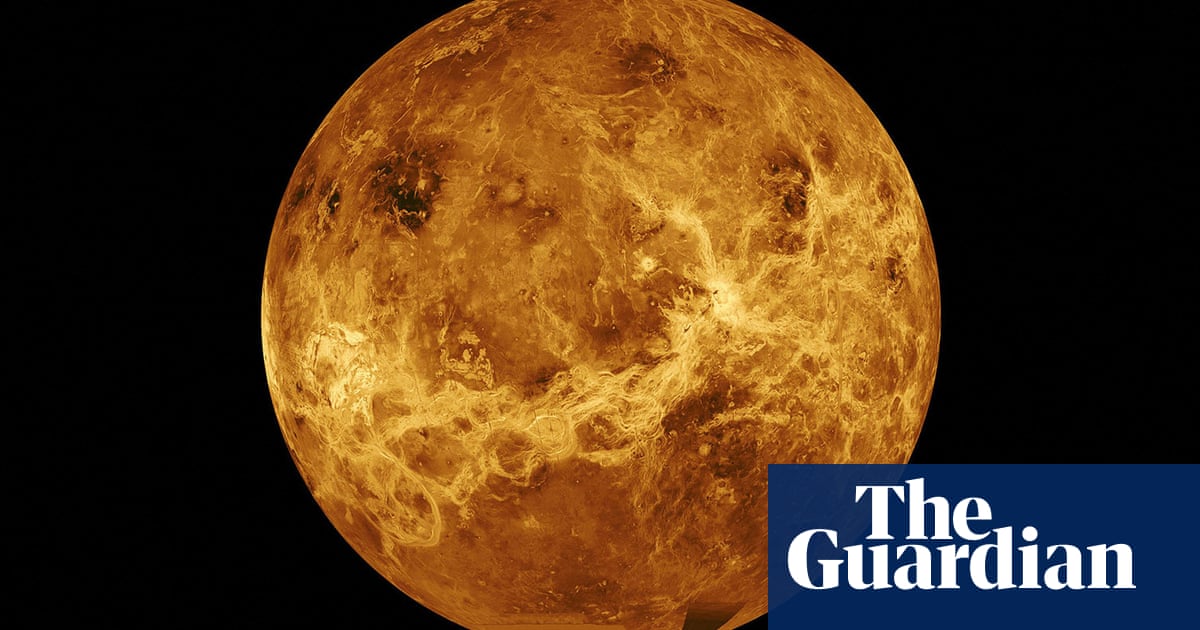
Scorching sufficient to soften steel and blanketed via a poisonous, crushing setting, Venus ranks some of the maximum opposed places within the sun gadget. However astronomers have reported the detection of 2 gases that might level to the presence of existence bureaucracy lurking within the Venusian clouds.Findings offered on the nationwide astronomy assembly in Hull on Wednesday bolster proof for a stinky fuel, phosphine, whose presence on Venus has been fiercely disputed.A separate group printed the tentative detection of ammonia, which on Earth is basically produced via organic task and commercial processes, and whose presence on Venus scientists stated may just no longer readily be defined via recognized atmospheric or geological phenomena.The so-called biosignature gases aren’t a smoking gun for extraterrestrial existence. However the statement will accentuate passion in Venus and lift the potential for existence having emerged or even flourished within the planet’s extra temperate previous and lingered directly to these days in wallet of the ambience.“It may well be that if Venus went via a heat, rainy section prior to now then as runaway world warming took impact [life] would have developed to continue to exist in the one area of interest left to it – the clouds,” stated Dr Dave Clements, a reader in astrophysics at Imperial School London, advised the assembly.The skin of Venus reaches about 450C, scorching sufficient to soften lead and zinc, the atmospheric drive is 90 instances that of the Earth’s floor and there are clouds of sulphuric acid. However about 50km (31 miles0 above the skin the temperature and drive are nearer to prerequisites on Earth – and doubtlessly with regards to survivable for terribly hardy microbes.On Earth, phosphine fuel is produced via microbes in oxygen-starved environments, similar to badger guts and penguin faeces. Different resources, similar to volcanic task, have a tendency to be so inefficient that on rocky planets the fuel is regarded as a marker for existence.A high-profile declare of phosphine detection on Venus in 2020 was once adopted via controversy after next observations failed to copy the discovering. Clements and co-workers’ newest observations with the James Clerk Maxwell telescope (JCMT), based totally in Hawaii, aimed to unravel the dispute. By way of monitoring the phosphine signature over the years, they have been in a position to improve proof for the presence of the fuel and located that its detection perceived to apply the planet’s day-night cycle.“Our findings recommend that after the ambience is bathed in daylight the phosphine is destroyed,” Clements stated. “All that we will be able to say is that phosphine is there. We don’t know what’s generating it. It can be chemistry that we don’t perceive. Or perhaps existence.”In a 2d communicate, Prof Jane Greaves, an astronomer at Cardiff College, offered initial observations from the Inexperienced Financial institution telescope indicating ammonia, which on Earth is made via both commercial processes or via nitrogen-converting micro organism.Greaves stated: “Although we showed either one of those [findings], it isn’t proof that we have got discovered those magic microbes and so they’re residing there these days,” including that there have been no longer but “any floor truths”.Prof Nikku Madhusudhan, an astrophysicist on the College of Cambridge, who was once no longer concerned with both paper, stated that typically evidence of a biosignature required the sign to be powerful and the molecules to be convincingly tied to existence.“In the case of Venus, either one of the ones are open questions,” he stated. “In the event that they truly ascertain phosphine and ammonia robustly it raises the probabilities of organic starting place. The herbal subsequent factor will probably be new folks will have a look at it and provides fortify or counter-arguments. The tale will probably be resolved via extra information.”He added: “All of that is grounds for optimism. If they may be able to display the indicators are there, just right for them.”Dr Robert Massey, the deputy govt director on the Royal Astronomical Society, stated: “Those are very thrilling findings however it will have to be wired that the consequences are most effective initial and extra paintings is wanted to be informed extra concerning the presence of those two possible biomarkers in Venus’s clouds. However, it’s attention-grabbing to assume that those detections may just level to both conceivable indicators of existence or some unknown chemical processes. It is going to be attention-grabbing to peer what additional investigations unearth over the approaching months and years.”
Indicators of 2 gases in clouds of Venus may just point out existence, scientists say









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2188460679-4f112c9e9def4df98120dc4919bbd105.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhattoExpectFromBitcoinandCryptocurrencyMarketsin2025-12ed9a9f2e8c42a5b2477933ea62fe0d.jpg)
