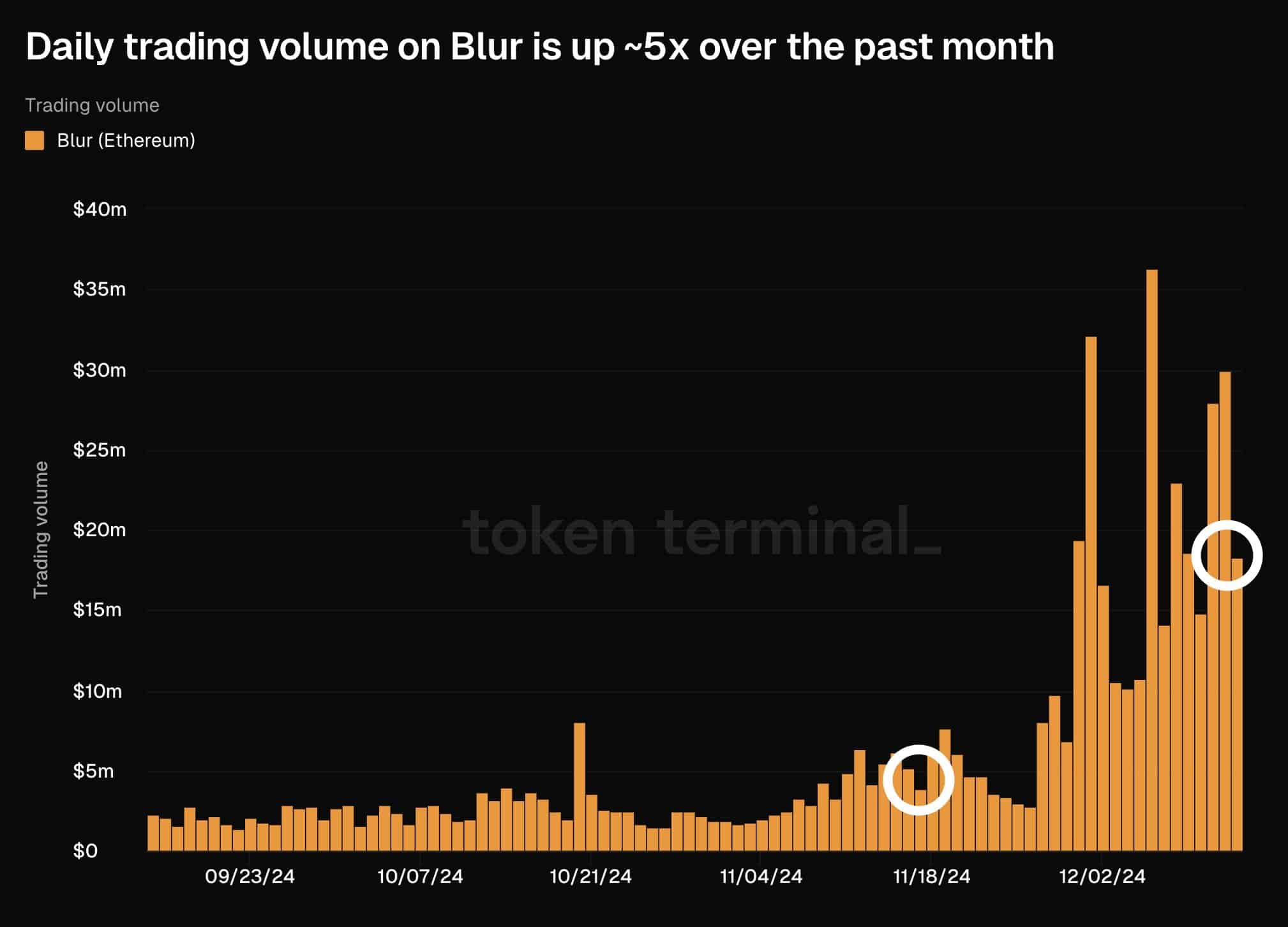
Scientists consider they’ve discovered a window into the daybreak of time on Earth, and it’s hidden underneath the Pacific Ocean.A crew led by way of geophysicist Simon Lamb, of the College of Wellington and scientist Cornel de Ronde, of GNS Science, stated the important thing to our previous lies in a far off nook of South Africa and manner down at the seafloor off the coast of New Zealand.So what do those two websites, on reverse facets of the sector, have in commonplace?In combination, they make clear the sector in its infancy, and be offering surprising clues concerning the origins of the planet we all know lately – and in all probability lifestyles itself.Writing for The Dialog, the scientists defined that their paintings started after de Ronde created a brand new, detailed geological map of a space referred to as the Barberton Greenstone Belt, which lies in South Africa’s highveld area. “The geological formations on this area have proved tough to decipher, in spite of many makes an attempt,” the pair write.They declare that the Belt’s rock mattress is inconsistent with our extensively approved figuring out of plate tectonics on the time.However, they declare, their new analysis has introduced up “the important thing to cracking this code.”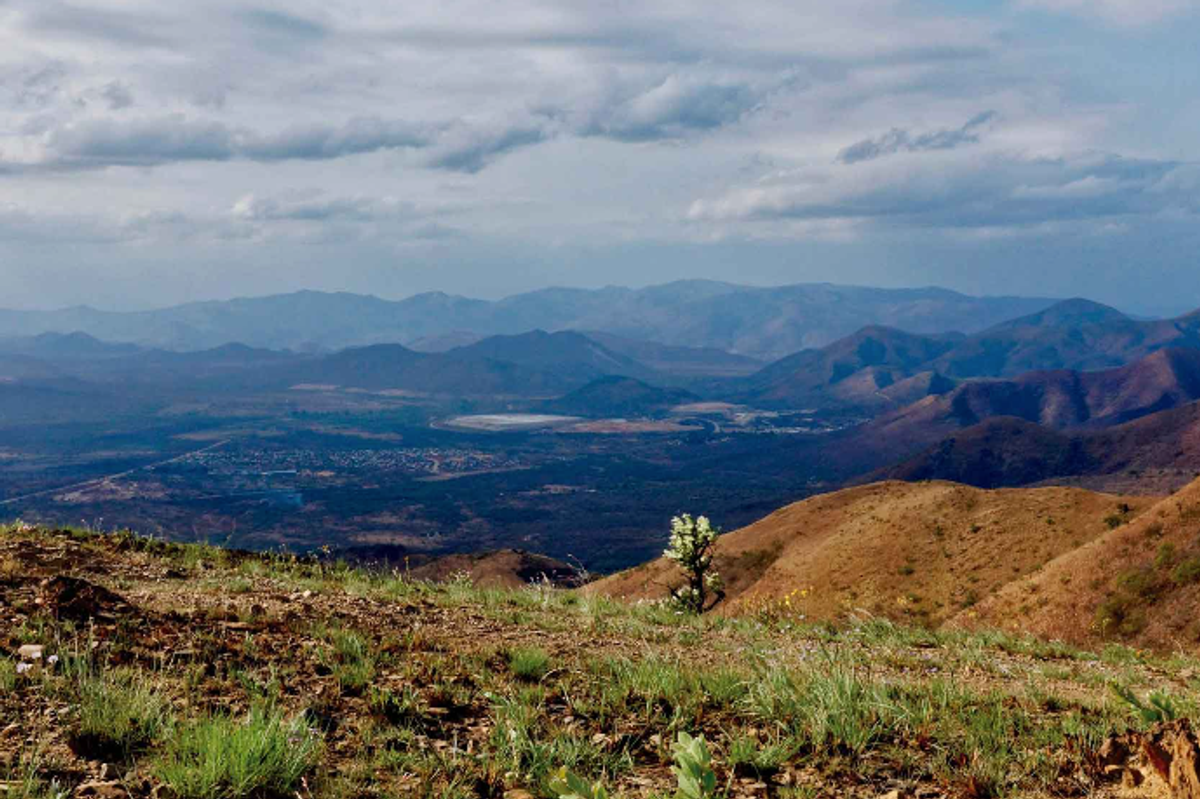 A bit of South Africa’s Barberton Greenstone Belt(Global Fee on Geoheritage)De Ronde’s map printed a fraction of the traditional deep seafloor within the Barberton Greenstone Belt, created some 3.3 billion years in the past, when the sector used to be an insignificant 1.2 billion years previous.“There used to be, alternatively, one thing very extraordinary about this seafloor,” Lamb and de Ronde write.“And it has taken our find out about of rocks laid down in New Zealand, on the different finish of the Earth’s lengthy historical past, to make sense of it.”The 2 professionals argue that the overall figuring out of early Earth as a fiery ball of molten magma, whose floor used to be too susceptible to shape inflexible plates – and, by way of extension, undergo earthquakes – is improper.Fairly, they posit, the younger planet used to be often rocked by way of massive earthquakes which have been induced every time one tectonic plate slid below some other in a subduction zone.Having a look at de Ronde’s map of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, they realised its “jumbled up” rock layers have been paying homage to newer submarine landslides that experience passed off in New Zealand.Those landslides have been induced by way of nice earthquakes alongside the rustic’s greatest fault, the megathrust within the Hikurangi subduction zone, the place the bedrock is manufactured from a mishmash of sedimentary rocks.The Hikurangi Subduction Zone Projectwww.youtube.comThese rocks have been firstly laid down at the seafloor off the coast of New Zealand some 20 million years in the past, at the edges of a deep oceanic trench, which used to be the web site of common massive earthquakes.Through making an allowance for the formation of this New Zealand rockbed, the professionals declare to have solved the thriller in the back of the Barberton Greenstone Belt formations.Like its younger successor, those buildings have been the “remnant of a big landslide containing sediments deposited each on land or in very shallow water, jumbled with those who amassed at the deep seafloor,” they have got concluded.Put merely, if the rock layers in New Zealand have been shaped by way of earthquakes, then so, too, have been those within the Barberton Greenstone Belt – subverting the idea that early Earth wasn’t provided to undergo such tremors.Moreover, Lamb and de Ronde counsel that their paintings “can have unlocked different mysteries, too,” as a result of, they indicate: “Subduction zones also are related to explosive volcanic eruptions.”They cite the instance of Tonga’s Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, which erupted in January 2022 with the power of a “60 Megaton atomic bomb” and despatched a limiteless cloud of ash into house, in which, over the next 11 hours, greater than 200,000 lightning moves flashed.“In the similar volcanic area, underwater volcanoes are erupting a particularly uncommon form of lava known as boninite. That is the nearest trendy instance of a lava that used to be commonplace within the early Earth,” they upload.
A bit of South Africa’s Barberton Greenstone Belt(Global Fee on Geoheritage)De Ronde’s map printed a fraction of the traditional deep seafloor within the Barberton Greenstone Belt, created some 3.3 billion years in the past, when the sector used to be an insignificant 1.2 billion years previous.“There used to be, alternatively, one thing very extraordinary about this seafloor,” Lamb and de Ronde write.“And it has taken our find out about of rocks laid down in New Zealand, on the different finish of the Earth’s lengthy historical past, to make sense of it.”The 2 professionals argue that the overall figuring out of early Earth as a fiery ball of molten magma, whose floor used to be too susceptible to shape inflexible plates – and, by way of extension, undergo earthquakes – is improper.Fairly, they posit, the younger planet used to be often rocked by way of massive earthquakes which have been induced every time one tectonic plate slid below some other in a subduction zone.Having a look at de Ronde’s map of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, they realised its “jumbled up” rock layers have been paying homage to newer submarine landslides that experience passed off in New Zealand.Those landslides have been induced by way of nice earthquakes alongside the rustic’s greatest fault, the megathrust within the Hikurangi subduction zone, the place the bedrock is manufactured from a mishmash of sedimentary rocks.The Hikurangi Subduction Zone Projectwww.youtube.comThese rocks have been firstly laid down at the seafloor off the coast of New Zealand some 20 million years in the past, at the edges of a deep oceanic trench, which used to be the web site of common massive earthquakes.Through making an allowance for the formation of this New Zealand rockbed, the professionals declare to have solved the thriller in the back of the Barberton Greenstone Belt formations.Like its younger successor, those buildings have been the “remnant of a big landslide containing sediments deposited each on land or in very shallow water, jumbled with those who amassed at the deep seafloor,” they have got concluded.Put merely, if the rock layers in New Zealand have been shaped by way of earthquakes, then so, too, have been those within the Barberton Greenstone Belt – subverting the idea that early Earth wasn’t provided to undergo such tremors.Moreover, Lamb and de Ronde counsel that their paintings “can have unlocked different mysteries, too,” as a result of, they indicate: “Subduction zones also are related to explosive volcanic eruptions.”They cite the instance of Tonga’s Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, which erupted in January 2022 with the power of a “60 Megaton atomic bomb” and despatched a limiteless cloud of ash into house, in which, over the next 11 hours, greater than 200,000 lightning moves flashed.“In the similar volcanic area, underwater volcanoes are erupting a particularly uncommon form of lava known as boninite. That is the nearest trendy instance of a lava that used to be commonplace within the early Earth,” they upload.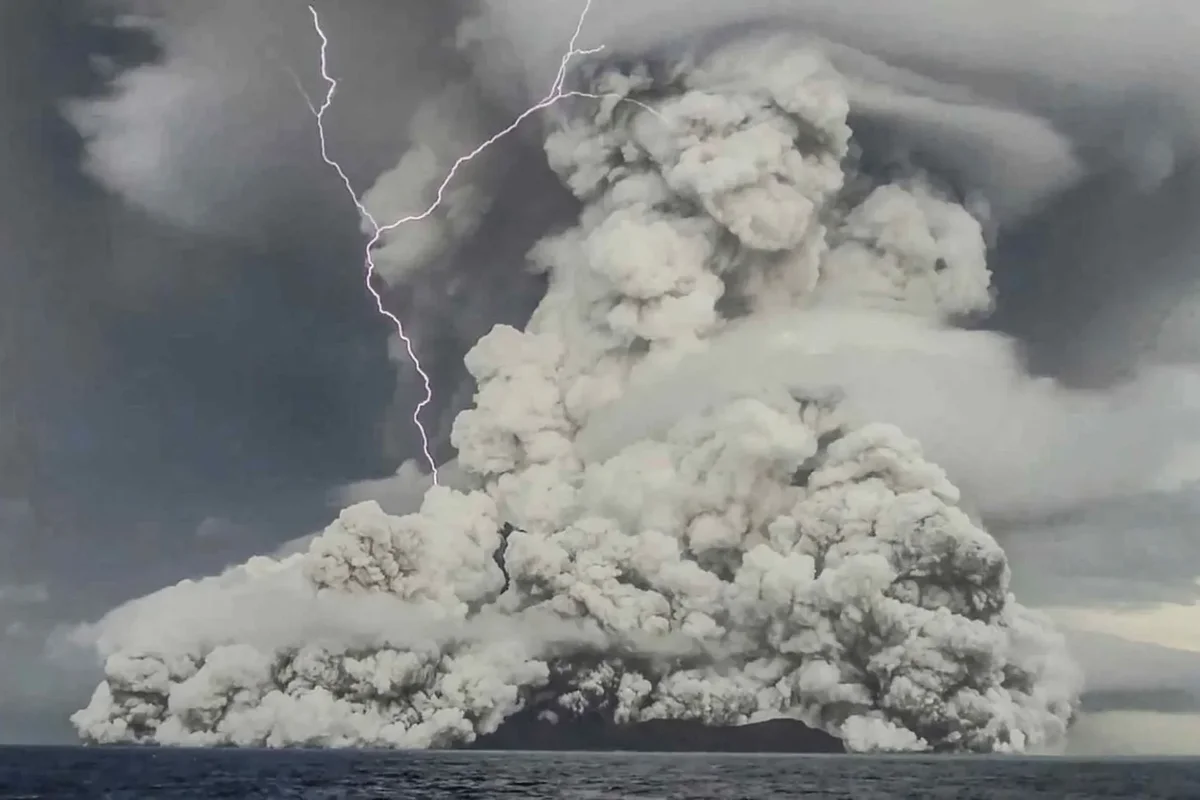 Clouds of ash pierced with lights spewed from the violent 2022 volcanic eruption( Tonga Geological Services and products by way of NOAA)Lamb and de Ronde argue that the massive amounts of volcanic ash discovered within the Barberton Greenstone Belt “is also an historic document of equivalent volcanic violence”. And, much more apparently, they counsel that the related lightning moves may just doubtlessly have “created the crucible for lifestyles the place the fundamental natural molecules have been solid.”In different phrases, subduction zones aren’t simply the supply of tectonic chaos, they might even have been the spark that ignited the flame of lifestyles itself.Join our unfastened Indy100 weekly newsletterHave your say in our information democracy. Click on the upvote icon on the most sensible of the web page to lend a hand elevate this text throughout the indy100 ratings
Clouds of ash pierced with lights spewed from the violent 2022 volcanic eruption( Tonga Geological Services and products by way of NOAA)Lamb and de Ronde argue that the massive amounts of volcanic ash discovered within the Barberton Greenstone Belt “is also an historic document of equivalent volcanic violence”. And, much more apparently, they counsel that the related lightning moves may just doubtlessly have “created the crucible for lifestyles the place the fundamental natural molecules have been solid.”In different phrases, subduction zones aren’t simply the supply of tectonic chaos, they might even have been the spark that ignited the flame of lifestyles itself.Join our unfastened Indy100 weekly newsletterHave your say in our information democracy. Click on the upvote icon on the most sensible of the web page to lend a hand elevate this text throughout the indy100 ratings
Extraordinary buildings found out within the Pacific may just trade our figuring out of Earth



)