A passing megastar is also chargeable for greater than three-fourths of the moons in our sun device because the stellar traveler flung huge rocky our bodies into our cosmic group, a brand new find out about suggests.This novel fashion demanding situations present notions of ways the sun device got here to appear how it does as of late.The sun device’s massive planets are well-known for his or her many moons. Saturn lately leads, with 146 moons ultimately rely, with Jupiter an in depth 2d at 95. A large number of those moons resemble Earth’s moon in some ways. For instance, they orbit their mother or father planets in the similar route as that of the planets’ rotation. Moreover, such moons, referred to as common moons, observe just about round paths that percentage a aircraft with the planets’ equators.However some satellites are a lot stranger. Take Phoebe, one among Saturn’s more odd moons. It has an oval-shaped, tilted orbit on which it strikes in the wrong way as Saturn rotates — a motion described as retrograde. In reality, satellites like Phoebe, often known as abnormal moons, outnumber common ones within the sun device 3 to 1.Scientists have up to now attributed the life of abnormal moons to the motion of Neptune around the sun device, in line with William Bottke, a planetary scientist on the Southwest Analysis Institute in Boulder, Colorado. Maximum astronomers suppose a crucial step within the sun device’s evolution was once Neptune’s migration outward during the precursor to the Kuiper Belt. Nowadays, the belt extends between 30 and 50 instances the space between Earth and the solar, however within the early sun device, the proto-Kuiper Belt lay a lot nearer to the solar.Comparable: Misplaced pictures recommend Mars’ mysterious moon Phobos is also a trapped comet in disguiseThis destabilized the rocky our bodies within the Kuiper Belt, sending maximum of them close to the enormous planets. From there, items with sure orbits may well be “captured” via the enormous planets, Bottke informed Reside Science in an electronic mail.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered instantly in your inbox.On the other hand, this situation cannot give an explanation for sure sides of the abnormal moons. For example, few have an overly crimson colour. However the brand new find out about, revealed Sept. 4 in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters, explains those oddities via offering an alternate principle: {that a} passing megastar “kicked” the moons in position.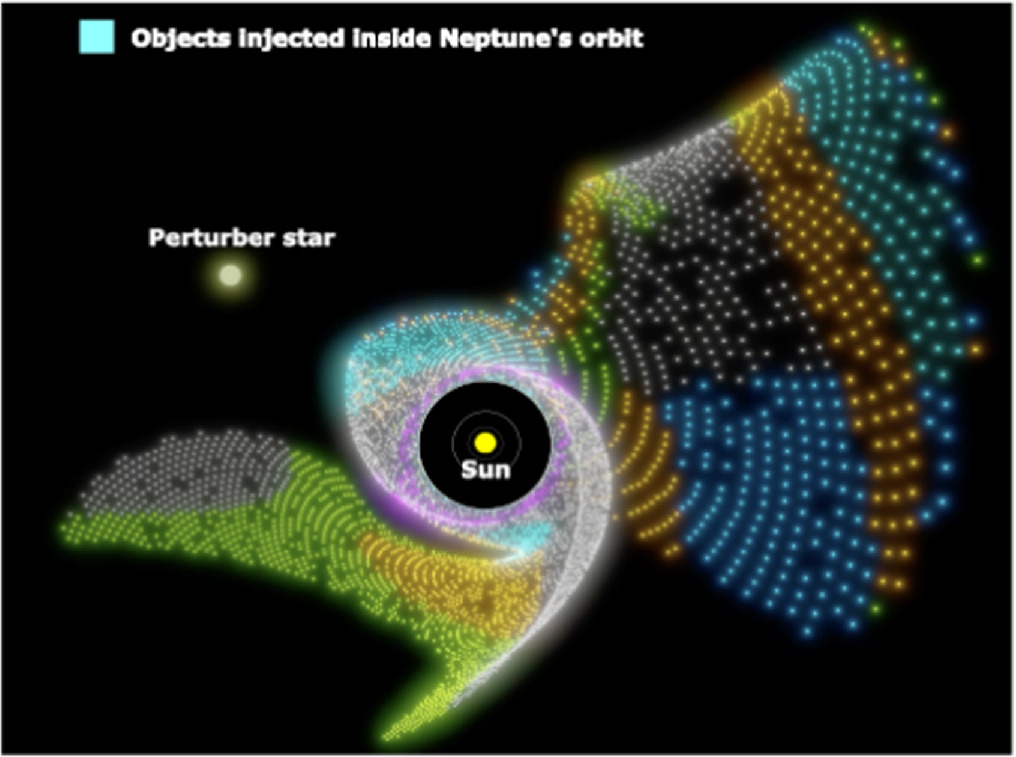 The megastar flung huge rocky our bodies (represented within the symbol as turquoise dots) into the sun device because it swung via. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Susanne Pfalzner, the find out about’s first creator and a professor of astronomy at Jülich Supercomputing Heart in Germany, informed Reside Science via electronic mail she was once impressed to discover this risk after a unique find out about confirmed {that a} megastar flying previous the sun device tossed Kuiper Belt items (KBOs) with reference to the planets.So Pfalzner and her colleagues simulated the motion of a celeb previous the adolescent sun device. Kind of four-fifths the present-day mass of the solar, this stellar customer was once modeled to brush via at roughly 110 Earth-sun distances. The researchers calculated how the gravity of each the solar and the visiting megastar altered the trajectories of hundreds of KBOs. Then, the staff studied how the KBOs’ orbits developed over a thousand million years.The researchers’ simulations confirmed that if the visiting megastar swooped previous at a 70-degree perspective to the ecliptic aircraft ― the aircraft through which Earth orbits the solar ― it catapulted more or less 7% of KBOs alongside stretched, oval-shaped orbits that introduced them close to the enormous planets. Lots of them — specifically the ones whose new paths introduced them close to Jupiter or Saturn — had retrograde orbits, and few have been very crimson― each tendencies that abnormal moons display as of late.The researchers discovered that over a thousand million years, the passing megastar kicked just about 85% of the flung KBOs from the sun device. Those who were not ejected shaped the abnormal moons, the researchers defined.The result of those simulations “have been an entire wonder,” Pfalzner mentioned. One benefit of this fashion is that it is more practical than older ones, since it will probably give an explanation for each how abnormal moons shaped and the way KBOs behave. But even so, stellar passages are somewhat not unusual — about 140 million stars within the Milky Means most probably skilled such flybys.On the other hand, no longer everybody consents with the find out about’s conclusions. Bottke, who wasn’t a part of the find out about, famous that “such a shockingly shut passage, even from the technology when our sun device was once in a stellar cluster, turns out impossible from a likelihood viewpoint A stellar stumble upon shut sufficient to seize abnormal satellites across the massive planets would additionally probably perturb the orbits of the enormous planets—sufficient that we’d see those results of their orbits as of late.”
The megastar flung huge rocky our bodies (represented within the symbol as turquoise dots) into the sun device because it swung via. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Susanne Pfalzner, the find out about’s first creator and a professor of astronomy at Jülich Supercomputing Heart in Germany, informed Reside Science via electronic mail she was once impressed to discover this risk after a unique find out about confirmed {that a} megastar flying previous the sun device tossed Kuiper Belt items (KBOs) with reference to the planets.So Pfalzner and her colleagues simulated the motion of a celeb previous the adolescent sun device. Kind of four-fifths the present-day mass of the solar, this stellar customer was once modeled to brush via at roughly 110 Earth-sun distances. The researchers calculated how the gravity of each the solar and the visiting megastar altered the trajectories of hundreds of KBOs. Then, the staff studied how the KBOs’ orbits developed over a thousand million years.The researchers’ simulations confirmed that if the visiting megastar swooped previous at a 70-degree perspective to the ecliptic aircraft ― the aircraft through which Earth orbits the solar ― it catapulted more or less 7% of KBOs alongside stretched, oval-shaped orbits that introduced them close to the enormous planets. Lots of them — specifically the ones whose new paths introduced them close to Jupiter or Saturn — had retrograde orbits, and few have been very crimson― each tendencies that abnormal moons display as of late.The researchers discovered that over a thousand million years, the passing megastar kicked just about 85% of the flung KBOs from the sun device. Those who were not ejected shaped the abnormal moons, the researchers defined.The result of those simulations “have been an entire wonder,” Pfalzner mentioned. One benefit of this fashion is that it is more practical than older ones, since it will probably give an explanation for each how abnormal moons shaped and the way KBOs behave. But even so, stellar passages are somewhat not unusual — about 140 million stars within the Milky Means most probably skilled such flybys.On the other hand, no longer everybody consents with the find out about’s conclusions. Bottke, who wasn’t a part of the find out about, famous that “such a shockingly shut passage, even from the technology when our sun device was once in a stellar cluster, turns out impossible from a likelihood viewpoint A stellar stumble upon shut sufficient to seize abnormal satellites across the massive planets would additionally probably perturb the orbits of the enormous planets—sufficient that we’d see those results of their orbits as of late.”













