Despite the fact that it’s been just about a decade since NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft visited Pluto, the dwarf planet continues to expose itself as a shockingly complicated international.Scientists learning spacecraft information of an atypical crater close to a vivid, heart-shaped area on Pluto referred to as Sputnik Planitia say they are going to have discovered a supervolcano that most likely erupted only some million years in the past. That may sound like a shockingly very long time in the past, however cosmically talking, it is lovely contemporary. For context, the sun gadget is greater than 4.5 billion years outdated. As a substitute of molten rock that blasts out of Earth’s volcanoes, then again, the 44-km-wide Kiladze crater seems to have spewed ice lava onto Pluto’s floor in a procedure referred to as cryovolcanism. The method, which additionally unfolds at the moons of gasoline giants in our sun gadget and most likely created different mystifying terrains on Pluto, is assumed to have thrusted water from the arena’s hidden subsurface ocean onto its floor, reshaping it throughout thousands and thousands of years.Volcanoes require some type of warmth supply to explode, so the hot job on Pluto suggests there may be extra warmth final within the dwarf planet’s inside than prior to now concept.Similar: Cracks on Pluto’s moon Charon is also proof of a frozen subsurface oceanResearchers analyzed pictures New Horizons had clicked of the Kiladze crater, which is living northeast of Sputnik Planitia. Whilst in the beginning the crater appeared very similar to the ones left at the back of by way of meteorite affects, it gave the impression to be lacking a central height another way anticipated for those geological phenomena. It additionally appeared quite elongated, in keeping with actions led to by way of tectonic forces from inside Pluto, in keeping with the brand new learn about, which is but to be peer-reviewed.Maximum of Pluto’s floor is blanketed with methane and nitrogen ice, so the “tip-off that Kiladze is other” from remainder of Pluto’s floor is the sturdy presence of water ice across the crater, learn about lead creator Dale Cruikshank, a professor at College of Central Florida, instructed Area.com. “The water ice stands proud obviously from the methane ice that covers a lot of the planet’s floor.”Pluto’s axis is tilted at a pointy 120 levels, which means that it spins nearly on its facet, resulting in dramatic adjustments in local weather because it circles the solar. In consequence, methane ice sublimates right into a haze of hydrocarbons within the dwarf planet’s surroundings, a few of which rain down as snow and coat its floor.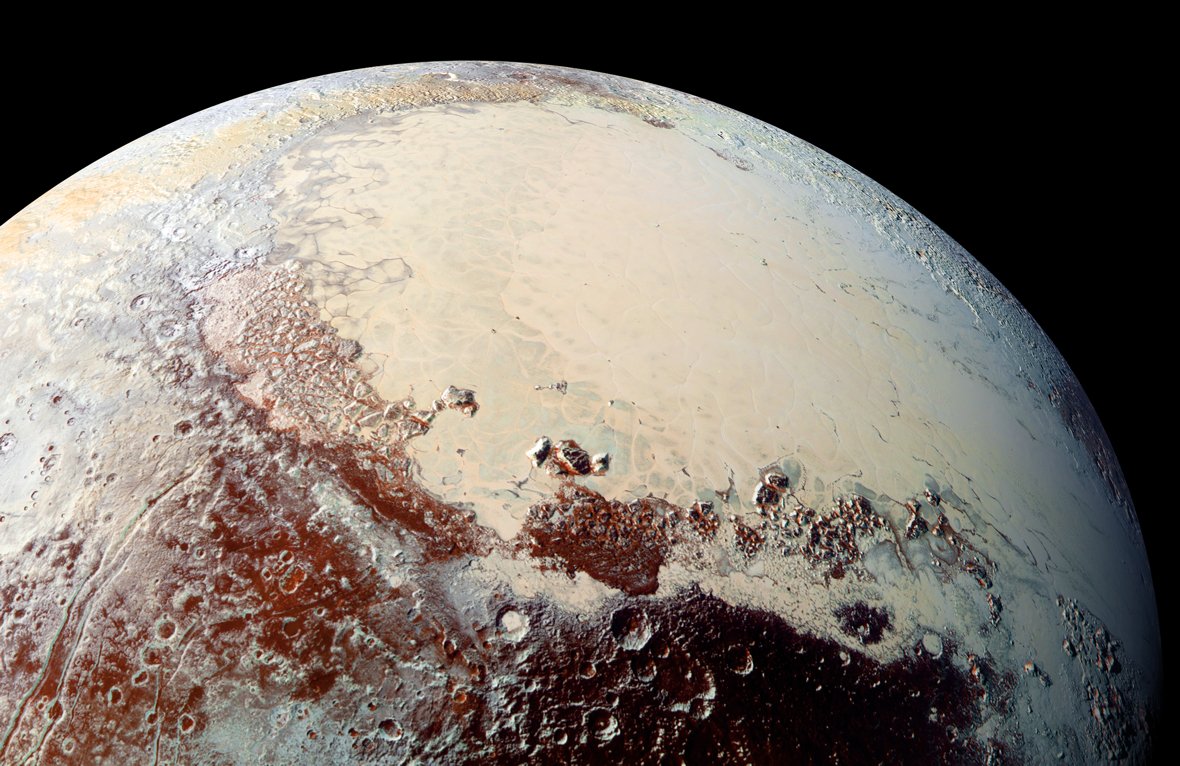  A view of Pluto’s heart-shaped Sputnik Planitia as imaged by way of New Horizons spacecraft in 2015. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Over Pluto’s 4.6 billion-year lifetime, scientists estimate this methane ice blanket will have to have got no less than 14 meters (46 ft) thick. “Even a centimeter or two of this natural smog would masks the water ice spectral signature we apply,” Cruikshank stated. This sort of layer would have shaped in simply 3 million years. This led Cruikshank and his crew to conclude Kiladze was once “alive” just a few million years in the past. Scientists do not absolutely know how cryovolcanic job works on Pluto. The arena is so small that it could have misplaced all warmth from its formation way back. One risk is the dwarf planet contained radioactive components in its core which launched warmth whilst decaying, even though earlier analysis advised there simply is probably not sufficient of those components to power-up Pluto. Regardless of the warmth supply may well be, then again, one thing seems to be retaining Pluto’s subsurface ocean from freezing.”Because the planet cooled, it’s believable that wallet of liquid water had been left at the back of, and most likely our eruptions of water onto the outside faucet into the ones wallet,” Cruikshank stated. However, the researcher added: “We do not know.”
A view of Pluto’s heart-shaped Sputnik Planitia as imaged by way of New Horizons spacecraft in 2015. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Over Pluto’s 4.6 billion-year lifetime, scientists estimate this methane ice blanket will have to have got no less than 14 meters (46 ft) thick. “Even a centimeter or two of this natural smog would masks the water ice spectral signature we apply,” Cruikshank stated. This sort of layer would have shaped in simply 3 million years. This led Cruikshank and his crew to conclude Kiladze was once “alive” just a few million years in the past. Scientists do not absolutely know how cryovolcanic job works on Pluto. The arena is so small that it could have misplaced all warmth from its formation way back. One risk is the dwarf planet contained radioactive components in its core which launched warmth whilst decaying, even though earlier analysis advised there simply is probably not sufficient of those components to power-up Pluto. Regardless of the warmth supply may well be, then again, one thing seems to be retaining Pluto’s subsurface ocean from freezing.”Because the planet cooled, it’s believable that wallet of liquid water had been left at the back of, and most likely our eruptions of water onto the outside faucet into the ones wallet,” Cruikshank stated. However, the researcher added: “We do not know.”
Supervolcano eruption on Pluto hints at hidden ocean underneath the outside