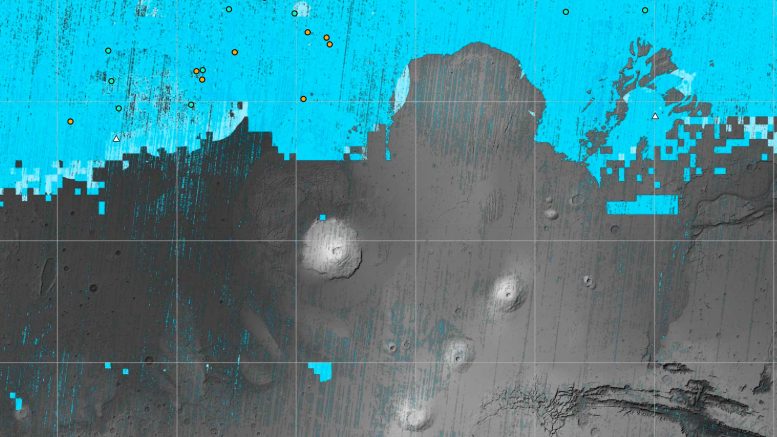
The blue spaces in this map of Mars are areas the place NASA missions have detected subsurface water ice (from the equator to 60 levels north latitude). Scientists can use the map – a part of the Subsurface Water Ice Mapping challenge – to come to a decision the place the primary astronauts to set foot at the Crimson Planet will have to land. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Planetary Science InstituteThe map may lend a hand the company come to a decision the place the primary astronauts to the Crimson Planet will have to land. The extra to be had water, the fewer missions will want to carry.Buried ice shall be a very important useful resource for the primary other people to set foot on Mars, serving as consuming water and a key component for rocket gas. However it could even be a big medical goal: Astronauts or robots may sooner or later drill ice cores a lot as scientists do on Earth, uncovering the local weather historical past of Mars and exploring possible habitats (previous or provide) for microbial lifestyles.
The blue spaces in this map of Mars are areas the place NASA missions have detected subsurface water ice (from the equator to 60 levels north latitude). Scientists can use the map – a part of the Subsurface Water Ice Mapping challenge – to come to a decision the place the primary astronauts to set foot at the Crimson Planet will have to land. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Planetary Science InstituteThe map may lend a hand the company come to a decision the place the primary astronauts to the Crimson Planet will have to land. The extra to be had water, the fewer missions will want to carry.Buried ice shall be a very important useful resource for the primary other people to set foot on Mars, serving as consuming water and a key component for rocket gas. However it could even be a big medical goal: Astronauts or robots may sooner or later drill ice cores a lot as scientists do on Earth, uncovering the local weather historical past of Mars and exploring possible habitats (previous or provide) for microbial lifestyles. Those Mars international maps display the most likely distribution of water ice buried inside the higher 3 toes (1 meter) of the planet’s floor and constitute the newest information from the SWIM challenge. Buried ice shall be a very important useful resource for astronauts on Mars, serving as consuming water and a key component for rocket gas. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/PSIMars’ Volatile Water SituationThe want to search for subsurface ice arises as a result of liquid water isn’t strong at the Martian floor: The ambience is so skinny that water straight away vaporizes. There’s quite a lot of ice on the Martian poles – most commonly made from water, even though carbon dioxide, or dry ice, may also be discovered as smartly – however the ones areas are too chilly for astronauts (or robots) to continue to exist for lengthy.Input the SWIM ProjectThat’s the place the NASA-funded Subsurface Water Ice Mapping challenge is available in. SWIM, because it’s identified, lately launched its fourth set of maps – probably the most detailed for the reason that challenge started in 2017.Led by means of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and controlled by means of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, SWIM pulls in combination information from a number of NASA missions, together with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars World Surveyor. The use of a mixture of information units, scientists have recognized the likeliest puts to seek out Martian ice which may be accessed from the outside by means of long term missions.
Those Mars international maps display the most likely distribution of water ice buried inside the higher 3 toes (1 meter) of the planet’s floor and constitute the newest information from the SWIM challenge. Buried ice shall be a very important useful resource for astronauts on Mars, serving as consuming water and a key component for rocket gas. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/PSIMars’ Volatile Water SituationThe want to search for subsurface ice arises as a result of liquid water isn’t strong at the Martian floor: The ambience is so skinny that water straight away vaporizes. There’s quite a lot of ice on the Martian poles – most commonly made from water, even though carbon dioxide, or dry ice, may also be discovered as smartly – however the ones areas are too chilly for astronauts (or robots) to continue to exist for lengthy.Input the SWIM ProjectThat’s the place the NASA-funded Subsurface Water Ice Mapping challenge is available in. SWIM, because it’s identified, lately launched its fourth set of maps – probably the most detailed for the reason that challenge started in 2017.Led by means of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and controlled by means of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, SWIM pulls in combination information from a number of NASA missions, together with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars World Surveyor. The use of a mixture of information units, scientists have recognized the likeliest puts to seek out Martian ice which may be accessed from the outside by means of long term missions. The ice-exposing affect crater on the heart of this symbol is an instance of what scientists search for when mapping puts the place long term astronauts will have to land on Mars. It’s considered one of a number of such affects included into the newest model of a sequence of NASA-funded maps of subsurface water ice at the Crimson Planet. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of ArizonaInstruments on those spacecraft have detected what seem like lots of subsurface frozen water alongside Mars’ mid-latitudes. The northern mid-latitudes are particularly sexy as a result of they have got a thicker surroundings than maximum different areas in the world, making it more uncomplicated to sluggish a descending spacecraft. The best astronaut touchdown websites could be a candy spot on the southernmost fringe of this area – a ways sufficient north for ice to be provide however shut sufficient to the equator to make sure the warmest imaginable temperatures for astronauts in an icy area.“In case you ship people to Mars, you need to get them as just about the equator as you’ll be able to,” stated Sydney Do, JPL’s SWIM challenge supervisor. “The fewer power it’s a must to deplete on protecting astronauts and their supporting apparatus heat, the extra you could have for different issues they’ll want.”
The ice-exposing affect crater on the heart of this symbol is an instance of what scientists search for when mapping puts the place long term astronauts will have to land on Mars. It’s considered one of a number of such affects included into the newest model of a sequence of NASA-funded maps of subsurface water ice at the Crimson Planet. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of ArizonaInstruments on those spacecraft have detected what seem like lots of subsurface frozen water alongside Mars’ mid-latitudes. The northern mid-latitudes are particularly sexy as a result of they have got a thicker surroundings than maximum different areas in the world, making it more uncomplicated to sluggish a descending spacecraft. The best astronaut touchdown websites could be a candy spot on the southernmost fringe of this area – a ways sufficient north for ice to be provide however shut sufficient to the equator to make sure the warmest imaginable temperatures for astronauts in an icy area.“In case you ship people to Mars, you need to get them as just about the equator as you’ll be able to,” stated Sydney Do, JPL’s SWIM challenge supervisor. “The fewer power it’s a must to deplete on protecting astronauts and their supporting apparatus heat, the extra you could have for different issues they’ll want.” On this artist’s thought, NASA astronauts drill into the Martian subsurface. The company has created new maps that display the place ice is perhaps to be simply obtainable to long term astronauts. Credit score: NASAEnhancing the Mapping ProcessPrevious iterations of the map depended on lower-resolution imagers, radar, thermal mappers, and spectrometers, all of which will trace at buried ice however can’t outright ascertain its presence or amount. For this newest SWIM map, scientists depended on two higher-resolution cameras aboard MRO. Context Digital camera information was once used to additional refine the northern hemisphere maps and, for the primary time, HiRISE (Top-Solution Imaging Science Experiment) information was once included to give you the maximum detailed standpoint of the ice’s boundary line as just about the equator as imaginable.Scientists mechanically use HiRISE to check recent affect craters brought about by means of meteoroids that can have excavated chunks of ice. A lot of these craters are not more than 33 toes (10 meters) in diameter, even though in 2022 HiRISE captured a 492-foot-wide (150-meter-wide) affect crater that exposed a motherlode of ice that were hiding underneath the outside.
On this artist’s thought, NASA astronauts drill into the Martian subsurface. The company has created new maps that display the place ice is perhaps to be simply obtainable to long term astronauts. Credit score: NASAEnhancing the Mapping ProcessPrevious iterations of the map depended on lower-resolution imagers, radar, thermal mappers, and spectrometers, all of which will trace at buried ice however can’t outright ascertain its presence or amount. For this newest SWIM map, scientists depended on two higher-resolution cameras aboard MRO. Context Digital camera information was once used to additional refine the northern hemisphere maps and, for the primary time, HiRISE (Top-Solution Imaging Science Experiment) information was once included to give you the maximum detailed standpoint of the ice’s boundary line as just about the equator as imaginable.Scientists mechanically use HiRISE to check recent affect craters brought about by means of meteoroids that can have excavated chunks of ice. A lot of these craters are not more than 33 toes (10 meters) in diameter, even though in 2022 HiRISE captured a 492-foot-wide (150-meter-wide) affect crater that exposed a motherlode of ice that were hiding underneath the outside. Boulder-size blocks of water ice may also be observed across the rim of an affect crater on Mars, as considered by means of the Top-Solution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE digital camera) aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The crater was once shaped on December 24, 2021, by means of a meteoroid strike within the Amazonis Planitia area. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona“Those ice-revealing affects supply a treasured type of flooring reality in that they display us places the place the presence of flooring ice is unequivocal,” stated Gareth Morgan, SWIM’s co-lead on the Planetary Science Institute. “We will be able to then use those places to check that our mapping strategies are sound.”New Discoveries and Long term ProspectsIn addition to ice-exposing affects, the brand new map comprises sightings by means of HiRISE of so-called “polygon terrain,” the place the seasonal growth and contraction of subsurface ice reasons the bottom to shape polygonal cracks. Seeing those polygons extending round recent, ice-filled affect craters is but every other indication that there’s extra ice hidden underneath the outside at those places.There are different mysteries that scientists can use the map to check, as smartly.“The volume of water ice present in places around the Martian mid-latitudes isn’t uniform; some areas appear to have greater than others, and no person in reality is aware of why,” stated Nathaniel Putzig, SWIM’s different co-lead on the Planetary Science Institute. “The most recent SWIM map may result in new hypotheses for why those diversifications occur.” He added that it will additionally lend a hand scientists tweak fashions of the way the traditional Martian local weather developed through the years, leaving better quantities of ice deposited in some areas and lesser quantities in others.SWIM’s scientists hope the challenge will function a basis for a proposed Mars Ice Mapper project – an orbiter that will be supplied with an impressive radar custom-designed to seek for near-surface ice past the place HiRISE has showed its presence.
Boulder-size blocks of water ice may also be observed across the rim of an affect crater on Mars, as considered by means of the Top-Solution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE digital camera) aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The crater was once shaped on December 24, 2021, by means of a meteoroid strike within the Amazonis Planitia area. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona“Those ice-revealing affects supply a treasured type of flooring reality in that they display us places the place the presence of flooring ice is unequivocal,” stated Gareth Morgan, SWIM’s co-lead on the Planetary Science Institute. “We will be able to then use those places to check that our mapping strategies are sound.”New Discoveries and Long term ProspectsIn addition to ice-exposing affects, the brand new map comprises sightings by means of HiRISE of so-called “polygon terrain,” the place the seasonal growth and contraction of subsurface ice reasons the bottom to shape polygonal cracks. Seeing those polygons extending round recent, ice-filled affect craters is but every other indication that there’s extra ice hidden underneath the outside at those places.There are different mysteries that scientists can use the map to check, as smartly.“The volume of water ice present in places around the Martian mid-latitudes isn’t uniform; some areas appear to have greater than others, and no person in reality is aware of why,” stated Nathaniel Putzig, SWIM’s different co-lead on the Planetary Science Institute. “The most recent SWIM map may result in new hypotheses for why those diversifications occur.” He added that it will additionally lend a hand scientists tweak fashions of the way the traditional Martian local weather developed through the years, leaving better quantities of ice deposited in some areas and lesser quantities in others.SWIM’s scientists hope the challenge will function a basis for a proposed Mars Ice Mapper project – an orbiter that will be supplied with an impressive radar custom-designed to seek for near-surface ice past the place HiRISE has showed its presence.