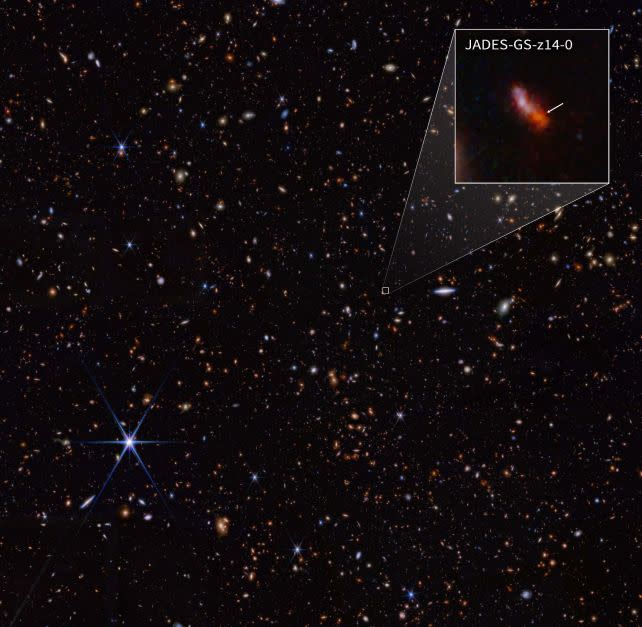
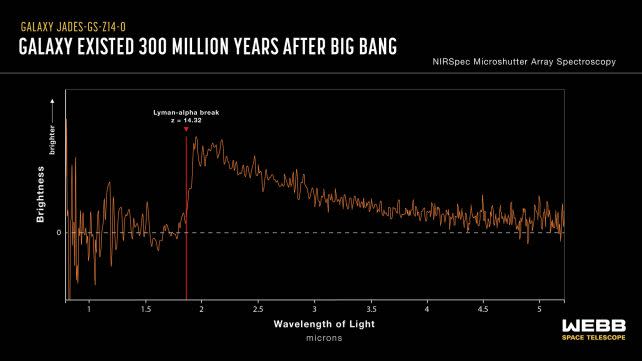
A newly found out galaxy has simply smashed the report for the earliest noticed but, presenting a big problem to our present fashions of galaxy formation.It is known as JADES-GS-z14-0, and it is brightly gleaming within the early Universe, because it seemed not up to 300 million years after the Giant Bang. A 2nd fresh discovery, known as JADES-GS-z14-1, used to be showed to be just about as remote.The detections, astronomers say, at the moment are “unambiguous”, this means that the Cosmic First light would possibly have some ‘splainin’ to do.”In January 2024, NIRSpec noticed this galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, for nearly ten hours, and when the spectrum used to be first processed, there used to be unambiguous proof that the galaxy used to be certainly at a redshift of 14.32, shattering the former most-distant galaxy report,” mentioned astronomers Stefano Carniani of Scuola Normale Superiore in Italy and Kevin Hainline of the College of Arizona.”From the pictures, the supply is located to be over 1,600 light-years throughout, proving that the sunshine we see is coming most commonly from younger stars and now not from emission close to a rising supermassive black hollow.”This a lot starlight signifies that the galaxy is a number of masses of thousands and thousands of occasions the mass of the Solar! This raises the query: How can nature make any such shiny, huge, and big galaxy in not up to 300 million years?”3 separate papers were penned at the topic, with one now newly printed in Nature.Two others on arXiv are but to be peer-reviewed, however all 3 have the similar conclusion: JADES-GS-z14-0 is for sure there, a shining datapoint that represents a brand new future of figuring out how the Universe shaped, on the very starting.Up till quite lately, we had little or no concrete wisdom concerning the length referred to as the Cosmic First light, the primary billion or so years after the Giant Bang 13.8 billion years in the past. That is since the early Universe used to be full of a fog of impartial hydrogen that scattered gentle, fighting it from spreading.This fog did not ultimate; it used to be ionized and cleared through the ultraviolet gentle blazed out through gadgets within the early Universe, and through the top of the Cosmic First light, house used to be clear.Via then, alternatively, there have been a complete bunch of stars and galaxies striking round. If we wish to understand how all of it shaped, we want so that you could see into the fog.This is among the issues JWST, with its tough infrared eyes, used to be designed to do. Infrared radiation is in a position to go back and forth thru dense media different gentle can not, its lengthy wavelengths in a position to cross thru with minimum scattering.It is been engaging in the JWST Complex Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), on the lookout for gadgets within the first 650 million years after the Giant Bang, with very fascinating effects.Something that we’ve got been again and again discovering is huge gadgets a lot previous than we think them. That is been lovely mind-blowing, as a result of we’ve got been running beneath the idea that such things as supermassive black holes and galaxies take a very long time to shape – a long way longer than the time frame by which we’re staring at them.However JADES-GS-z14-0 takes the cake. It is very huge, and really shiny, on no account what astronomers have predicted that galaxies seem like within the early Universe.At first, the scale of it presentations that many of the gentle must be coming from stars, slightly than the blaze of sunshine from the distance round a rising supermassive black hollow.
Research of its gentle unearths the presence of a large number of mud and oxygen, which is surprising so early on. Such heavy components would want to be made inside of stars which then want to explode. Those options counsel that a number of generations of big stars should have lived and died already through 300 million years after the Giant Bang.For the reason that the very biggest stars nowadays have lifespans of most effective round a couple of million years, that isn’t unimaginable, however nonetheless now not slightly what astronomers anticipated to seek out.All in combination, the galaxy means that we want to reconsider the early Universe, appearing that the huge collection of gentle assets we see there can’t be fully defined through rising black holes. By some means, huge, shiny, well-formed galaxies can bring together early within the Cosmic First light.”JADES-GS-z14-0 now turns into the archetype of this phenomenon,” Carniani mentioned. “It’s surprising that the Universe could make any such galaxy in most effective 300 million years.”The invention paper led through Carniani has been printed in Nature. Different papers learning the homes of the galaxy’s gentle may also be discovered on arXiv right here and right here.An previous model of this newsletter used to be printed in Might 2024.Similar Information
Astronomers Simply Found out The Earliest Galaxy We’ve got Ever Observed