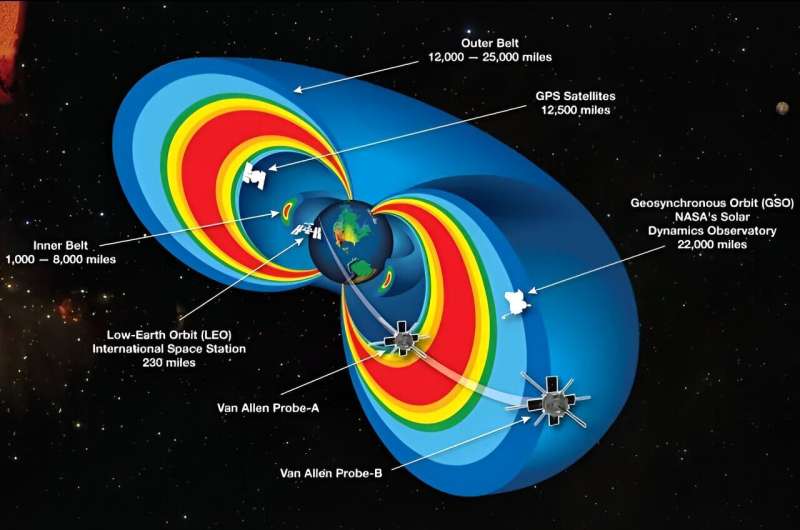
This graphic displays a cutaway style of Earth’s radiation belts with the 2 Van Allen Probes satellites flying thru them. Credit score: NASA representation
Two College of Alaska Fairbanks scientists have found out a brand new form of “whistler,” an electromagnetic wave that carries an excessive amount of lightning power to the Earth’s magnetosphere.
The analysis is printed as of late in Science Advances.
Vikas Sonwalkar, a professor emeritus, and Amani Reddy, an assistant professor, found out the brand new form of wave. The wave carries lightning power, which enters the ionosphere at low latitudes, to the magnetosphere. The power is mirrored upward by means of the ionosphere’s decrease boundary, at about 55 miles altitude, within the reverse hemisphere.
It used to be in the past believed, the authors write, that lightning power coming into the ionosphere at low latitudes remained trapped within the ionosphere and subsequently used to be now not attaining the radiation belts. The belts are two layers of charged debris surrounding the planet and held in position by means of Earth’s magnetic box.
“We as a society are depending on house generation,” Sonwalkar stated. “Trendy verbal exchange and navigation programs, satellites, and spacecraft with astronauts aboard stumble upon destructive vigorous debris of the radiation belts, which will harm electronics and motive most cancers.
“Having a greater working out of radiation belts and the number of electromagnetic waves, together with the ones originating in terrestrial lightning, that have an effect on them is necessary for human operations in house,” he stated.
Sonwalkar and Reddy’s discovery is a kind of whistler wave they name a “specularly mirrored whistler.” Whistlers produce a whistling sound when performed thru a speaker.
Lightning power coming into the ionosphere at upper latitudes reaches the magnetosphere as a unique form of whistler known as a magnetospherically mirrored whistler, which undergoes a number of reflections throughout the magnetosphere.
The ionosphere is a layer of Earth’s higher surroundings characterised by means of a top focus of ions and loose electrons. It’s ionized by means of sun radiation and cosmic rays, making it conductive and the most important for radio verbal exchange as it displays and modifies radio waves.
Earth’s magnetosphere is a area of house surrounding the planet and created by means of Earth’s magnetic box. It supplies a protecting barrier that stops lots of the sun wind’s debris from attaining the ambience and harming lifestyles and generation.
Sonwalkar and Reddy’s analysis displays that each varieties of whistlers—specularly mirrored whistlers and magnetospherically mirrored whistlers—coexist within the magnetosphere.
Of their analysis, the authors used plasma wave information from NASA’s Van Allen Probes, which introduced in 2012 and operated till 2019, and lightning information from the International Vast Lightning Detection Community.
They evolved a wave propagation style that, when bearing in mind specularly mirrored whistlers, confirmed the doubling of lightning power attaining the magnetosphere.
Evaluation of plasma wave information from the Van Allen Probes confirmed that specularly mirrored whistlers are a commonplace magnetospheric phenomenon.
The vast majority of lightning happens on the low latitudes, which might be tropical and subtropical areas liable to thunderstorm construction.
“This means that specularly mirrored whistlers almost definitely elevate a better a part of lightning power to the magnetosphere relative to that carried by means of magnetospherically mirrored whistlers,” Sonwalkar stated.
The have an effect on of lightning-generated whistler waves on radiation belt physics and their use in far off sensing of magnetospheric plasma were researched because the Nineteen Fifties.
Sonwalkar and Reddy are with the Division of Electric and Pc Engineering within the UAF School of Engineering and Mines. Reddy may be affiliated with the UAF Geophysical Institute.
Sonwalkar and Reddy’s analysis is supported by means of grants from the Nationwide Science Basis and NASA EPSCoR, the Established Program to Stimulate Aggressive Analysis.
Additional info:
Vikas S. Sonwalkar et al, Specularly mirrored whistler: A low-latitude channel to couple lightning power to the magnetosphere, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado2657
Equipped by means of
College of Alaska Fairbanks
Quotation:
Scientists uncover phenomenon impacting Earth’s radiation belts (2024, August 17)
retrieved 17 August 2024
from
This record is matter to copyright. Except for any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.