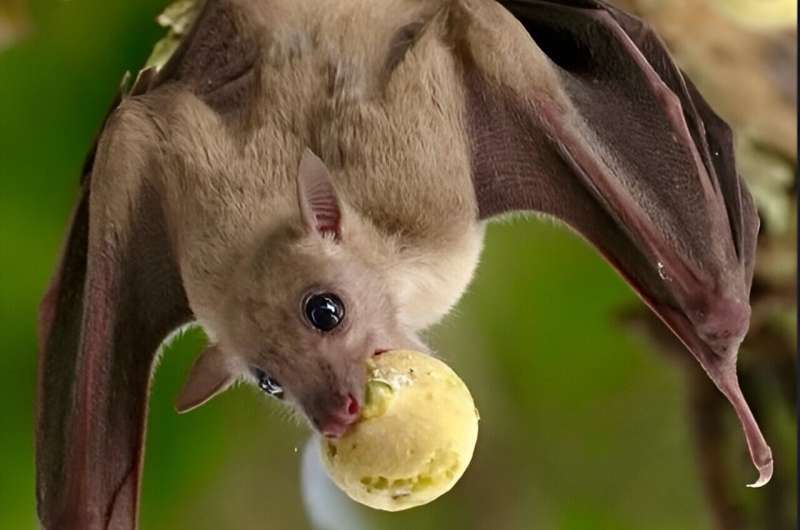
Fruit bat. Credit score: Yuval Barkai
Researchers at Tel Aviv College have tracked free-ranging Egyptian fruit bats from a colony primarily based within the TAU’s I. Meier Segals Lawn for Zoological Analysis to reply to a long-standing clinical query: Do animals have excessive and complicated cognitive talents, prior to now attributed best to people? Particularly, the learn about targeted at the characteristics of episodic reminiscence, psychological time go back and forth, making plans forward, and not on time gratification, arriving at extremely thought-provoking conclusions.
The paper is revealed in Present Biology.
The learn about used to be led through Prof. Yossi Yovel and Dr. Lee Harten from the Faculty of Zoology and Sagol Faculty of Neuroscience at Tel Aviv College. Different researchers incorporated Xing Chen, Adi Rachum, Michal Handel, and Aya Goldstein from the Faculty of Zoology; Lior de Marcas from the Sagol Faculty of Neuroscience, and Maya Fenigstein Levi and Shira Rosencwaig from the Nationwide Public Well being Laboratory of Israel’s Ministry of Well being.
Prof. Yovel explains, “For a few years, the cognitive talents to recall private stories (episodic reminiscence) and plan forward had been thought to be unique to people. However an increasing number of research have advised that more than a few animals additionally possess such features, however the vast majority of those research had been performed underneath laboratory stipulations, since box research on those problems are tough to accomplish. Making an attempt to check those talents in wild animals, we designed a singular experiment depending at the colony of free-ranging fruit bats primarily based in TAU’s I. Meier Segals Lawn for Zoological Analysis.”
The researchers assumed that bats relying on fruit timber for his or her survival would want to broaden a capability to trace the supply of meals each spatially (the place are the fruit timber?) and over the years (when does each and every tree give fruit?). Navigating via landscapes with a large number of fruit and nectar timber, they’d want to mentally monitor the sources with the intention to revisit them on the suitable time.
To check this speculation, a tiny high-resolution GPS tracker used to be connected to each and every bat, enabling the documentation of flight routes and timber visited for lots of months. The huge knowledge gathered on this manner used to be completely analyzed, generating some superb effects.

Fruit bat. Credit score: Tel Aviv College
The primary analysis query used to be: Do bats shape a time map of their minds? To discover this factor, the researchers averted the bats from leaving the colony for various sessions of time, from in the future to every week.
Dr. Harten says, “We needed to look whether or not the bats may inform that point had elapsed and behave accordingly. We discovered that once in the future of captivity, the bats would go back to timber visited at the earlier night time. On the other hand, when an entire week had long gone through, the older bats, in response to previous revel in, have shyed away from timber that had stopped bearing fruit within the period.
“In different phrases, they had been ready to estimate how a lot time had handed since their ultimate discuss with to each and every tree, and knew which timber bore fruit for a little while and had been not price visiting. Younger, green bats had been not able to try this, indicating that that is an received talent that should be realized.”
Whilst the primary analysis query checked out previous stories, the second one handled the longer term: Do the bats showcase future-oriented behaviors? Are they able to making plans forward? To handle this factor, the researchers seen each and every bat’s path to the primary tree of the night, perhaps indicative of plans made earlier than leaving the colony.
Researcher Chen Xing states, “We discovered that normally the bats fly at once to a particular tree they know, from time to time 20 or half-hour away. Being hungry, they fly sooner when that tree is additional away, suggesting that they plan the place they’re heading. Additionally, serious about their selected goal, they’ll go through different timber, even excellent assets visited simply the day prior to this—indicating a capability for not on time gratification. We additionally discovered that the primary bats to depart the colony make a choice timber bearing end result wealthy in sugar, whilst the bats that depart later search proteins.”
These kinds of findings recommend that the bats plan their foraging earlier than they depart the colony, and know precisely the place they’re flying and what sort of nourishment they’re in search of.
Prof. Yovel provides, “The cognitive hole between people and animals is likely one of the most attractive problems in science. Our learn about demonstrates that fruit bats are able to somewhat a fancy decision-making procedure involving the 3 questions indicative of cognitive talents: The place? (each and every tree’s location); When? (when the tree bears fruit); and What? (the nourishment it supplies—sugar vs. proteins).
“As soon as once more, we discover that the distance isn’t clean-cut, and that people don’t seem to be as distinctive as some would possibly assume. It sounds as if, people and animals are all positioned on a spectrum, with nearly any human skill present in animals as neatly.”
Additional info:
Lee Harten et al, Time-mapping and future-oriented conduct in free-ranging wild fruit bats, Present Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.05.046
Supplied through
Tel-Aviv College
Quotation:
Wild bats discovered to own excessive cognitive talents prior to now thought to be unique to people (2024, July 1)
retrieved 1 July 2024
from
This record is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.