A style of SpaceX’s Starship Tremendous Heavy rocket has handed NASA wind tunnel trying out, marking every other milestone in its construction as a part of plans to release long run Artemis missions to the moon.NASA examined a 1.2% scale style of the Tremendous Heavy rocket within the transonic Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel on the house company’s Ames Analysis Middle in California’s Silicon Valley. The style used to be subjected to high-speed compelled air, simulating the air resistance and go with the flow the booster will revel in throughout other levels of flight, in keeping with a commentary from NASA. Power-measuring sensors had been affixed to the rocket style, permitting researchers to look at its steadiness and aerodynamic efficiency because it persevered wind speeds starting from Mach .7, or about 537 miles according to hour, to Mach 1.4, or about 1,074 miles according to hour. For reference, Mach 1 is the rate that sound waves go back and forth, or 761 miles according to hour, at sea degree.Tremendous Heavy is supplied with 4 grid fins, which lend a hand stabilize and keep an eye on the automobile throughout re-entry. A number of grid fin configurations had been examined below various aerodynamic prerequisites inside the wind tunnel simulations, which happened over a two week time frame previous within the 12 months. Similar: SpaceX’s Starship would possibly not be approved to fly once more till overdue November, FAA says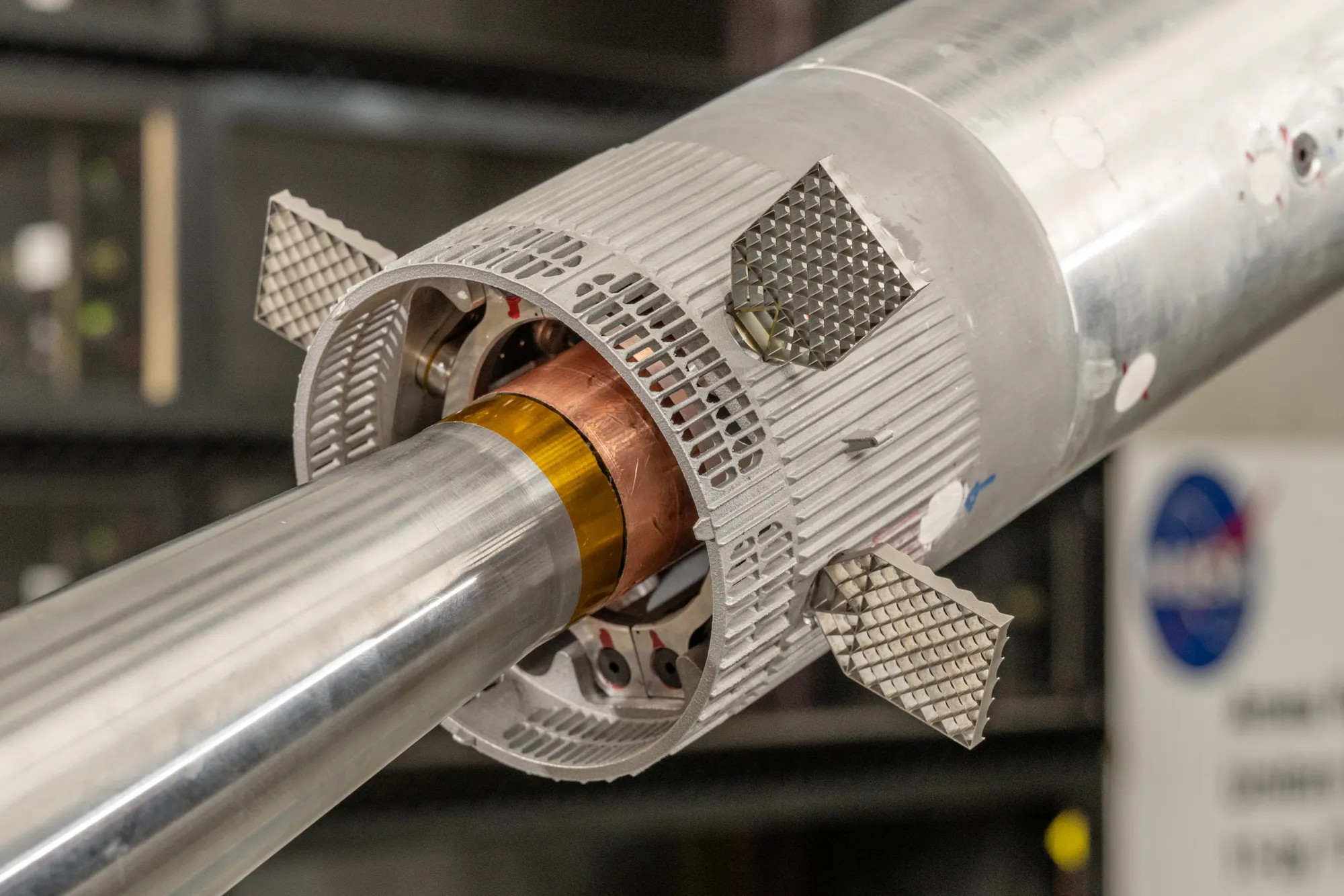 4 grid fins at the Tremendous Heavy rocket lend a hand stabilize and keep an eye on the rocket because it re-enters Earth’s setting after launching Starship to a lunar trajectory. Engineers examined the results of quite a lot of aerodynamic prerequisites on a number of grid fin configurations throughout wind tunnel trying out. (Symbol credit score: NASA)The information accrued throughout the checks will likely be used to replace flight tool for check flights of Tremendous Heavy and Starship and to refine the outside design of long run variations of the booster, NASA officers mentioned. Tremendous Heavy is the primary degree, or booster, of theStarship release machine and is designed by way of SpaceX to be totally reusable, which means that when it separates from Starship in house, it’s anticipated to go back to Earth intact. Finding out the style’s steadiness within the wind tunnel checks is vital to the spacecraft’s a success re-entry to Earth’s setting, in keeping with the commentary. Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!
4 grid fins at the Tremendous Heavy rocket lend a hand stabilize and keep an eye on the rocket because it re-enters Earth’s setting after launching Starship to a lunar trajectory. Engineers examined the results of quite a lot of aerodynamic prerequisites on a number of grid fin configurations throughout wind tunnel trying out. (Symbol credit score: NASA)The information accrued throughout the checks will likely be used to replace flight tool for check flights of Tremendous Heavy and Starship and to refine the outside design of long run variations of the booster, NASA officers mentioned. Tremendous Heavy is the primary degree, or booster, of theStarship release machine and is designed by way of SpaceX to be totally reusable, which means that when it separates from Starship in house, it’s anticipated to go back to Earth intact. Finding out the style’s steadiness within the wind tunnel checks is vital to the spacecraft’s a success re-entry to Earth’s setting, in keeping with the commentary. Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!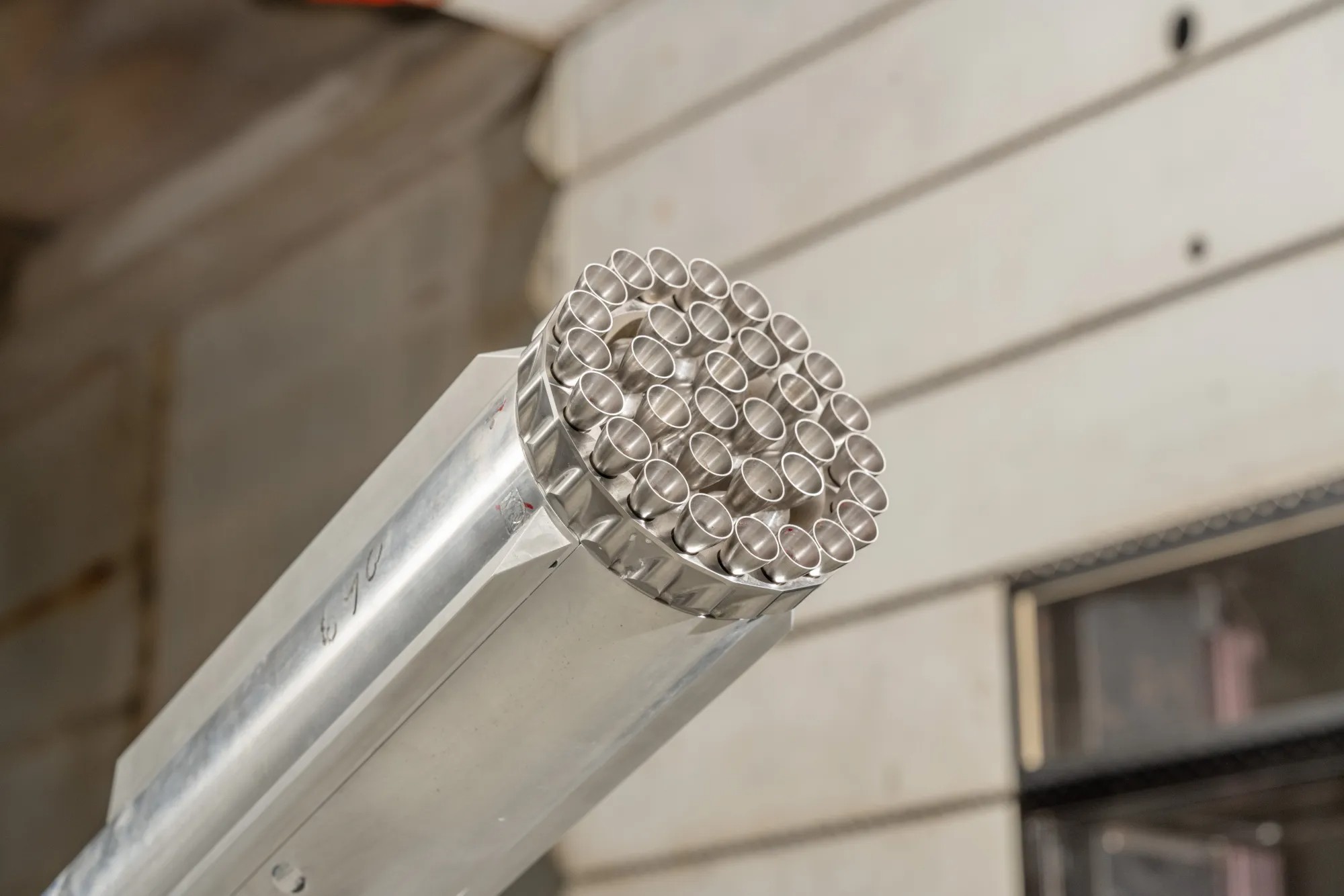 Wind tunnel trying out at NASA’s Ames Analysis Middle helped engineers higher perceive the aerodynamic forces the SpaceX Tremendous Heavy rocket, with its 33 Raptor engines, reviews throughout quite a lot of levels of flight. On account of the trying out, engineers up to date flight keep an eye on algorithms and changed the outside design of the rocket. (Symbol credit score: NASA)For Artemis missions, which purpose to land people at the moon for the primary time because the Apollo program, Starship will likely be used to hold astronauts to and from the Lunar Gateway and the moon’s floor. “With Artemis, NASA will discover extra of the Moon than ever prior to, learn to are living and paintings clear of house, and get ready for long run human exploration of the Crimson Planet,” NASA officers mentioned within the commentary.
Wind tunnel trying out at NASA’s Ames Analysis Middle helped engineers higher perceive the aerodynamic forces the SpaceX Tremendous Heavy rocket, with its 33 Raptor engines, reviews throughout quite a lot of levels of flight. On account of the trying out, engineers up to date flight keep an eye on algorithms and changed the outside design of the rocket. (Symbol credit score: NASA)For Artemis missions, which purpose to land people at the moon for the primary time because the Apollo program, Starship will likely be used to hold astronauts to and from the Lunar Gateway and the moon’s floor. “With Artemis, NASA will discover extra of the Moon than ever prior to, learn to are living and paintings clear of house, and get ready for long run human exploration of the Crimson Planet,” NASA officers mentioned within the commentary.
SpaceX Tremendous Heavy rocket will get supersonic wind tunnel check for NASA’s Artemis moon missions (pictures)