![]() The Mars Interest rover landed within the Gale crater on Mars on August sixth, 2012. Within the 12 years since, the rover has noticed a large number of superb issues on Mars and brought 1000’s of pictures, many in contrast to the rest ever noticed sooner than. One such distinctive photograph is the first-ever photograph of Earth and the Martian moon Phobos as noticed from Mars. PetaPixel chatted with Mark Lemmon, an established Mars Interest workforce member and astronomer on the Area Science Institute, concerning the new symbol, finding out a lot more about how the workforce captured the brand new pictures and what the groundbreaking photograph manner for humanity’s exploration of house at massive. The pictures had been captured the usage of Interest’s Mast Digital camera, often referred to as Mastcam. This colour digital camera usually captures panoramic pictures and movies of the Pink Planet’s floor and atmospheric options. This is a 1.9-megapixel digital camera, that means it captures 1,600 x 1,200-pixel pictures. Then again, the workforce often combines a couple of frames into a bigger composite or landscape, which is able to lend a hand amplify the efficient answer of the Mastcam. For instance, in 2022, PetaPixel wrote about Mastcam taking pictures 133 pictures to create an expansive landscape that confirmed proof of previous local weather exchange on Mars.
The Mars Interest rover landed within the Gale crater on Mars on August sixth, 2012. Within the 12 years since, the rover has noticed a large number of superb issues on Mars and brought 1000’s of pictures, many in contrast to the rest ever noticed sooner than. One such distinctive photograph is the first-ever photograph of Earth and the Martian moon Phobos as noticed from Mars. PetaPixel chatted with Mark Lemmon, an established Mars Interest workforce member and astronomer on the Area Science Institute, concerning the new symbol, finding out a lot more about how the workforce captured the brand new pictures and what the groundbreaking photograph manner for humanity’s exploration of house at massive. The pictures had been captured the usage of Interest’s Mast Digital camera, often referred to as Mastcam. This colour digital camera usually captures panoramic pictures and movies of the Pink Planet’s floor and atmospheric options. This is a 1.9-megapixel digital camera, that means it captures 1,600 x 1,200-pixel pictures. Then again, the workforce often combines a couple of frames into a bigger composite or landscape, which is able to lend a hand amplify the efficient answer of the Mastcam. For instance, in 2022, PetaPixel wrote about Mastcam taking pictures 133 pictures to create an expansive landscape that confirmed proof of previous local weather exchange on Mars. ![]() ‘NASA’s Interest Mars rover used its Mast Digital camera, or Mastcam, to seize this view of Earth surroundings whilst Phobos, one in every of Mars’ two moons, is emerging. It’s the 1st time a picture of the 2 celestial our bodies were captured in combination from the outside of Mars,’ NASA explains. Earth and Phobos are visual close to the highest of the body and are noticed clearer within the header photograph above and extra pictures beneath. | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS As Lemmon explains, Mastcam has two cameras, a 34mm one and a 100mm one. Whilst the 100mm digital camera can see extra far-off items, additionally it is extra at risk of movement blur. “Mastcam is at the rover essentially as a panorama digital camera to report the geology. It most commonly takes colour footage, but it surely has a filter out wheel for multispectral imaging to lend a hand assess composition and sun imaging,” Lemmon says.
‘NASA’s Interest Mars rover used its Mast Digital camera, or Mastcam, to seize this view of Earth surroundings whilst Phobos, one in every of Mars’ two moons, is emerging. It’s the 1st time a picture of the 2 celestial our bodies were captured in combination from the outside of Mars,’ NASA explains. Earth and Phobos are visual close to the highest of the body and are noticed clearer within the header photograph above and extra pictures beneath. | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS As Lemmon explains, Mastcam has two cameras, a 34mm one and a 100mm one. Whilst the 100mm digital camera can see extra far-off items, additionally it is extra at risk of movement blur. “Mastcam is at the rover essentially as a panorama digital camera to report the geology. It most commonly takes colour footage, but it surely has a filter out wheel for multispectral imaging to lend a hand assess composition and sun imaging,” Lemmon says.
“The closing is a part of my factor (atmospheric science is my day task, and I moonlight as an astronomer). Pictures of the Solar are taken to measure the mud content material of the ambience as one a part of the meteorology marketing campaign, and eclipse/transit movies lend a hand to measure the orbital evolution of the moons. After one of the crucial filter out wheels failed closing yr, each cameras were left within the transparent place for colour imaging.” ![]() A demonstration of the Mars Interest rover | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech For the brand new composite symbol appearing Phobos and Earth, Lemmon says the Mastcam collection began 93 seconds sooner than Phobos handed Earth. “The cameras had been aimed toward Earth and took 5 pictures at 0.75 seconds each and every, which used to be selected to keep watch over movement blur for the 100mm digital camera,” Lemmon explains. “The center symbol of that set used to be the anchor for the inset, with Earth and Phobos closest to one another.” The Mastcam has f/10 lenses, in order Lemmon notes, the optics aren’t what astrophotographers on Earth would historically use for low-light imaging. The composite used to be “a easy model of an astrophotography stacking method with a slight twist,” Lemmon says, as he and the workforce labored to stack pictures to get the cleanest symbol imaginable.
A demonstration of the Mars Interest rover | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech For the brand new composite symbol appearing Phobos and Earth, Lemmon says the Mastcam collection began 93 seconds sooner than Phobos handed Earth. “The cameras had been aimed toward Earth and took 5 pictures at 0.75 seconds each and every, which used to be selected to keep watch over movement blur for the 100mm digital camera,” Lemmon explains. “The center symbol of that set used to be the anchor for the inset, with Earth and Phobos closest to one another.” The Mastcam has f/10 lenses, in order Lemmon notes, the optics aren’t what astrophotographers on Earth would historically use for low-light imaging. The composite used to be “a easy model of an astrophotography stacking method with a slight twist,” Lemmon says, as he and the workforce labored to stack pictures to get the cleanest symbol imaginable. ![]() Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
The digital camera then began doing a two-by-five symbol mosaic, “snaking downward to the horizon,” of 10-second exposures. Lemmon apprehensive the sky can be too darkish for the reason that the photographs had been captured after sundown and following a mud typhoon, however the ultimate outcome labored smartly after corrections. ![]() Phobos (left) and Earth (proper) | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS The overall composite comprises pictures shot right through sunlight so as to add extra foreground element. Nonetheless, Lemmon explains that the ensuing symbol is “no longer a ways from how it will were perceived” via an individual status subsequent to Interest on Mars as Earth and Phobos handed via. “Our dynamic vary and talent to evolve to light-level diversifications transcend print and standard track features,” Lemmon says. “Earth would were the ‘first megastar’ noticed within the diminishing twilight and as brilliant because the brightest stars we see right here [on Earth]. I’m positive an individual viewing that scene would have additionally noticed our Moon, slightly under and to the left of Earth, even supposing it wasn’t brilliant sufficient with the quick exposures and the sky background.” Every other problem Lemmon and the remainder of the workforce face is slow harm to the Mastcam’s symbol sensors. Having been on Mars for a dozen years, the rover has been uncovered to consistent radiation ranges very similar to a U2 undercover agent airplane’s flight point. Whilst radiation moves at the detector are “most commonly risk free,” from time to time they reason harm.
Phobos (left) and Earth (proper) | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS The overall composite comprises pictures shot right through sunlight so as to add extra foreground element. Nonetheless, Lemmon explains that the ensuing symbol is “no longer a ways from how it will were perceived” via an individual status subsequent to Interest on Mars as Earth and Phobos handed via. “Our dynamic vary and talent to evolve to light-level diversifications transcend print and standard track features,” Lemmon says. “Earth would were the ‘first megastar’ noticed within the diminishing twilight and as brilliant because the brightest stars we see right here [on Earth]. I’m positive an individual viewing that scene would have additionally noticed our Moon, slightly under and to the left of Earth, even supposing it wasn’t brilliant sufficient with the quick exposures and the sky background.” Every other problem Lemmon and the remainder of the workforce face is slow harm to the Mastcam’s symbol sensors. Having been on Mars for a dozen years, the rover has been uncovered to consistent radiation ranges very similar to a U2 undercover agent airplane’s flight point. Whilst radiation moves at the detector are “most commonly risk free,” from time to time they reason harm. ![]() Lemmon despatched this uncropped, unfinished symbol alongside, which presentations the 5×2 composite minus the closing body, with a low gamma. “The 1x1x5 is already in, and I shrank the report for measurement. The rover’s tilt is plain. The projected house is 10.5 levels large,” Lemmon explains. “Occasional moves reason harm, typically noticed as an important elevation in a pixel’s darkish present — a sign noticed within the pixel even with out mild. It has modified dramatically because the digital camera used to be within the lab. It has even modified because the center of closing yr, the closing time lets use the sun filters to get a ‘darkish’ symbol within the daylight hours when the digital camera is heat. For standard exposures of a number of milliseconds, that is no downside. Even for many astronomical imaging, it’s not an issue because the moons and stars transfer and the recent pixels don’t. Lengthy-exposure panorama pictures had been a problem,” says Lemmon.
Lemmon despatched this uncropped, unfinished symbol alongside, which presentations the 5×2 composite minus the closing body, with a low gamma. “The 1x1x5 is already in, and I shrank the report for measurement. The rover’s tilt is plain. The projected house is 10.5 levels large,” Lemmon explains. “Occasional moves reason harm, typically noticed as an important elevation in a pixel’s darkish present — a sign noticed within the pixel even with out mild. It has modified dramatically because the digital camera used to be within the lab. It has even modified because the center of closing yr, the closing time lets use the sun filters to get a ‘darkish’ symbol within the daylight hours when the digital camera is heat. For standard exposures of a number of milliseconds, that is no downside. Even for many astronomical imaging, it’s not an issue because the moons and stars transfer and the recent pixels don’t. Lengthy-exposure panorama pictures had been a problem,” says Lemmon.
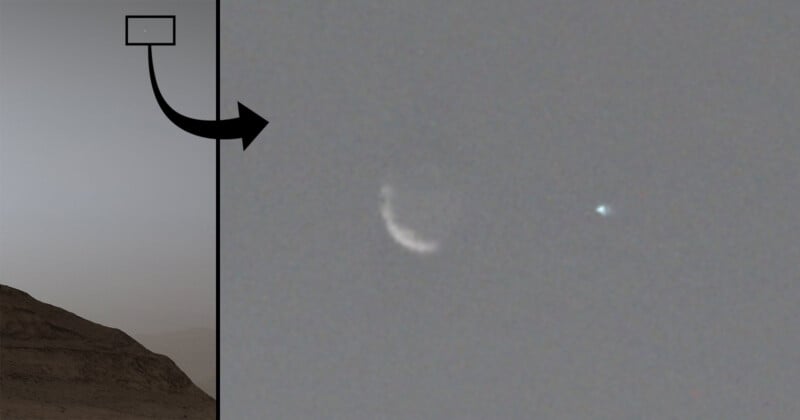
A Impressive Picture Months within the Making The speculation for the picture used to be “a number of months previous,” however the real making plans and execution phases got here in combination in no time. “On August twenty ninth, I seemed for an opportunity, having famous that used to be a time when Earth can be a night megastar. I unintentionally discovered Earth close to Deimos after I checked what the sky can be like for an arbitrary evening. Deimos is small, even if no longer a skinny crescent, so I seemed for Phobos and located that the nearest night-time method of the yr used to be September fifth,” Lemmon explains. He and a couple of digital camera uplink leads started making plans on August thirtieth after receiving the go-ahead from the Interest mission scientist. The Interest workforce deliberate the September fifth actions on September 2d, and the rover would, thankfully, be completing an job proper about when it will be had to seize the specified pictures. “The workforce used to be very supportive,” Lemmon provides. ![]() This symbol presentations a crop inset of Phobos (left) and Earth (the smaller speck). | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS About 90 mins sooner than the picture collection seize used to be deliberate to start out, Lemmon used to be strolling his canine sooner than first light in Texas and seemed as much as see Mars within the evening sky, realizing that Interest would quickly be taking pictures the deliberate pictures. As soon as symbol seize started, the pictures made it to Earth temporarily. Lemmon used to be operating on a draft of the composite later that day, even supposing finalizing the picture took some other week or so. Despite the fact that the September fifth plan labored out exceptionally smartly, Lemmon says there have been different choices.
This symbol presentations a crop inset of Phobos (left) and Earth (the smaller speck). | Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS About 90 mins sooner than the picture collection seize used to be deliberate to start out, Lemmon used to be strolling his canine sooner than first light in Texas and seemed as much as see Mars within the evening sky, realizing that Interest would quickly be taking pictures the deliberate pictures. As soon as symbol seize started, the pictures made it to Earth temporarily. Lemmon used to be operating on a draft of the composite later that day, even supposing finalizing the picture took some other week or so. Despite the fact that the September fifth plan labored out exceptionally smartly, Lemmon says there have been different choices.
“We had backup choices: 5 days later with even darker stipulations, and 5 days after beneath a lot brighter skies when the items will have been arduous to look. I believe we were given the most productive of the alternatives via a ways.” Impressed Through a Mythical Area Picture Lemmon used to be impressed via one of the vital iconic house pictures ever captured, 1990’s Faded Blue Dot. The picture captured on February 14th, 1990, via NASA’s Voyager 1, presentations Earth from 3.7 billion miles (six billion kilometers) away. ![]() A reprocessed model of Voyager 1’s ‘Faded Blue Dot’ symbol. | Credit score: The revised symbol used to be processed via JPL engineer and symbol processing fanatic Kevin M. Gill with enter from two of the picture’s authentic planners, Sweet Hansen and William Kosmann. That symbol presentations Earth so small within the body, however because the overdue Carl Sagan, who did as a lot to encourage love and sweetness of house as somebody in historical past, stated: “Glance once more at that dot. That’s right here. That’s house. That’s us.” “I used to be impressed via the Faded Blue Dot symbol when it got here out, and Carl Sagan’s ideas on it resonated. As we move out and discover, it’s herbal and crucial to appear again on occasion,” Lemmon says. Whilst he admits that pictures like this don’t “advance our figuring out of Mars’ historical past,” it is very important to proceed to contextualize the challenge. “Firstly, we’re exploring,” he says. “And, so far as I will be able to inform, few other people can have a look at a picture like this and — figuring out what the little blue speck is — no longer get some sense of the vastness of the universe and the smallness of our position in it. A picture of the Martian sky, with the ridge in entrance and Earth above, would were sufficient. Having Phobos in body with Earth, dwarfing it, provides some other layer.”
A reprocessed model of Voyager 1’s ‘Faded Blue Dot’ symbol. | Credit score: The revised symbol used to be processed via JPL engineer and symbol processing fanatic Kevin M. Gill with enter from two of the picture’s authentic planners, Sweet Hansen and William Kosmann. That symbol presentations Earth so small within the body, however because the overdue Carl Sagan, who did as a lot to encourage love and sweetness of house as somebody in historical past, stated: “Glance once more at that dot. That’s right here. That’s house. That’s us.” “I used to be impressed via the Faded Blue Dot symbol when it got here out, and Carl Sagan’s ideas on it resonated. As we move out and discover, it’s herbal and crucial to appear again on occasion,” Lemmon says. Whilst he admits that pictures like this don’t “advance our figuring out of Mars’ historical past,” it is very important to proceed to contextualize the challenge. “Firstly, we’re exploring,” he says. “And, so far as I will be able to inform, few other people can have a look at a picture like this and — figuring out what the little blue speck is — no longer get some sense of the vastness of the universe and the smallness of our position in it. A picture of the Martian sky, with the ridge in entrance and Earth above, would were sufficient. Having Phobos in body with Earth, dwarfing it, provides some other layer.”
As Lemmon explains, in the beginning look, the picture would possibly appear bland. Then again, when the viewer appears nearer, it turns into obvious that it’s an “alien” panorama with an alien moon and Earth. “I believe it turns into an overly particular symbol — its energy isn’t within the pixels however within the viewer’s talent to consider that speck is us.” Symbol credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
How the Mars Interest Rover Captured a Distinctive Portrait of Earth from 140 Million Miles Away