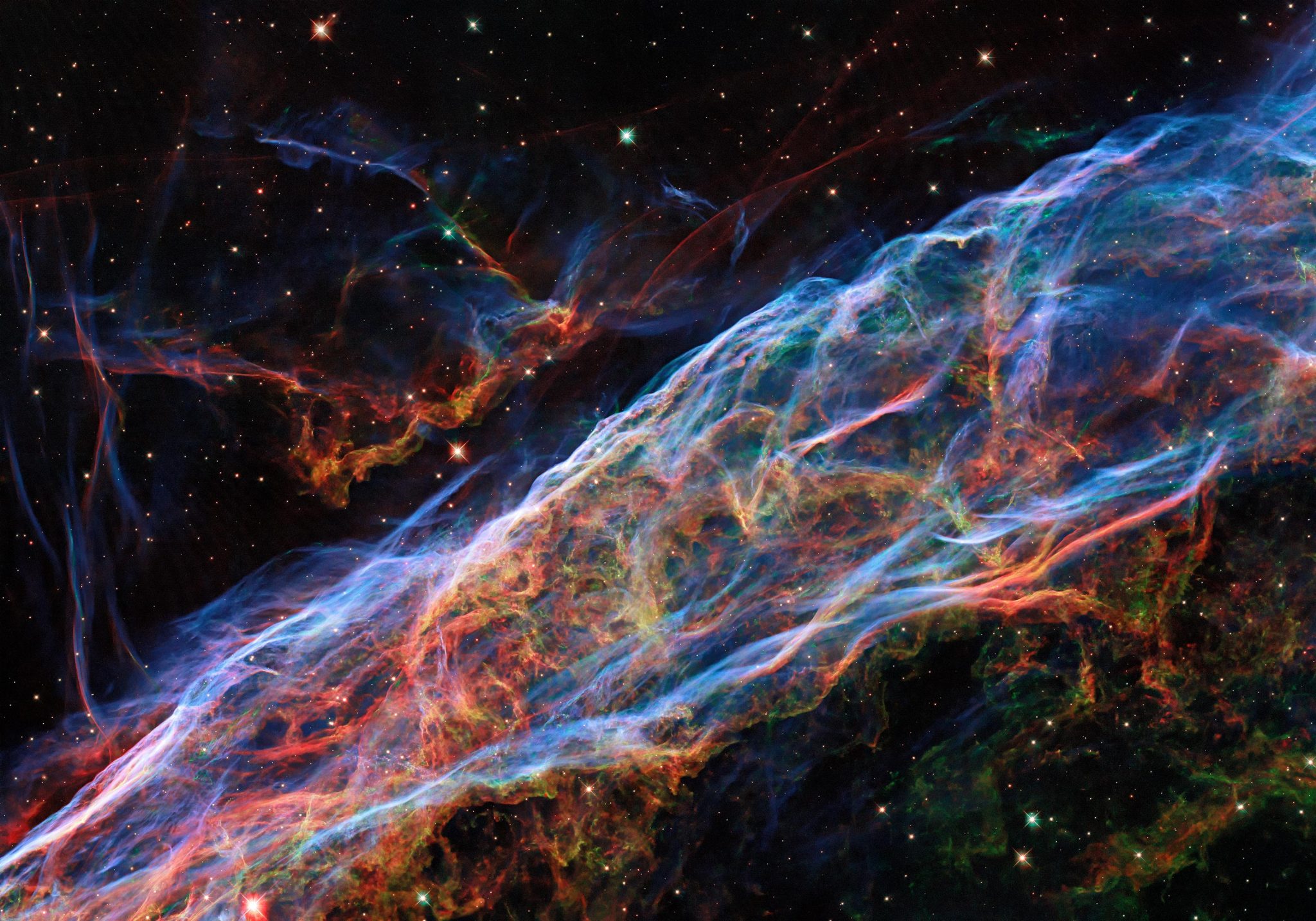
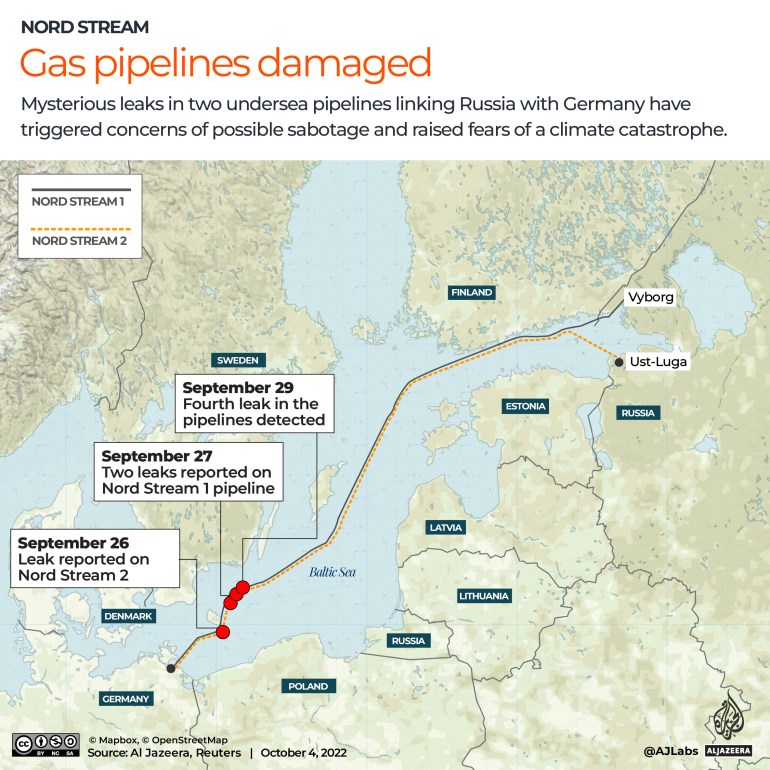
This symbol taken by way of NASA’s Hubble House Telescope displays a part of the Veil Nebula or Cygnus Loop. To create this colourful symbol, observations have been taken by way of Hubble’s Huge Box Digital camera 3 tool the use of 5 other filters. New post-processing strategies have additional enhanced main points of emissions from doubly ionized oxygen (proven right here in sunglasses of blue), ionized hydrogen, and ionized nitrogen (proven right here in sunglasses of crimson). Credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Z. LevayINFUSE, a brand new sounding rocket project, is launching to check the Cygnus Loop supernova remnants. Using a singular tool that mixes imaging and spectroscopy, it seeks to discover the mysteries of stellar explosions and their function in developing new celestial our bodies.A brand new sounding rocket project is headed to area to know how explosive stellar deaths lay the groundwork for brand spanking new megastar programs. The Integral Box Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Experiment, or INFUSE, sounding rocket project, will release from the White Sands Missile Vary in New Mexico on October 29, 2023, at 9:35 p.m. MDT.The Cygnus Loop: A Celestial PhenomenonFor a couple of months each and every 12 months, the constellation Cygnus (Latin for “swan”) swoops throughout the northern hemisphere’s evening sky. Simply above its wing is a favourite goal for yard astronomers {and professional} scientists alike: the Cygnus Loop, often referred to as the Veil Nebula.
This symbol taken by way of NASA’s Hubble House Telescope displays a part of the Veil Nebula or Cygnus Loop. To create this colourful symbol, observations have been taken by way of Hubble’s Huge Box Digital camera 3 tool the use of 5 other filters. New post-processing strategies have additional enhanced main points of emissions from doubly ionized oxygen (proven right here in sunglasses of blue), ionized hydrogen, and ionized nitrogen (proven right here in sunglasses of crimson). Credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Z. LevayINFUSE, a brand new sounding rocket project, is launching to check the Cygnus Loop supernova remnants. Using a singular tool that mixes imaging and spectroscopy, it seeks to discover the mysteries of stellar explosions and their function in developing new celestial our bodies.A brand new sounding rocket project is headed to area to know how explosive stellar deaths lay the groundwork for brand spanking new megastar programs. The Integral Box Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Experiment, or INFUSE, sounding rocket project, will release from the White Sands Missile Vary in New Mexico on October 29, 2023, at 9:35 p.m. MDT.The Cygnus Loop: A Celestial PhenomenonFor a couple of months each and every 12 months, the constellation Cygnus (Latin for “swan”) swoops throughout the northern hemisphere’s evening sky. Simply above its wing is a favourite goal for yard astronomers {and professional} scientists alike: the Cygnus Loop, often referred to as the Veil Nebula. This symbol displays an indication of the constellation Cygnus, Latin for “swan,” within the evening sky. The Cygnus Loop supernova remnant, often referred to as the Veil Nebula, is situated close to one of the vital swan’s wings, defined right here in an oblong field.
This symbol displays an indication of the constellation Cygnus, Latin for “swan,” within the evening sky. The Cygnus Loop supernova remnant, often referred to as the Veil Nebula, is situated close to one of the vital swan’s wings, defined right here in an oblong field.
Credit score: NASAThe Cygnus Loop is the remnant of a celeb that used to be as soon as 20 occasions the dimensions of our Solar. Some 20,000 years in the past, that megastar collapsed below its personal gravity and erupted right into a supernova. Even from 2,600 light-years away, astronomers estimate the flash of sunshine would had been vivid sufficient to peer from Earth throughout the day.Supernovae: Galactic ArchitectsSupernovae are a part of an excellent existence cycle. They spray heavy metals solid in a celeb’s core into the clouds of surrounding mud and gasoline. They’re the supply of all chemical components in our universe heavier than iron, together with those who make up our personal our bodies. From the churned-up clouds and megastar stuff left of their wake, gases and dirt from supernovae progressively clump in combination to shape planets, stars, and new megastar programs.“Supernovae like the person who created the Cygnus Loop have an enormous affect on how galaxies shape,” mentioned Brian Fleming, a analysis professor on the College of Colorado Boulder and main investigator for the INFUSE project.Figuring out Supernova DynamicsThe Cygnus Loop supplies an extraordinary take a look at a supernova blast nonetheless in development. Already over 120 light-years throughout, the huge cloud continues to be increasing as of late at roughly 930,000 miles in keeping with hour (about 1.5 million kilometers in keeping with hour).What our telescopes seize from the Cygnus Loop isn’t the supernova blast itself. As an alternative, we see the mud and gasoline superheated by way of the surprise entrance, which glows because it cools backpedal.“INFUSE will apply how the supernova dumps power into the Milky Manner by way of catching mild given off simply because the blast wave crashes into wallet of chilly gasoline floating across the galaxy,” Fleming mentioned.Cutting edge Instrumentation: INFUSETo see that surprise entrance at its scorching edge, Fleming and his crew have advanced a telescope that measures far-ultraviolet mild – a type of mild too lively for our eyes to peer. This mild finds gasoline at temperatures between 90,000 and 540,000 levels Fahrenheit (about 50,000 to 300,000 levels Celsius) this is nonetheless scorching after affect.INFUSE is an integral box spectrograph, the primary tool of its form to fly to area. The tool combines the strengths of 2 techniques of finding out mild: imaging and spectroscopy. Your conventional telescopes have cameras that excel at developing photographs – appearing the place mild is coming from, faithfully revealing its spatial association. However telescopes don’t separate mild into other wavelengths or “colours” – as an alternative, the entire other wavelengths overlap one any other within the ensuing symbol.Spectroscopy, however, takes a unmarried beam of sunshine and separates it into its part wavelengths or spectrum, a lot as a prism separates mild right into a rainbow. This process finds a wide variety of details about what the sunshine supply is fabricated from, its temperature, and the way it’s transferring. However spectroscopy can best take a look at a unmarried sliver of sunshine at a time. It’s like having a look on the evening sky thru a slender keyhole. PhD pupil Emily Witt installs the sophisticated symbol slicer – the core optical generation for INFUSE – onto its mount in a CU-LASP blank room forward of integration into the payload. Credit score: CU Boulder LASP/Brian FlemingThe INFUSE tool captures a picture after which “slices” it up, lining up the slices into one large “keyhole.” The spectrometer can then unfold each and every of the slices into its spectrum. This information may also be reassembled right into a three-d symbol that scientists name a “information dice” – like a stack of pictures the place each and every layer finds a particular wavelength of sunshine.Implications and Long term ProspectsUsing the information from INFUSE, Fleming and his crew won’t best determine explicit components and their temperatures, however they’ll additionally see the place the ones other components lie alongside the surprise entrance.“It’s an excessively thrilling venture to be part of,” mentioned lead graduate pupil Emily Witt, additionally at CU Boulder, who led lots of the meeting and checking out of INFUSE and can lead the information research. “With those first-of-their-kind measurements, we will be able to higher know how those components from the supernova combine with the surroundings round them. It’s a large step towards figuring out how subject matter from supernovas turns into a part of planets like Earth or even other folks like us.”To get to area, the INFUSE payload will fly aboard a sounding rocket. Those nimble, crewless rockets release into area for a couple of mins of information assortment sooner than falling again to the bottom. The INFUSE payload will fly aboard a two-stage Black Brant 9 sounding rocket, aiming for a top altitude of about 150 miles (240 kilometers), the place it’ll make its observations, sooner than parachuting again to the bottom to be recovered. The crew hopes to improve the tool and release once more. In truth, portions of the INFUSE rocket are themselves repurposed from the DEUCE project, which introduced from Australia in 2022.NASA’s Sounding Rocket Program is performed on the company’s Wallops Flight Facility at Wallops Island, Virginia, which is controlled by way of NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. NASA’s Heliophysics Department manages the sounding rocket program for the company. The improvement of the INFUSE payload used to be supported by way of NASA’s Astrophysics Department.
PhD pupil Emily Witt installs the sophisticated symbol slicer – the core optical generation for INFUSE – onto its mount in a CU-LASP blank room forward of integration into the payload. Credit score: CU Boulder LASP/Brian FlemingThe INFUSE tool captures a picture after which “slices” it up, lining up the slices into one large “keyhole.” The spectrometer can then unfold each and every of the slices into its spectrum. This information may also be reassembled right into a three-d symbol that scientists name a “information dice” – like a stack of pictures the place each and every layer finds a particular wavelength of sunshine.Implications and Long term ProspectsUsing the information from INFUSE, Fleming and his crew won’t best determine explicit components and their temperatures, however they’ll additionally see the place the ones other components lie alongside the surprise entrance.“It’s an excessively thrilling venture to be part of,” mentioned lead graduate pupil Emily Witt, additionally at CU Boulder, who led lots of the meeting and checking out of INFUSE and can lead the information research. “With those first-of-their-kind measurements, we will be able to higher know how those components from the supernova combine with the surroundings round them. It’s a large step towards figuring out how subject matter from supernovas turns into a part of planets like Earth or even other folks like us.”To get to area, the INFUSE payload will fly aboard a sounding rocket. Those nimble, crewless rockets release into area for a couple of mins of information assortment sooner than falling again to the bottom. The INFUSE payload will fly aboard a two-stage Black Brant 9 sounding rocket, aiming for a top altitude of about 150 miles (240 kilometers), the place it’ll make its observations, sooner than parachuting again to the bottom to be recovered. The crew hopes to improve the tool and release once more. In truth, portions of the INFUSE rocket are themselves repurposed from the DEUCE project, which introduced from Australia in 2022.NASA’s Sounding Rocket Program is performed on the company’s Wallops Flight Facility at Wallops Island, Virginia, which is controlled by way of NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. NASA’s Heliophysics Department manages the sounding rocket program for the company. The improvement of the INFUSE payload used to be supported by way of NASA’s Astrophysics Department.
Rocketing to the Stars: NASA’s INFUSE Probes Scorching Supernova Secrets and techniques