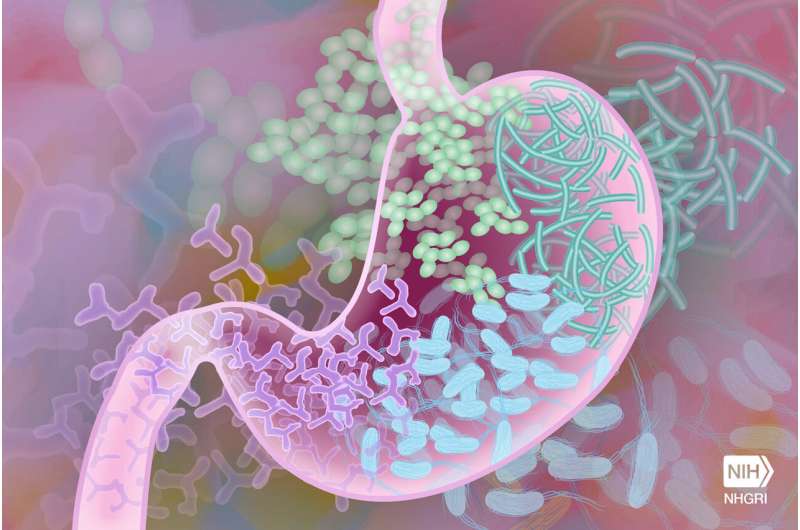
Representation of micro organism within the human intestine. Credit score: Darryl Leja, Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute, Nationwide Institutes of Well being
The biggest and maximum ethnically and geographically complete investigation to this point of the intestine microbiome of other people with sort 2 diabetes (T2D), prediabetes, and wholesome glucose standing has discovered that particular viruses and genetic variants inside micro organism correspond with adjustments in intestine microbiome serve as and T2D chance.
Result of the learn about—which represents a collaboration throughout Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium, the Large Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Harvard T.H. Chan Faculty of Public Well being—are printed in Nature Drugs.
“The microbiome is very variable throughout other geographic places and racial and ethnic teams. In case you simplest learn about a small, homogeneous inhabitants, you’re going to most certainly omit one thing,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Daniel (Dong) Wang, MD, ScD, of the Channing Department of Community Drugs at Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium, Large, and Harvard Chan Faculty. “Our learn about is by means of a ways the biggest and maximum various learn about of its type.”
“The intestine microbiome’s dating to complicated, continual, heterogeneous sicknesses like T2D is slightly delicate,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Curtis Huttenhower, Ph.D. of Harvard Chan Faculty and Large. “Similar to research of huge human populations were the most important for figuring out human genetic variation, massive and various populations are important—and an increasing number of possible—for detailed microbiome variation research as neatly.”
T2D impacts roughly 537 million other people international. In T2D, the frame regularly loses its talent to keep watch over blood sugar successfully. Analysis during the last decade has connected adjustments within the intestine microbiome—the choice of micro organism, fungi, and viruses that inhabit our intestines—to the advance of T2D. Then again, prior research of the intestine microbiome and its position in T2D were too small and sundry in learn about design to attract vital conclusions.
This paper analyzed knowledge from the newly established Microbiome and Cardiometabolic Illness Consortium (MicroCardio). The investigation integrated newly generated knowledge and the ones at first captured all over a number of different experiments, encompassing a complete of 8,117 intestine microbiome metagenomes from ethnically and geographically various individuals.
Other folks integrated within the learn about had T2D, prediabetes, or no adjustments of their blood sugar ranges and hailed from the U.S., Israel, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Germany, France, and China. Co-first authors at the paper are Zhendong Mei, Ph.D., of the Channing Department of Community Drugs at Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium and Large, in addition to Fenglei Wang, Ph.D., of Harvard Chan Faculty and Large.
“With this massive learn about, we requested two questions. One is, ‘What are the jobs of species and traces that make up the intestine microbiome in sort 2 diabetes?’ The opposite query is, ‘What are those microbes doing?'” Wang mentioned. “After we analyzed this knowledge, we discovered a rather constant set of microbial species connected to sort 2 diabetes throughout our learn about populations. Lots of the ones species have by no means been reported sooner than.”
To know the position of those microbes within the intestine, the group analyzed species’ purposeful talents. Other traces of a microbial species could have numerous purposes, like the power to make a selected amino acid. The group discovered that sure traces had purposes that can be connected to numerous T2D illness chance.
One main purposeful distinction they noticed was once {that a} pressure of Prevotella copri—a commonplace microbe within the intestine that has the capability to provide massive quantities of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)—was once extra often observed in diabetes sufferers’ intestine microbiomes. Earlier research have proven that folks with chronically prime blood ranges of BCAAs have the next chance of weight problems and T2D.
The researchers additionally discovered proof suggesting that bacteriophages—viruses that infect micro organism—might be riding one of the adjustments they detected inside sure traces of intestine micro organism.
“Our findings associated with bacteriophages had been very unexpected,” Wang mentioned. “This might imply that the virus infects the micro organism and adjustments its serve as in some way that will increase or decreases sort 2 diabetes chance, however extra paintings is had to perceive this connection.”
In every other research, the group studied a small subset of samples from sufferers newly identified with T2D to evaluate microbiomes which are much less more likely to were impacted by means of drugs use or long-term prime glucose standing. Their effects had been very similar to their better findings, in line with Wang.
“We consider that adjustments within the intestine microbiome reason sort 2 diabetes,” mentioned Wang. “The adjustments to the microbiome might occur first, and diabetes develops later, now not the wrong way round—even supposing long term potential or interventional research are had to turn out this relation firmly.”
“If those microbial options are causal, we will give you the option to modify the microbiome and scale back sort 2 diabetes chance,” he added. “The microbiome is amenable to intervention—which means you’ll trade your microbiome, as an example, with nutritional adjustments, probiotics, or fecal transplants.”
One main limitation of the learn about is that, for essentially the most section, it checked out sufferers’ microbiomes at one cut-off date. It did not have a look at adjustments to the intestine microbiome or illness standing through the years. Long term research that construct in this paintings come with finding out this hyperlink over a longer duration and inspecting the strain-specific purposes to know higher how they result in T2D.
“A get advantages and a problem of the human microbiome is that it’s extremely customized,” mentioned Huttenhower. “The truth that we each and every have extremely distinct microbial communities and microbial genetics implies that very massive inhabitants research are had to in finding constant patterns. However after we do, person microbiomes have the possible to be reshaped to assist scale back illness chance.”
Additional information:
Mei, Z et al. Pressure-Explicit intestine microbial signatures in Kind 2 Diabetes Published by means of a Move-Cohort Research of 8,117 Metagenomes, Nature Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03067-7
Supplied by means of
Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium
Quotation:
Find out about hyperlinks intestine microbiome adjustments to higher chance of sort 2 diabetes (2024, June 25)
retrieved 26 June 2024
from
This report is topic to copyright. Excluding any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions simplest.