Abstract: Other people elderly 60 and over are much more likely to be influenced by means of others’ impulsive monetary choices than more youthful adults. Researchers discovered that older members, particularly the ones with upper emotional empathy, had been much more likely to modify their monetary personal tastes after gazing impulsive habits.Against this, more youthful adults tended to stay with their authentic monetary alternatives. Those findings may just tell interventions to lend a hand older adults make higher monetary choices in a socially influenced international.Key Information:Older adults are extra influenced by means of others’ impulsive monetary choices.More youthful adults face up to social affect, keeping up authentic monetary personal tastes.Emotional empathy in older adults might build up susceptibility to impulsive affect.Supply: College of BirminghamOlder persons are much more likely to be influenced by means of the impulsive monetary personal tastes of others than their more youthful opposite numbers, in step with a brand new learn about.Analysis lead by means of psychologists on the College of Birmingham and the College of Oxford revealed lately in Communications Psychology, finds that folks elderly 60 and over are extra susceptible to being influenced by means of other folks in the case of making impulsive monetary choices in comparison to younger adults elderly between 18 -36.The learn about got down to discover not on time gratification and the way our willingness to attend and social affect expand and vary throughout our lifespan. To check how age impacts those behaviours, a bunch of 76 younger adults (elderly 18–36) and 78 older adults (elderly 60–80) had been recruited.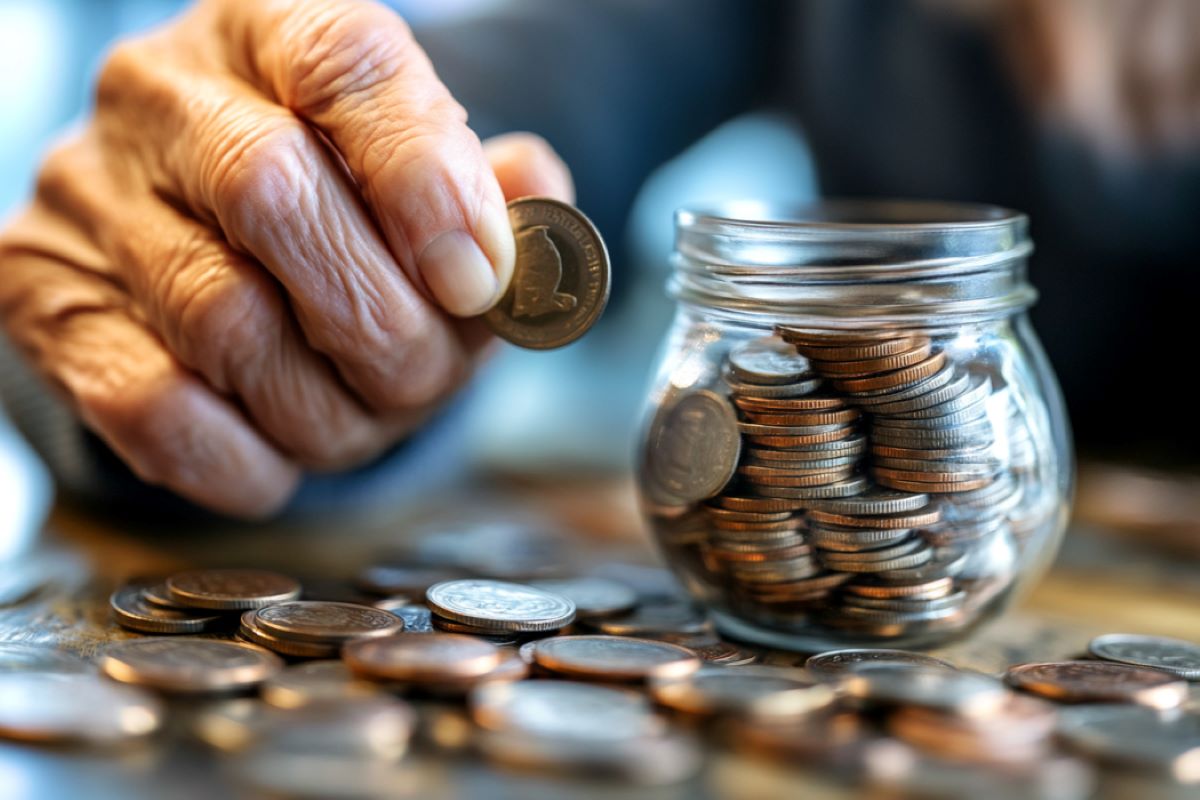  The consequences confirmed that older other folks had been extra vulnerable to social affect, particularly from the extra impulsive individual. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThese members had been sparsely matched in line with gender, intelligence, and years of training. Older adults had been getting older healthily and underwent thorough screening to make sure they had been freed from dementia or different components that would possibly impact their decision-making without reference to age.Senior creator Professor Patricia Lockwood from the College of Birmingham mentioned: “In an technology of an getting older inhabitants and lengthening incorrect information, it is important to know how getting older impacts other folks’s susceptibility to steer. One key space the place other folks is also influenced is of their personal tastes for receiving cash quicker moderately than later. This data is important for growing interventions to make sure other folks make just right monetary alternatives throughout their lives.”All members finished a decision-making job wherein they had been required to make a chain of alternatives about two other choices: an impulsive one that led to receiving a smaller amount of cash straight away; or a extra restrained one that supposed receiving a bigger amount of cash after a extend.Since any such choices can be realised as an advantage cost on the finish of the experiment, members knew that their alternatives had actual penalties, motivating them to expose their authentic monetary personal tastes.Following their preliminary resolution, members then noticed and realized concerning the alternatives made by means of two ‘other folks’ who had finished the similar decision-making job earlier than (if truth be told generated by means of a pc).One set of choices favoured the fast, extra impulsive choices, whilst the opposite set leaned in opposition to the not on time, extra restrained choices, in comparison to the members’ personal choices. After all, the members made such choices for themselves all over again.This allowed the researchers to use complex mathematical modelling to exactly quantify the members’ monetary personal tastes and assess how those personal tastes had been influenced by means of others.The consequences confirmed that older other folks had been extra vulnerable to social affect, particularly from the extra impulsive individual. After seeing somebody who constantly chooses the impulsive possibility, older adults had been much more likely to modify their desire to make impulsive choices themselves. Against this, more youthful adults had been extra proof against such affect, tending to stay with their authentic desire even after seeing somebody time and again go for the impulsive possibility.The researchers additionally measured other folks’s self-reported emotional reviews to look if there have been variations between other folks in how inclined they had been to social affect.Among older adults, those that reported upper ranges of affective empathy (i.e., a better skill to really feel others’ feelings) and reported being extra emotionally motivated had been extra strongly suffering from impulsive social affect.Senior creator Professor Patricia Lockwood mentioned: ‘Those findings spotlight that there may well be necessary variations in how older adults are influenced by means of other folks’s monetary choices in comparison to more youthful adults.“If showed by means of additional analysis, they may tell evidence-based programmes that toughen other folks to make smart monetary choices all through their lives, and realise if their very own choices may well be negatively suffering from the ones round them.”Lead creator Zhilin Su commented: “In an technology of top ranges of incorrect information on social media it is important to know the science at the back of social affect so we will make a significant and sure affect on other folks’s lives.”About this psychology and growing older analysis newsAuthor: Tony Moran
The consequences confirmed that older other folks had been extra vulnerable to social affect, particularly from the extra impulsive individual. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThese members had been sparsely matched in line with gender, intelligence, and years of training. Older adults had been getting older healthily and underwent thorough screening to make sure they had been freed from dementia or different components that would possibly impact their decision-making without reference to age.Senior creator Professor Patricia Lockwood from the College of Birmingham mentioned: “In an technology of an getting older inhabitants and lengthening incorrect information, it is important to know how getting older impacts other folks’s susceptibility to steer. One key space the place other folks is also influenced is of their personal tastes for receiving cash quicker moderately than later. This data is important for growing interventions to make sure other folks make just right monetary alternatives throughout their lives.”All members finished a decision-making job wherein they had been required to make a chain of alternatives about two other choices: an impulsive one that led to receiving a smaller amount of cash straight away; or a extra restrained one that supposed receiving a bigger amount of cash after a extend.Since any such choices can be realised as an advantage cost on the finish of the experiment, members knew that their alternatives had actual penalties, motivating them to expose their authentic monetary personal tastes.Following their preliminary resolution, members then noticed and realized concerning the alternatives made by means of two ‘other folks’ who had finished the similar decision-making job earlier than (if truth be told generated by means of a pc).One set of choices favoured the fast, extra impulsive choices, whilst the opposite set leaned in opposition to the not on time, extra restrained choices, in comparison to the members’ personal choices. After all, the members made such choices for themselves all over again.This allowed the researchers to use complex mathematical modelling to exactly quantify the members’ monetary personal tastes and assess how those personal tastes had been influenced by means of others.The consequences confirmed that older other folks had been extra vulnerable to social affect, particularly from the extra impulsive individual. After seeing somebody who constantly chooses the impulsive possibility, older adults had been much more likely to modify their desire to make impulsive choices themselves. Against this, more youthful adults had been extra proof against such affect, tending to stay with their authentic desire even after seeing somebody time and again go for the impulsive possibility.The researchers additionally measured other folks’s self-reported emotional reviews to look if there have been variations between other folks in how inclined they had been to social affect.Among older adults, those that reported upper ranges of affective empathy (i.e., a better skill to really feel others’ feelings) and reported being extra emotionally motivated had been extra strongly suffering from impulsive social affect.Senior creator Professor Patricia Lockwood mentioned: ‘Those findings spotlight that there may well be necessary variations in how older adults are influenced by means of other folks’s monetary choices in comparison to more youthful adults.“If showed by means of additional analysis, they may tell evidence-based programmes that toughen other folks to make smart monetary choices all through their lives, and realise if their very own choices may well be negatively suffering from the ones round them.”Lead creator Zhilin Su commented: “In an technology of top ranges of incorrect information on social media it is important to know the science at the back of social affect so we will make a significant and sure affect on other folks’s lives.”About this psychology and growing older analysis newsAuthor: Tony Moran
Supply: College of Birmingham
Touch: Tony Moran – College of Birmingham
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: The findings will seem in Communications Psychology
Older Adults Extra Liable to Impulsive Monetary Affect – Neuroscience Information