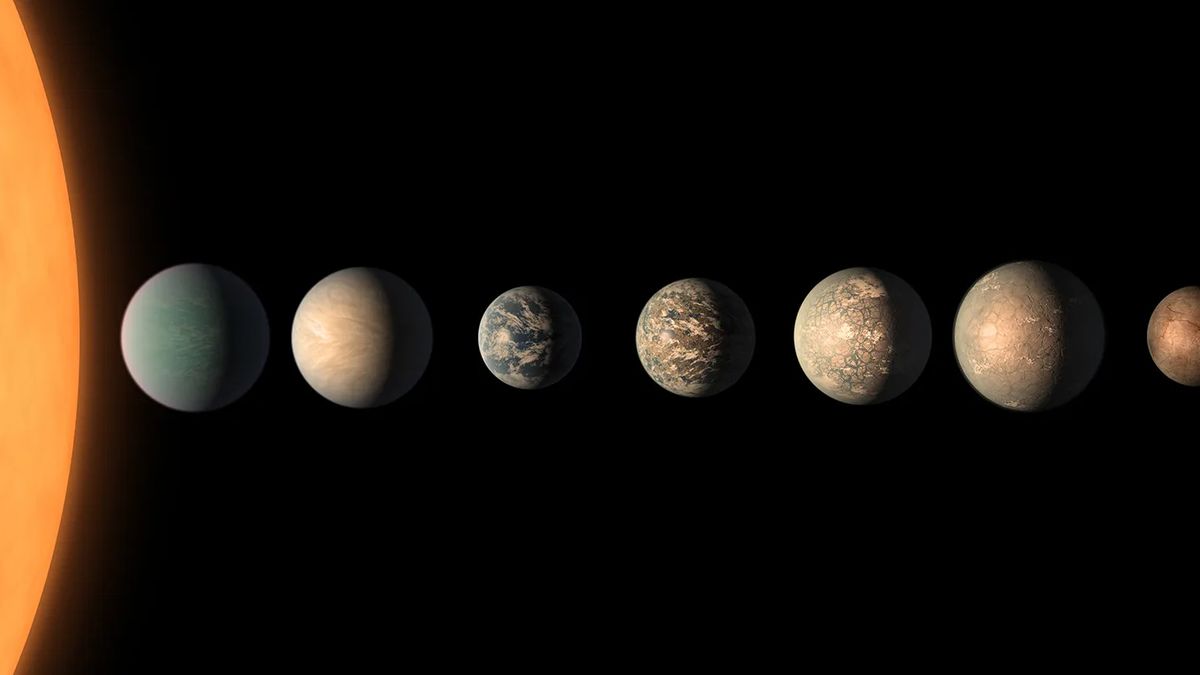
Scientists will have in any case printed the historical past of the tantalizing TRAPPIST-1 device, an intricate selection of seven worlds that sit down about 40 light-years clear of us. Those worlds, many astronomers and astrobiologists say, might be offering us a promising likelihood of discovering existence out of doors the sun device — however in addition they show off atypical orbital patterns. The newly defined historical past of TRAPPIST-1 might, finally, provide an explanation for how the ones patterns got here to be.When planets shape round a tender celebrity, their orbital classes steadily input “resonances” with each and every different. An on a regular basis instance of a resonance has to do with pushing anyone on a playground swing — in case you time the rush to coincide with the herbal frequency of the swing, corresponding to when the swing is almost about to return down, your push would magnify the scale of the swing’s arc.In a similar way, planets steadily in finding themselves in resonances with each and every different. As an example, an internal planet can orbit precisely two times for each and every one orbit of an outer planet. It is a 2:1 resonance, and prefer pushing a kid on a swing amplifies how briskly they swing, the change of gravitational power between resonant planets in most cases makes their orbits volatile, amplifying orbital classes till the planets in the end transfer out of resonance with one every other. Some other commonplace planetary resonance is 3:2. Similar: TRAPPIST-1: A information to the device with 7 Earth-size exoplanetsFor the above explanation why, planetary resonances steadily transform volatile over the years, corresponding to in our sun device — however now not all the time. Some planetary programs organize to stay their resonance patterns, and TRAPPIST-1 is a kind of programs. Techniques with strong resonances are without a doubt aided by way of how compact the device is; TRAPPIST-1’s seven worlds are unfold throughout not up to 8 million kilometers, and they’d all simply have compatibility throughout the orbit of Mercury more than one instances over.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!TRAPPIST-1’s outer 3 planets — designated f, g and h — are in a series of three:2 resonances.”The outer planets behave correctly, so that you can discuss, with the better anticipated resonances,” stated Gabriele Pichierri, who’s a planetary scientist at Caltech, in a commentary. “However the internal ones have resonances which can be a little bit spicier.”As an example, the orbital classes of the 2 innermost planets, b and c, are in an 8:5 resonance, which means planet b orbits 8 instances for each and every 5 orbits of planet c. In the meantime, planets c and d are in a 5:3 resonance. So, how did those complicated preparations rise up?Pichierri is the lead writer of a brand new analysis paper that delves into the early historical past of TRAPPIST-1 to find how its planets wound up on this refined configuration. The team discovered a tale of a moving protoplanetary disk of gasoline and mud blended with tough torques that driven the planets round.The innermost planets would have shaped first, so Pichierri and his crew divided the TRAPPIST-1 device into two sub-groups — the interior planets b, c, d and e, and the outer planets f, g and h. (In contrast to our sun device, wherein the outer planets are gasoline giants, the outer planets of TRAPPIST-1 are rocky worlds.) Their modeling known 3 stages within the evolution of the device. Here is what the crew discovered.Within the first section, the 4 innermost planets all get started existence in 3:2 resonances with each and every different, so b and c are in a three:2 orbital resonance, as are c and d, and d and e. As the interior planets shaped out of subject material from the protoplanetary disk, and their burgeoning pink dwarf celebrity ignited nuclear fusion in its core and produced radiation that started to burn up the disk, the interior fringe of the disk would have receded outwards.In the second one section, planet e, anchored within the receding internal fringe of the disk, would have discovered itself being dragged outwards, clear of planets b, c and d and against the worlds forming within the outer a part of the device. This had the impact of inflicting the orbits of planets b, c and d to waver, and so they crossed in the course of the 8:5 and 5:3 resonances as their orbital classes widened, however had been then driven again by the use of a gravitational torque (a twisting, rotational pressure) from the outer device, till they settled into the 8:5 and 5:3 resonances that they’ve lately.What of planet e, even though? Through the general section, the 3 outer worlds had shaped. Regularly, when planets shape in a protoplanetary disk, they shed orbital angular momentum, exchanging this angular momentum with the disk that they’re accreting subject material from in an effort to develop. This ends up in them migrating against the interior fringe of the disk. Within the TRAPPIST-1 device, this most likely had the impact of pushing planet e again, till the interior and outer portions of the planetary device settled into the configuration that they’re in lately. “Through having a look at TRAPPIST-1, we’ve been ready to check thrilling new hypotheses for the evolution of planetary programs,” stated Pichierri. “TRAPPIST-1 could be very fascinating as a result of it’s so intricate: it’s an extended planetary chain, and it’s a really perfect exemplar for trying out selection theories about planetary device formation.”The analysis used to be printed on Aug. 20 within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
Why the 7 worlds of TRAPPIST-1 waltz in atypical patterns