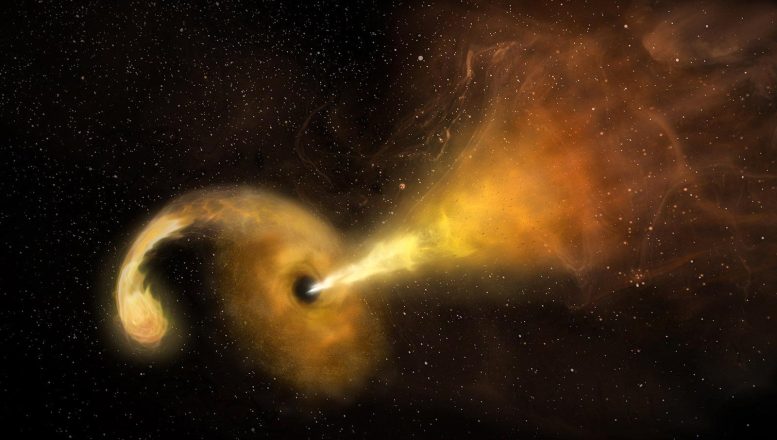
Artist’s conception of a tidal disruption match (TDE), a celebrity being shredded by means of the robust gravity of a supermassive black hollow. Subject material from the megastar spirals right into a disk rotating across the black hollow, and a jet of debris is ejected. Credit score: Sophia Dagnello, NRAO/AUI/NSF
Artist’s conception of a tidal disruption match (TDE), a celebrity being shredded by means of the robust gravity of a supermassive black hollow. Subject material from the megastar spirals right into a disk rotating across the black hollow, and a jet of debris is ejected. Credit score: Sophia Dagnello, NRAO/AUI/NSF
Black holes, historically elusive and invisible, are being unveiled throughout the remark of tidal disruption occasions (TDEs) the place stars are violently destroyed, producing luminous flares observable throughout huge distances.
The dramatic dimming of a gentle supply ~ 860 million light-years clear of Earth confirms the accuracy of an in depth style evolved by means of a workforce of astrophysicists from Syracuse College, MIT, and the House Telescope Science Institute.
Working out Black Holes Thru TDEs
Robust telescopes like NASA’s Hubble, James Webb, and Chandra X-ray Observatory supply scientists a window into deep house to probe the physics of black holes. Whilst one may surprise how you’ll be able to “see” a black hollow, which famously absorbs all gentle, that is made imaginable by means of tidal disruption occasions (TDEs) – the place a celebrity is destroyed by means of a supermassive black hollow and will gasoline a “luminous accretion flare.” With luminosities 1000’s of billions of instances brighter than the Solar, accretion occasions allow astrophysicists to review supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at cosmological distances.
TDEs happen when a celebrity is violently ripped aside by means of a black hollow’s immense gravitational box. Because the megastar is shredded, its remnants are reworked right into a move of particles that rains back off onto the black hollow to shape a extremely popular, very shiny disk of subject matter swirling across the black hollow, known as an accretion disc. Scientists can learn about those to make direct observations of TDEs, and examine the ones to theoretical fashions to narrate observations to bodily homes of disrupted stars and their disrupting black holes.
 Virtual representation of a celebrity losing stellar particles because it orbits a supermassive black hollow. This artist’s impact represents the middle of a galaxy about 860 million light-years from Earth. Credit score: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss
Virtual representation of a celebrity losing stellar particles because it orbits a supermassive black hollow. This artist’s impact represents the middle of a galaxy about 860 million light-years from Earth. Credit score: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss
Inventions in Black Hollow Analysis
A workforce of physicists from Syracuse College, MIT, and the House Telescope Science Institute used detailed modeling to are expecting the brightening and dimming of AT2018fyk, which is a repeating partial TDE, which means the high-density core of the megastar survived the gravitational interplay with the SMBH, permitting it to orbit the black hollow and be shredded greater than as soon as.
The style predicted that AT2018fyk would “dim” in August 2023, a forecast which was once showed when the supply went darkish closing summer season, offering proof that their style delivers a brand new approach to probe the physics of black holes. Their effects had been revealed in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
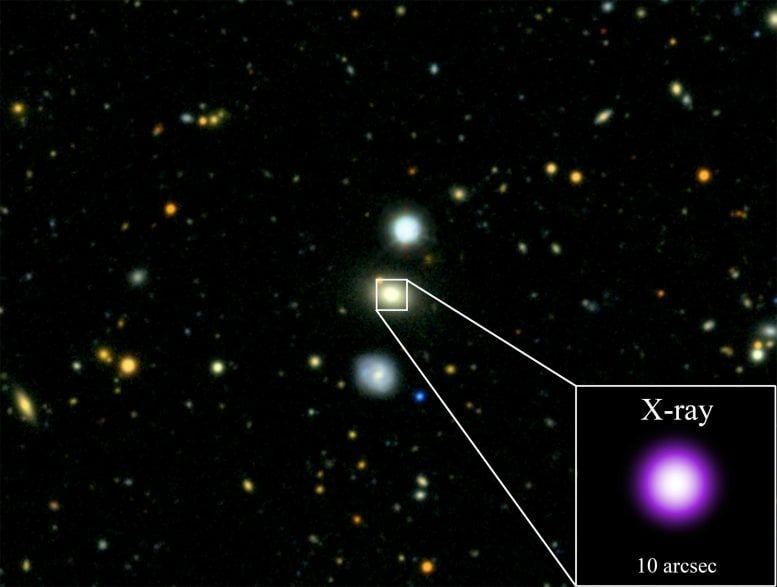 X-ray and optical symbol of AT2018fyk. Credit score: X-ray: NASA/SAO/Kavli Inst. at MIT/D.R. Pasham; Optical: NSF/Legacy Survey/SDSS
X-ray and optical symbol of AT2018fyk. Credit score: X-ray: NASA/SAO/Kavli Inst. at MIT/D.R. Pasham; Optical: NSF/Legacy Survey/SDSS
A Prime Power Supply
Because of extremely detailed extragalactic surveys, scientists are tracking extra coming and going gentle resources than ever prior to. Surveys pan complete hemispheres looking for unexpected brightening or dimming of resources, which tells researchers that one thing has modified. In contrast to the telescope for your front room that may most effective center of attention visual gentle, telescopes comparable to Chandra can come across gentle resources in what’s known as the X-ray spectrum emitted from subject matter this is tens of millions of levels in temperature.
Visual gentle and X-rays are each types of electromagnetic radiation, however X-rays have shorter wavelengths and extra calories. Very similar to the way in which by which your range turns into “purple scorching” after you flip it on, the gasoline comprising a disc “glows” at other temperatures, with the freshest subject matter closest to the black hollow. On the other hand, as a substitute of radiating its calories at optical wavelengths visual to the attention, the freshest gasoline in an accretion disc emits within the X-ray spectrum. Those are the similar X-rays utilized by docs to symbol your bones and that may move thru comfortable tissue, and as a result of this relative transparency, the detectors utilized by NASA X-ray telescopes are particularly designed to come across this high-energy radiation.’
A Repeat Efficiency
In January 2023, a workforce of physicists, together with Eric Coughlin, a professor at Syracuse College’s Division of Physics, Dheeraj R. “DJ” Pasham, a analysis scientist at MIT, and Thomas Wevers, a Fellow on the House Telescope Science Institute, revealed a paper in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters that proposed an in depth style for a repeating partial TDE. Their effects had been the primary to map a celebrity’s unexpected go back orbit a few supermassive black hollow – revealing new details about one of the most cosmos’ maximum excessive environments.
The workforce primarily based their learn about on a TDE referred to as AT2018fyk (AT stands for “Astrophysical Brief”), the place a celebrity was once proposed to be captured by means of a SMBH thru an alternate procedure referred to as “Hills seize.” Firstly a part of a binary device (two stars that orbit one every other beneath their mutual gravitational enchantment), one of the most stars was once hypothesized to had been captured by means of the gravitational box of the black hollow and the opposite (non-captured) megastar was once ejected from the middle of the galaxy at speeds related to ~ 1000 km/s.
As soon as sure to the SMBH, the megastar powering the emission from AT2018fyk has been many times stripped of its outer envelope every time it passes thru its level of closest way with the black hollow. The stripped outer layers of the megastar shape the intense accretion disk, which researchers can learn about the use of X-Ray and Ultraviolet /Optical telescopes that practice gentle from far-off galaxies.
Whilst TDEs are in most cases “once-and-done” since the excessive gravitational box of the SMBH destroys the megastar, which means that the SMBH fades again into darkness following the accretion flare, AT2018fyk introduced the original alternative to probe a repeating partial TDE.
The analysis workforce has used a trio of telescopes to make the preliminary and follow-up detections: Swift and Chandra, each operated by means of NASA, and XMM-Newton, which is a Ecu undertaking. First noticed in 2018, AT2018fyk is ~ 860 million light-years away, which means that as a result of the time it takes gentle to commute, it came about in “real-time” ~ 860 million years in the past.
The workforce used detailed modeling to forecast that the sunshine supply would unexpectedly disappear round August 2023 and brighten once more when the freshly stripped subject matter accretes onto the black hollow in 2025.
Probing the Long run: Predictions and Implications
Confirming the accuracy in their style, the workforce reported an X-ray drop in flux over a span of 2 months, beginning on August 14, 2023. This unexpected alternate will also be interpreted as the second one emission shutoff.
“The noticed emission shutoff presentations that our style and assumptions are viable, and means that we’re actually seeing a celebrity being slowly wolfed by means of and really huge black hollow,” says Coughlin. “In our paper closing 12 months, we used constraints from the preliminary outburst, dimming, and rebrightening to are expecting that AT2018fyk will have to show a unexpected and speedy dimming in August of 2023, if the megastar survived the second one stumble upon that fueled the second one brightening.”
The truth that the device displayed this predicted shutoff due to this fact implies a number of distinctions concerning the megastar and the black hollow:
the megastar survived its 2nd stumble upon with the black hollow;
the speed of go back of stripped particles to the black hollow is tightly coupled to the brightness of AT2018fyk;
and the orbital duration of the megastar concerning the black hollow is ~ 1300 days, or about 3.5 years.
The second one cutoff signifies that every other rebrightening will have to occur between Might and August of 2025, and if the megastar survived the second one stumble upon, a 3rd shutoff is anticipated to happen between January and July of 2027.
As for whether or not we will rely on seeing a rebrightening in 2025, Coughlin says the detection of a 2nd cutoff signifies that the megastar has had extra mass freshly stripped, which will have to go back to the black hollow to supply a 3rd brightening.
“The one uncertainty is within the top of the emission,” he says. “The second one re-brightened top was once significantly dimmer than the primary, and it’s, sadly, imaginable that the 3rd outburst will probably be dimmer nonetheless. That is the one factor that will restrict the detectability of this 3rd outburst.”
Coughlin notes that this style indicates a thrilling new approach to learn about the extremely uncommon occurrences of repeating partial TDEs, which might be believed to happen as soon as each million years in a given galaxy. So far, he says scientists have encountered most effective 4 to 5 methods that show this conduct.
“With the appearance of progressed detection era uncovering extra repeating partial TDEs, we look ahead to that this style will probably be an very important instrument for scientists in figuring out those discoveries,” he says.
Reference: “A Possible 2d Shutoff from AT2018fyk: An Up to date Orbital Ephemeris of the Surviving Celebrity beneath the Repeating Partial Tidal Disruption Match Paradigm” by means of Dheeraj Pasham, E. R. Coughlin, M. Guolo, T. Wevers, C. J. Nixon, Jason T. Hinkle and A. Bandopadhyay, 14 August 2024, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad57b3




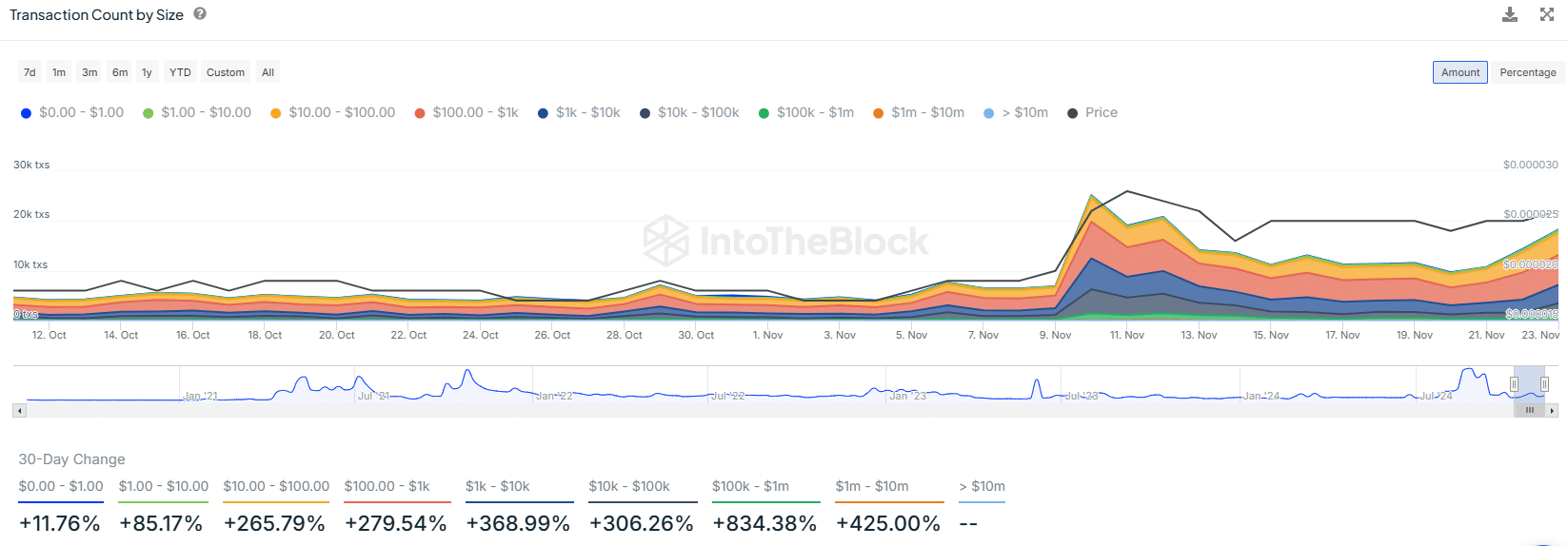
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BTCUSDChart-c26e5881ebc34f33910ad841d6c8862c.gif)