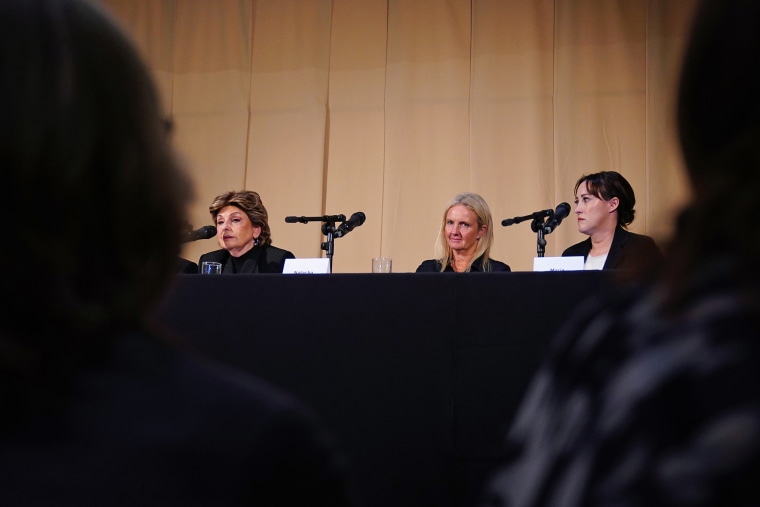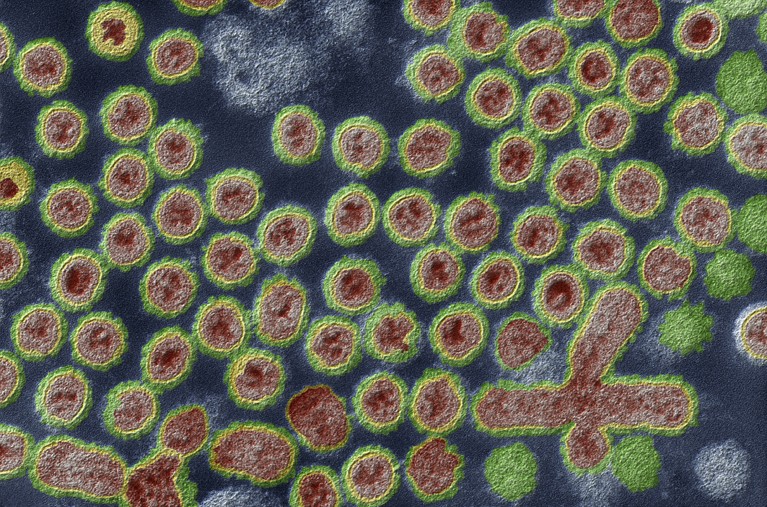
Those chook flu virus debris (artificially colored) had been imaged by means of an electron microscope.Credit score: Eye of Science/Science Picture Library
All eyes are on Missouri.Researchers are anxiously watching for knowledge from the midwestern state a couple of mysterious chook flu an infection in an individual who had no identified touch with possible animal carriers of the illness. The knowledge may just divulge whether or not the continuing US chook flu outbreak in dairy farm animals has reached a dreaded turning level: the emergence of a plague able to spreading from human to human.
 Large quantities of bird-flu virus present in uncooked milk of inflamed cows
Large quantities of bird-flu virus present in uncooked milk of inflamed cows
To this point, knowledge from the mysterious an infection are few and a long way between: small snippets of the H5N1 virus’s genome series and an incomplete an infection timeline. Ratcheting up considerations is the truth that no Missouri dairy farms have reported a chook flu outbreak; this could be as a result of there in reality aren’t any infections, or since the state does now not require farmers to check their cows for the virus.“The worry is that the virus is spreading throughout the neighborhood at low ranges, and that is the primary time that we’re detecting it,” says Scott Hensley, a viral immunologist on the College of Pennsylvania Perelman College of Drugs in Philadelphia. “There’s no knowledge to indicate that to be the case, however that’s the concern.”A thriller caseOn 6 September, Missouri public-health officers and the USA Facilities for Illness Keep watch over and Prevention (CDC) introduced that an grownup within the state had evolved signs together with chest ache, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, and was once hospitalized owing to different clinical stipulations. That particular person didn’t develop into significantly in poor health and has recovered from the an infection. Exams printed it to be H5N1 influenza, frequently known as chook flu.Since March, when the H5N1 virus was once first detected in US dairy farm animals, there were greater than a dozen circumstances of human an infection that had been traced again to touch with inflamed animals, together with cows and birds. The Missouri case stands proud as a result of investigators discovered no such hyperlink and no tie to unprocessed meals merchandise, corresponding to uncooked milk, from doubtlessly inflamed cattle.
 If chook flu sparks a human pandemic, your previous immunity may just assist
If chook flu sparks a human pandemic, your previous immunity may just assist
This raised the chance that the virus may have developed not to handiest infect people, but in addition to unfold between other folks. If this is the case, this will increase the danger of it sweeping via human populations, doubtlessly triggering a deadly outbreak.However that’s now not the one chance, cautions Jürgen Richt, a veterinary virologist at Kansas State College in Ny. “It’s a thriller case,” he says. “So you need to throw your web a little bit wider. Possibly they wiped clean out a chook feeder within the family. Did they pass to a state truthful? What sort of meals did they eat?”Extra considerations had been raised concerning the Missouri case on 13 September, when the CDC introduced that two individuals who had shut touch with the hospitalized particular person had additionally develop into in poor health round the similar time. One in all them was once now not examined for flu; the opposite examined damaging.That take a look at result’s encouraging however now not definitive, says Hensley, since the pattern can have been accumulated when the person’s viral ranges had been too low for detection — once they began to get better, as an example. A key subsequent step might be to check all 3 other folks for antibodies towards the tension of H5N1 chook flu that has been infecting farm animals. Such antibodies, specifically within the two contacts, can be definitive proof of previous an infection.Genomic sleuthingWhile researchers look forward to the antibody effects, they’re combing via patchy genome-sequence knowledge from virus samples from the hospitalized particular person. This would yield any indicators that the virus may have tailored to human hosts. The hunt is a problem, alternatively: the samples contained very low ranges of viral RNA — so little that some researchers have shied clear of analysing the sequences altogether.
 Hen flu virus has been spreading amongst US cows for months, RNA unearths
Hen flu virus has been spreading amongst US cows for months, RNA unearths
“What I might need to see is upper high quality,” says Ryan Langlois, a viral immunologist on the College of Minnesota Clinical College in Minneapolis. “I’m very leery about deciphering the rest from partial sequences.”However for Hensley, one characteristic of the series fragments instantly leapt out: a unmarried alternate within the string of amino acids that shape a flu protein referred to as hemagglutinin (the ‘H’ in H5N1). That protein sits at the floor of influenza viruses, the place it is helping the viruses bind to and infect host cells. Additionally it is a goal of flu vaccines.The alternate that Hensley discovered creates a web site to which a big sugar molecule can bind. That sugar, he says, may just then act as an umbrella, shielding the swath of hemagglutinin underneath it. This can be a alternate that his laboratory has studied in different flu lines, and it might impact how the virus binds to host cells — in addition to whether or not vaccines being evolved towards the H5N1 virus present in farm animals can acknowledge and carry out neatly towards the virus detected in Missouri.Surveillance gapsEven if the sequences had been to be had, researchers know little about which genetic adjustments may permit chook flu viruses to higher infect people or to develop into airborne, says virologist Yoshihiro Kawaoka on the College of Wisconsin–Madison. Earlier studies1,2 had advised that adjustments to a gene encoding a protein liable for copying the viral genome might be an important for permitting the virus to copy in mammalian cells. However researchers had been not able to series that gene from the isolate from Missouri.In the meantime, the CDC has issued contracts to 5 firms in america to supply trying out services and products for H5N1 and different rising pathogens. Checking out of farm animals additionally must be stepped forward in order that public-health officers will know which areas of the rustic to surveil for infections in people, says Seema Lakdawala, a virologist at Emory College in Atlanta, Georgia. In america, maximum trying out of farm animals is regulated on the state stage, however just a handful of states have required regimen trying out on some dairy farms.Public-health staff nonetheless don’t have a just right care for on what number of US herds have cows inflamed with H5N1, or whether or not farm animals have immunity after contracting chook flu or can develop into reinfected, she says.Whilst researchers wait for more info, Hensley cautions towards panic. “This would nonetheless be a one-off case and now not the signal of one thing larger,” he says.










:quality(70)/d1hfln2sfez66z.cloudfront.net/08-05-2022/t_5a73b571249f4ecaa3796d454ba10094_name_Legionnaires_disease_What_you_need_to_kn_62ecff7929f670627413c241_1_Aug_05_2022_12_12_34_poster.jpg)

