Vegetation rising on the backside of huge sinkholes in China are so awash in vitamins, they develop quicker than their surface-dwelling opposite numbers, all whilst the use of much less of a elementary development block, a brand new find out about unearths.The sinkholes, known as “tiankeng,” are one of the most last-remaining herbal refuges for historic forests and might harbor species unknown to science — however precisely how the ones species can thrive on the backside of those deep pits used to be unclear.Seems, laurels, nettles and ferns that are living inside of tiankeng thrive off of enormous shares of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium and magnesium, all of which restrict plant expansion in different environments, the place they’re scarce. However as a result of those vitamins are considerable in tiankeng, the vegetation slurp them up so they are able to develop tall and profit from the slivers of daylight that extend them, in line with a find out about printed on-line July 20 within the Chinese language Magazine of Plant Ecology.”Vegetation can adapt to adversarial environments via adjusting their nutrient content material,” researchers wrote within the find out about, which used to be translated from Mandarin the use of Google Translate.Little or no gentle reaches the ground of tiankeng, this means that “heavenly pits” in Mandarin. Tiankeng are 330-foot-deep (100 meters) holes in China’s southwestern karst panorama. Those deep pits harbor vegetation that desire moisture and color, together with species distinctive to the area, in line with the find out about.Similar: 2 vegetation randomly mated as much as 1 million years in the past to present upward push to probably the most global’s hottest beverages”Because of the towering cliffs and steep terrain of the tiankeng, it’s been much less disturbed via human actions,” the researchers wrote. Tiankeng are refuges for contemporary karst woodland vegetation, together with the Nepali hog plum (Choerospondias axillaris) and the Chinese language rain bell (Strobilanthes cusia), they wrote.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered directly in your inbox.For the find out about, the researchers accumulated samples from 64 plant species outside and inside tiankeng in Leye County, in China’s Guangxi area. Leye County is house to the Dashiwei Tiankeng Workforce, a geological marvel comprising 30 sinkholes in a panorama spanning 7.7 sq. miles (20 sq. kilometers). To decide if the nutrient absorption and expansion methods of those vegetation differed relying on their setting, the group measured the carbon and nutrient content material in every pattern.Vegetation rising inside of tiankeng had decrease carbon contents than the ones rising out of doors, however that they had upper ranges of each different component the researchers measured, corresponding to calcium and potassium, in addition to upper expansion charges.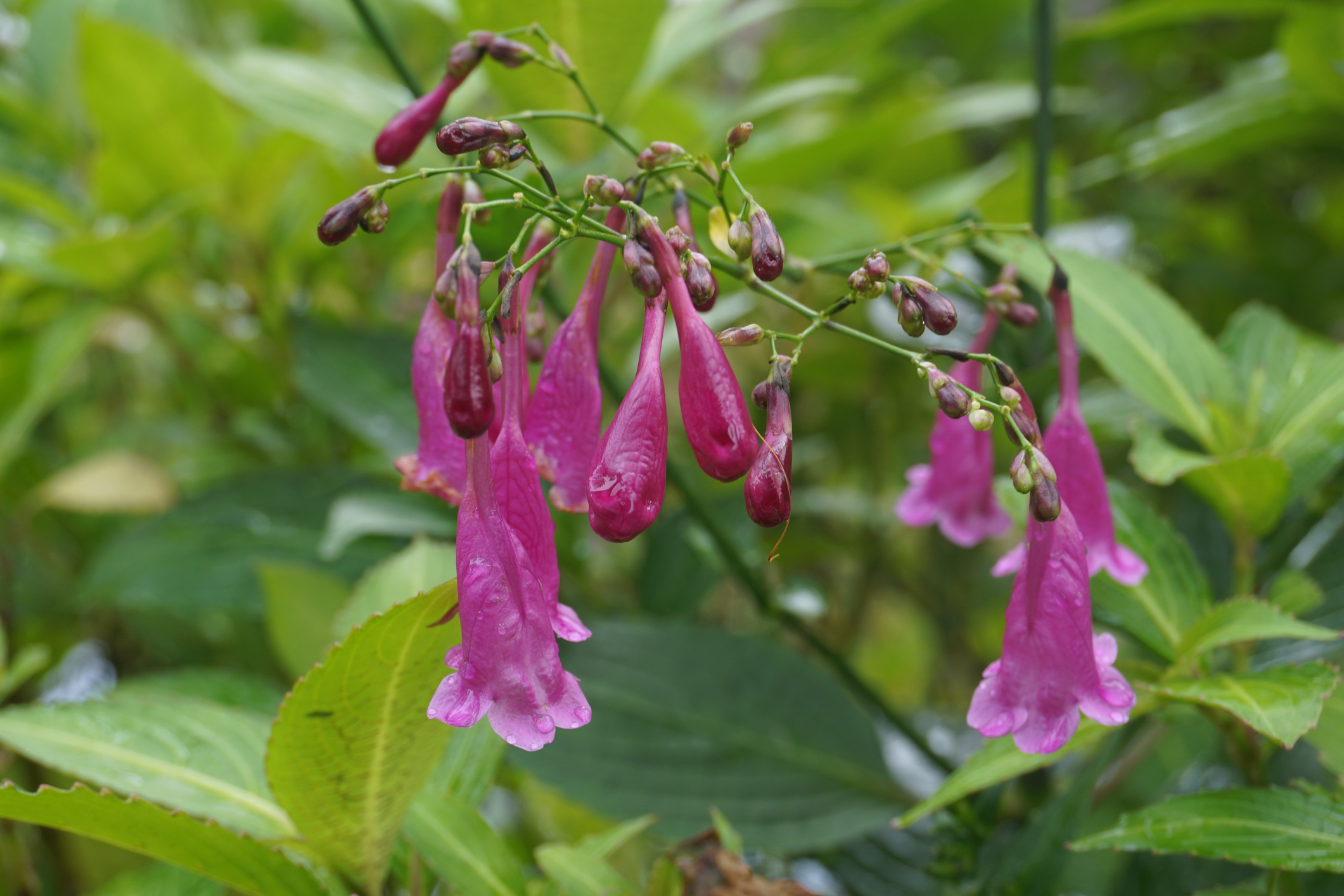 The Chinese language rain bell (Strobilanthes cusia), sometimes called Assam indigo, is a contemporary karst plant discovered on the backside of sinkholes in China. (Symbol credit score: dnixdony by the use of Getty Photographs)Carbon is very important in vegetation, making up a lot in their “skeletons” and constructions that support water retention, in line with the find out about. However the humid stipulations inside of tiankeng imply vegetation get via simply tremendous with decrease ranges of carbon of their tissues as a result of they don’t want to keep as a lot water. Vegetation rising on the floor contained extra carbon, most likely as a result of “the woodland out of doors the pit has prime gentle depth, fast water evaporation, deficient soil, higher interference from human actions and simple soil loss,” the researchers wrote.In comparison with floor vegetation, vegetation rising inside of tiankeng had upper ranges of nitrogen and phosphorus, either one of which vegetation draw from the soil. Soil on the backside of tiankeng contained extra of those parts than floor soils did, indicating that vegetation absorbed them extra simply. Karst soil is wealthy in calcium and magnesium, and tiankeng vegetation confirmed a ways upper ranges of those parts than floor vegetation. In addition they had upper ranges of potassium, regardless of potassium being moderately scarce in karst soils.Tiankeng vegetation take in vitamins extra readily than “conservative” floor vegetation, as a result of vitamins are extra considerable within the shady depths of sinkholes and as the vegetation want to develop taller, in line with the find out about.”The soil dietary standing within the tiankeng woodland is just right,” the researchers wrote, and vegetation have developed to make the most productive of the to be had sources to develop rapid and harvest extra gentle.
The Chinese language rain bell (Strobilanthes cusia), sometimes called Assam indigo, is a contemporary karst plant discovered on the backside of sinkholes in China. (Symbol credit score: dnixdony by the use of Getty Photographs)Carbon is very important in vegetation, making up a lot in their “skeletons” and constructions that support water retention, in line with the find out about. However the humid stipulations inside of tiankeng imply vegetation get via simply tremendous with decrease ranges of carbon of their tissues as a result of they don’t want to keep as a lot water. Vegetation rising on the floor contained extra carbon, most likely as a result of “the woodland out of doors the pit has prime gentle depth, fast water evaporation, deficient soil, higher interference from human actions and simple soil loss,” the researchers wrote.In comparison with floor vegetation, vegetation rising inside of tiankeng had upper ranges of nitrogen and phosphorus, either one of which vegetation draw from the soil. Soil on the backside of tiankeng contained extra of those parts than floor soils did, indicating that vegetation absorbed them extra simply. Karst soil is wealthy in calcium and magnesium, and tiankeng vegetation confirmed a ways upper ranges of those parts than floor vegetation. In addition they had upper ranges of potassium, regardless of potassium being moderately scarce in karst soils.Tiankeng vegetation take in vitamins extra readily than “conservative” floor vegetation, as a result of vitamins are extra considerable within the shady depths of sinkholes and as the vegetation want to develop taller, in line with the find out about.”The soil dietary standing within the tiankeng woodland is just right,” the researchers wrote, and vegetation have developed to make the most productive of the to be had sources to develop rapid and harvest extra gentle.