The opportunity of the avian flu to leap from birds to cows to people has some scientists a great deal involved.That very situation has already happened two times in the USA because the spring of 2024 – when the primary cows within the country started to fall unwell with extremely pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI).
Researchers at Iowa State College have now led a learn about on two dairy cows in Texas that had been inflamed with the H5N1 pressure to higher know how those transmissions took place.
Within the respiration tissue and mammary glands of each inflamed cows, the staff discovered receptors utilized by a complete host of flu traces, together with those who originate in birds, pigs, or even people.
With all the ones receptors placing out in combination, it is imaginable that if an epidemic infects a cellular, it may well ‘be informed its secrets and techniques’ and mutate to connect to different receptors at the cellular as neatly, reminiscent of the ones frequently present in people.
Whilst fowl flu is fatal amongst avians, it sort of feels to pressure a pointy, short-lived, and non-lethal drop in milk manufacturing when it infects cows. Dairy cows in the United States are the primary showed cows to had been inflamed globally, and professionals nonetheless do not understand how the virus, which advanced to contaminate birds, is spreading from cow to cow.
The brand new learn about issues to the milking procedure as a mechanism of unfold. It identifies H5N1-friendly receptors in cow mammary glands, which is helping provide an explanation for the virus’s ordinary have an effect on at the animals’ milk.
Dairy staff say the milk appears thick and discolored when a cow is inflamed, and if the milk is uncooked and unpasteurized, scientists suspect this can be a supply of transmission for different mammals, together with ourselves.
Top ranges of the H5N1 virus had been present in infected cow milk, in line with officers at the United States Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention (CDC). On the other hand, they word, “sporadic human infections without a ongoing unfold won’t trade the CDC possibility overview for the United States common public, which CDC considers to be low.”
Fortunately, the 2 dairy staff in the United States who stuck the H5N1 virus from dairy cows skilled simplest minor signs and recovered with out infecting any person else, however the pathogen that inflamed them did display relating to indicators of adaptation to mammal our bodies when analyzed via scientists.
Whether or not the ones variations happened within the dairy cows or the dairy staff is unknown, however scientists at Iowa State are prepared to determine extra.
Influenza A viruses, like H5N1, are identified to contaminate cells by means of receptors product of sialic acids. The ones viral traces that advanced to contaminate birds desire positive sialic acid receptors in comparison to those who advanced to contaminate mammals. Even all the way down to the species stage, influenza A viruses are moderately explicit about the place they connect to cells.
Researchers at Iowa State College and the College of Georgia are nervous via the expression and distribution of sialic acids they discovered within the respiration tract and mammary glands of dairy cows inflamed with H5N1.
Each places appear to be vulnerable to avian influenza, they usually display indicators of harboring imaginable viral replication.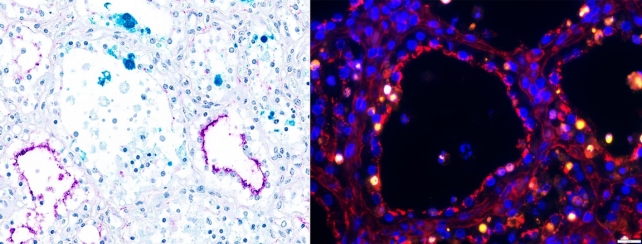 Microscope photographs of mammary gland tissue from a dairy cow inflamed with H5N1. At the left, cells inflamed with influenza are turquoise and flu receptors are magenta. At the proper, infections are brilliant yellow and receptors are brilliant pink. (Christopher Siepker and Tyler Hurt/Iowa State College)Like coronavirus, the influenza virus is “inherently error-prone,” the authors write, including that “an infection of recent host species offers the virus further alternatives to copy and due to this fact mutate to be higher adapt to novel hosts.”
Microscope photographs of mammary gland tissue from a dairy cow inflamed with H5N1. At the left, cells inflamed with influenza are turquoise and flu receptors are magenta. At the proper, infections are brilliant yellow and receptors are brilliant pink. (Christopher Siepker and Tyler Hurt/Iowa State College)Like coronavirus, the influenza virus is “inherently error-prone,” the authors write, including that “an infection of recent host species offers the virus further alternatives to copy and due to this fact mutate to be higher adapt to novel hosts.”
“The unfold of [influenza A virus] to tissues out of doors of the respiration tract is uncommon,” writes the staff of researchers.
They believe it’s imaginable that the mildly acidic setting within the cow mammary gland, coupled with the presence of sialic acid receptors, may just predispose cows to H5N1 an infection.
Those hypotheses must be studied additional, however the findings underline the “pressing want” to know how the avian influenza virus is infecting such a lot of mammal species.
It is usually a very powerful reminder to customers to all the time drink pasteurized milk.The learn about used to be printed in Rising Infectious Sicknesses.
New Fowl Flu Discovery Suggests Cows Are a Danger For Long run Pandemics








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2150879228-fad22bc836f0447c83ae797e2b768ce0.jpg)