If we took a scenic force via each and every technology of astronomy, we would get started someplace amongst historical people questioning why there are desk bound fireflies caught within the sky. We might shuttle via libraries with scrolls about how the ones fireflies are, in truth, siblings to our massive yellow solar, after which via rooms with books about how our complete international is someway orbiting that solar.Sooner or later, we would finish up looking at scientists uncover the drive of gravity being dependent at the cloth of spacetime, acquiring pictures of iridescent galaxies rather than the Milky Method and calculating the stern limits of supermassive black holes.However simply as we start coming near our go out into the existing day, I feel we would get started looking at one thing beautiful attention-grabbing. We might begin to see the rising bond between astronomer and system enabling us to open cosmic doorways extra briefly. Aritra Ghosh, a postdoctoral fellow on the College of Washington, is a kind of astronomers.Ghosh just lately, for example, controlled to verify that galaxies in denser areas of the universe can also be up to 25% higher than galaxies with a identical mass and form in much less dense areas. “Dimension” on this case refers to a galaxy’s radius that accommodates 50% of its general mild emission. This can be a tremendous lead to itself, however importantly, it is key to focus on the way it used to be completed: through the usage of system finding out to review extra person galaxies than the human frame might be able to analyze in a single lifetime. To be exact, there have been 2,894,716 galaxies within the dataset.”During the last decade, many astronomers, like me, have performed painstaking research to broaden accept as true with in system finding out, appearing that it may reflect conventional ways,” Ghosh advised Area.com. “In spite of everything, we will be able to get started leveraging those ways to tease out new clinical effects.”This large galaxy pattern set, in reality, got here from an much more huge set that Ghosh controlled to acquire with the assistance of system finding out. That unique set, completed with a surveying software referred to as GaMPEN, encompassed knowledge surrounding 7,805,186 galaxies — the smaller subset for this new find out about used to be decided on in response to the place the galaxies are within the sky. In one millisecond, GaMPEN can decide the construction of a galaxy in response to a parameter the person chooses; Ghosh and fellow researchers used a parameter that exposed what fraction of sunshine comes from a galaxy’s outer disk when in comparison to its central bulge.”I sought after to exhibit to the wider neighborhood how system finding out and massive imaging datasets can also be blended to make growth on long-standing questions in astrophysics,” Ghosh stated.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Then, of the ones just about 8 million topics, Ghosh pulled out the ones in spaces the place he knew the universe’s density by way of earlier calculations. Within the paintings, “dense” environments encapsulated many stuff, together with spaces the place you would to find superclusters of galaxies. The ones are massive conglomerations of many galaxy clusters (one galaxy cluster can comprise as much as 1,000 person galaxies!) normally situated within the threads of the cosmic internet permeating our complete universe. You’ll bring to mind them because the universe’s downtown hotspots.”Our collaborators in Japan, led through Rhythm Shimakawa, measured environmental densities,” Ghosh stated. “They used a non-ML pc set of rules to put circles with radii of 30 million light-years in numerous parts of the sky and depend the collection of galaxies inside of each and every circle — circles in denser areas have a higher-than-average depend.”As soon as the subset used to be recognized, Ghosh and his crew started taking a look at correlations between galactic measurement and setting.For the reason that mass of a galaxy is strongly associated with its measurement and its setting — for example, extra huge galaxies are anticipated to be higher and are living in denser environments — the crew when put next the sizes of galaxies with the similar mass in numerous environments. “Since huge galaxies are uncommon,” Ghosh defined, “we collaborated with theoretical astrophysicists to broaden a brand new metric for the correlation research.”Plus, no longer simplest is that this the biggest catalog ever used for a find out about about galactic measurement and setting — and, Ghosh speculates, possibly within the most sensible 5 for any astrophysical find out about — nevertheless it additionally sports activities an error correction mechanism Ghosh says used to be kind of absent in earlier identical research, thank you partially to the system finding out part.Talking of the ones earlier research, the end result that higher galaxies are extra into supercluster towns than rural cosmic cities used to be somewhat of a wonder — regardless of it sounding fairly intuitive. As Ghosh explains, many scientists who’ve studied the bits and bobs of galaxies in clusters believed that sturdy dynamical forces inside of the ones clusters would regularly strip topic clear of a galaxy, thus making it smaller in measurement.However the crew noticed higher galaxies in dense, supercluster environments. Bizarre.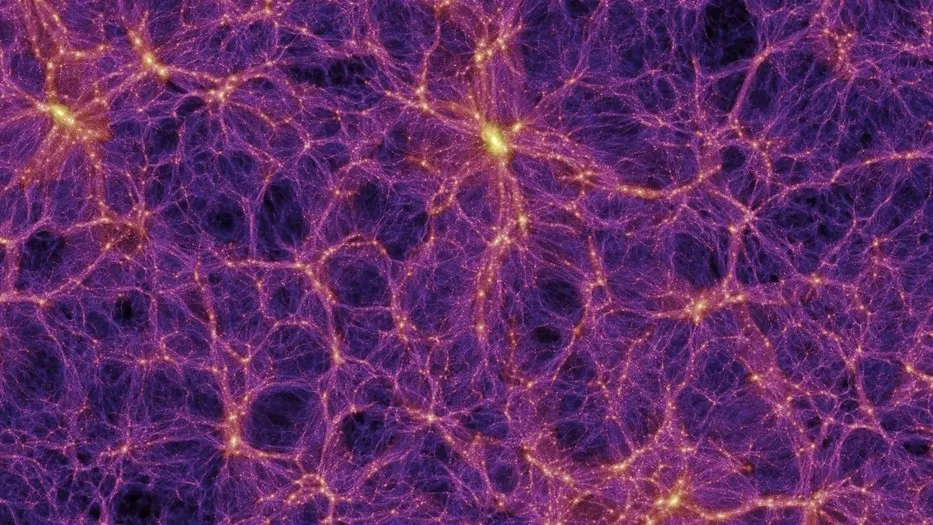 An influence of the cosmic internet around the universe that unites galaxies. (Symbol credit score: ESA/ Springel et al., Virgo Consortium)”We examined our correlation set of rules over smaller subsets first,” Ghosh stated. “The ‘Aha!’ second used to be once we carried out the research on all the pattern of three million galaxies for the primary time, and spotted the sturdy certain correlation.”As to why this may well be? Neatly, there are some chances. One has to do with the type of “topic” advised to get stripped off galaxies in dense spaces of the universe — standard topic made up of same old protons, neutrons and electrons. This raises the query: What about darkish topic? Possibly this invisible substance has a task to play in holding galaxies higher. It would not be a really far-fetched concept, seeing as scientists have proven that almost all huge galaxies are living inside of a halo of darkish topic, together with our personal Milky Method.
An influence of the cosmic internet around the universe that unites galaxies. (Symbol credit score: ESA/ Springel et al., Virgo Consortium)”We examined our correlation set of rules over smaller subsets first,” Ghosh stated. “The ‘Aha!’ second used to be once we carried out the research on all the pattern of three million galaxies for the primary time, and spotted the sturdy certain correlation.”As to why this may well be? Neatly, there are some chances. One has to do with the type of “topic” advised to get stripped off galaxies in dense spaces of the universe — standard topic made up of same old protons, neutrons and electrons. This raises the query: What about darkish topic? Possibly this invisible substance has a task to play in holding galaxies higher. It would not be a really far-fetched concept, seeing as scientists have proven that almost all huge galaxies are living inside of a halo of darkish topic, together with our personal Milky Method.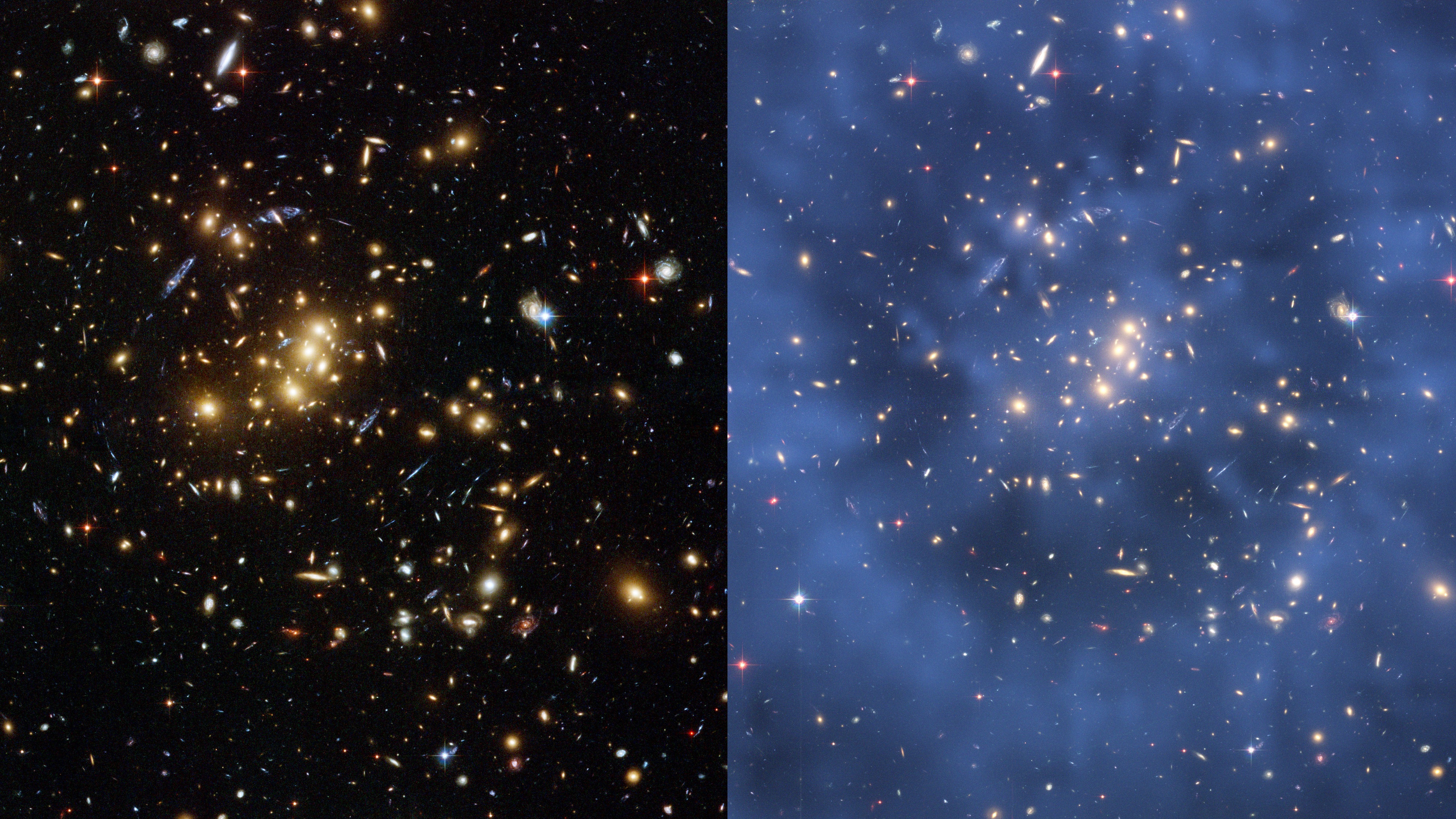 Two perspectives of a galaxy cluster are observed. At the proper, spaces the place darkish topic is predicted to exist are shaded in blue. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, M.J. Jee and H. Ford (Johns Hopkins College))”Our paintings presentations that whilst you common over many, many clusters, darkish topic turns into the main driver, reversing the fad observed in person clusters,” Ghosh stated.Alternatively, additionally it is imaginable that galaxies in denser environments occur to be higher once they first shape; nonetheless additional, there is a probability dense environments building up the likelihood and simplicity of galactic mergers.”A captivating follow-up paintings can be to test how this consequence adjustments whilst you alternate the radius of the circle inside of which you’re measuring densities,” Ghosh stated. “What when you use a radius of one million light-years as a substitute of 30? This may increasingly let us know how physics at other scales of the universe impacts galaxies another way.”Within the intervening time, the crew has its eyes set at the upcoming Rubin Observatory, slated to look its break of day of the cosmos in early 2025, and the large datasets it’s designed to provide.”My present fellowship is targeted at the Rubin Observatory, Ghosh stated, “which is able to follow 20 billion galaxies over its lifetime.”And, even though Rubin someway manages to seek out some further puzzle items underneath the sofa fairly than put a couple of at the desk in combination, there may be nonetheless a concrete luck to Ghosh’s find out about. It is proof that machines can also be relied on with questions concerning the universe we introduced them into.The find out about used to be revealed on Aug. 14 in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Two perspectives of a galaxy cluster are observed. At the proper, spaces the place darkish topic is predicted to exist are shaded in blue. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, M.J. Jee and H. Ford (Johns Hopkins College))”Our paintings presentations that whilst you common over many, many clusters, darkish topic turns into the main driver, reversing the fad observed in person clusters,” Ghosh stated.Alternatively, additionally it is imaginable that galaxies in denser environments occur to be higher once they first shape; nonetheless additional, there is a probability dense environments building up the likelihood and simplicity of galactic mergers.”A captivating follow-up paintings can be to test how this consequence adjustments whilst you alternate the radius of the circle inside of which you’re measuring densities,” Ghosh stated. “What when you use a radius of one million light-years as a substitute of 30? This may increasingly let us know how physics at other scales of the universe impacts galaxies another way.”Within the intervening time, the crew has its eyes set at the upcoming Rubin Observatory, slated to look its break of day of the cosmos in early 2025, and the large datasets it’s designed to provide.”My present fellowship is targeted at the Rubin Observatory, Ghosh stated, “which is able to follow 20 billion galaxies over its lifetime.”And, even though Rubin someway manages to seek out some further puzzle items underneath the sofa fairly than put a couple of at the desk in combination, there may be nonetheless a concrete luck to Ghosh’s find out about. It is proof that machines can also be relied on with questions concerning the universe we introduced them into.The find out about used to be revealed on Aug. 14 in The Astrophysical Magazine.
The most important galaxies are living in our universe’s supercluster ‘towns’