Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
Again in mid-2022, there used to be a dispute over the cosmic distance checklist. Again in 2016, a galaxy recognized from inside the Hubble Extremely Deep Box, GN-z11, set a definitive checklist: it got here to us from when the Universe used to be simply 407 million years outdated, or most effective ~3% of its provide age. However a couple of years later, some have been claiming {that a} new galaxy, HD1, used to be much more remote, main HD1 to make an look (quickly) atop such vaunted lists as Wikipedia’s record of essentially the most remote astronomical items or even within the Guinness guide of worldwide data. No much less a supply than Harvard College touted it as essentially the most remote object of all-time.Neither “record-holder” would closing for lengthy as soon as the JWST technology started, alternatively. Once the primary deep-field picture used to be launched, just about 100 applicants emerged for what can be a record-breaking galaxy in that individual field-of-view. In December of 2022, a slew of recent galaxies have been introduced, with essentially the most remote, JADES-GS-z13-0, coming from when the Universe used to be simply 320 million years outdated: 2.3% of its provide age. Then, on Would possibly 30, 2024, a brand new cosmic record-breaker surpassed all of them: JADES-GS-z14-0, whose mild used to be emitted when the Universe used to be most effective 285 million years outdated: 2.1% of its present age.However what about all the different ultra-distant galaxy applicants? Why hasn’t the cosmic distance checklist fallen again and again over, and why haven’t we discovered anything else even previous than the galaxies at the moment recognized? It’s a deep query with an implausible medical solution.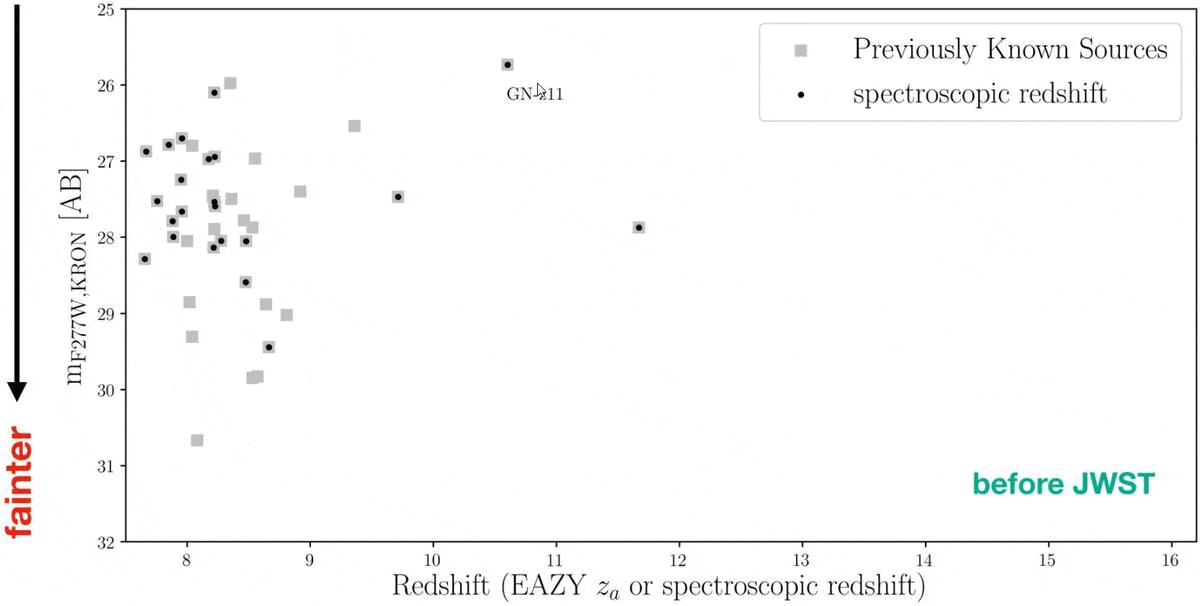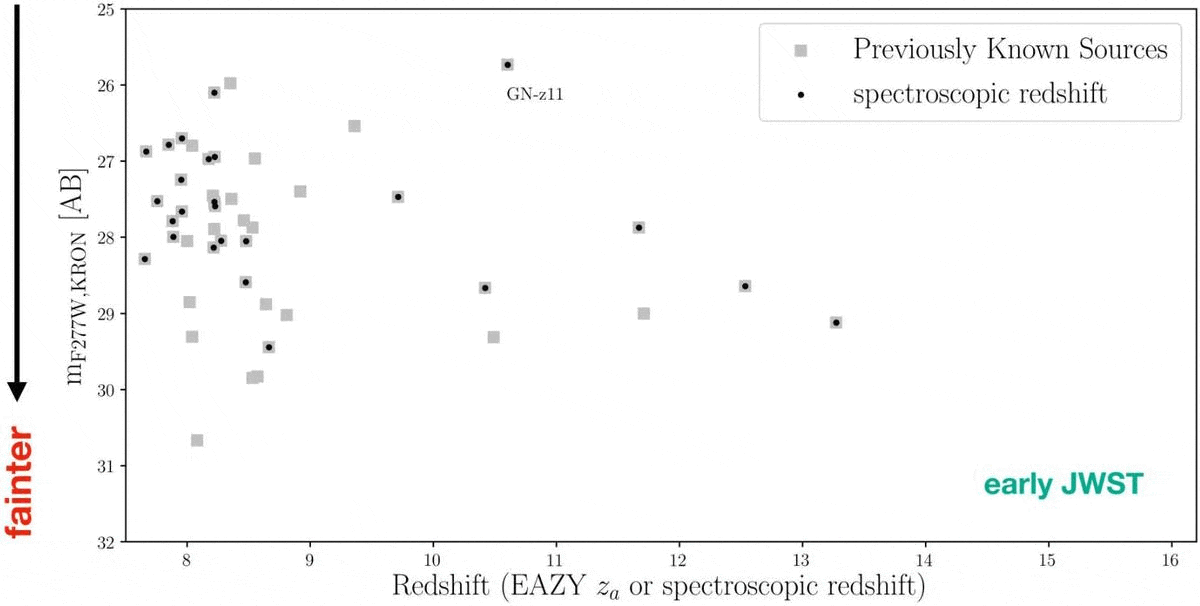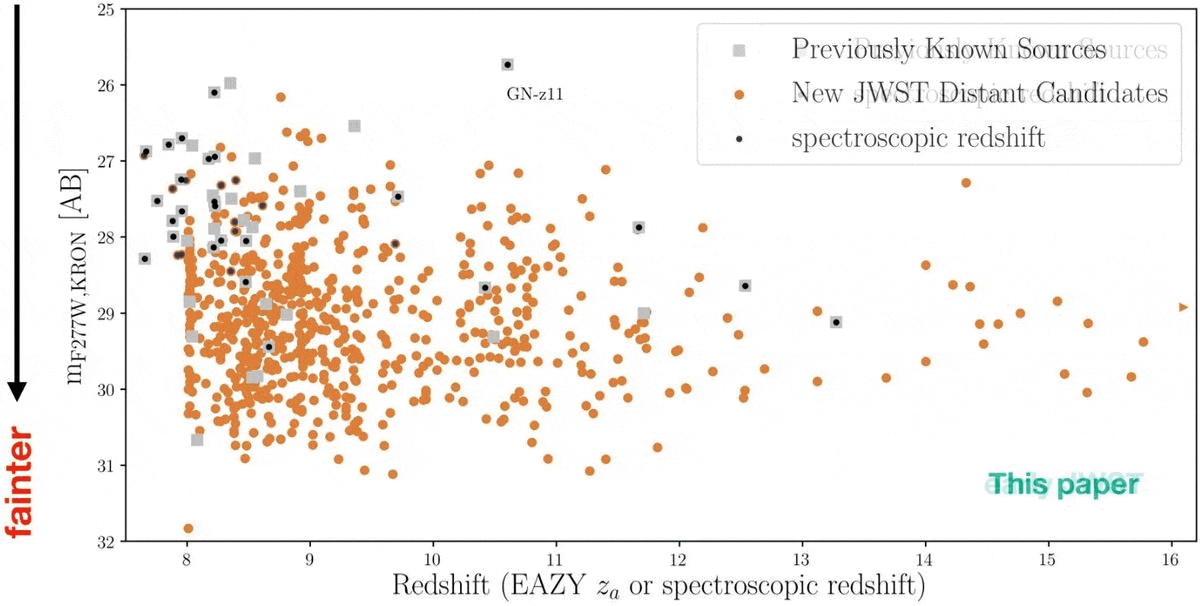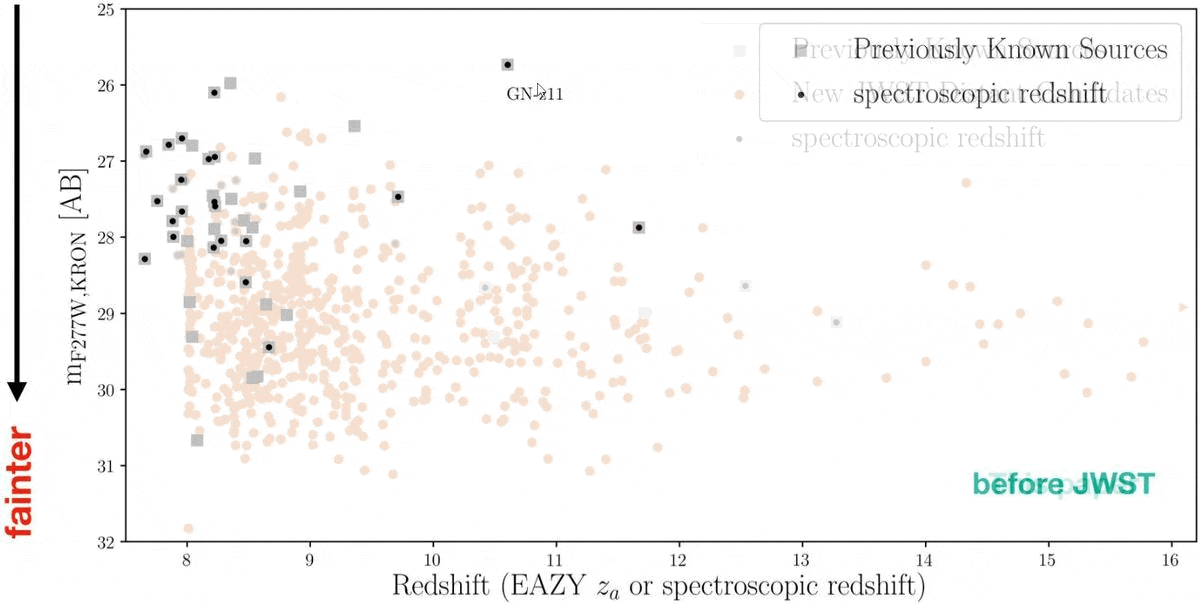 Sooner than JWST, there have been about 40 ultra-distant galaxy applicants recognized, basically by way of Hubble’s observations. Early JWST effects printed many extra ultra-distant galaxy applicants, however now a whopping 717 of them had been present in simply the JADES 125 square-arcminute field-of-view. All the night time sky is greater than 1 million occasions grander in scale. Whilst some applicants will continue to exist spectroscopic follow-up, others won’t. A lot science is still carried out.
Sooner than JWST, there have been about 40 ultra-distant galaxy applicants recognized, basically by way of Hubble’s observations. Early JWST effects printed many extra ultra-distant galaxy applicants, however now a whopping 717 of them had been present in simply the JADES 125 square-arcminute field-of-view. All the night time sky is greater than 1 million occasions grander in scale. Whilst some applicants will continue to exist spectroscopic follow-up, others won’t. A lot science is still carried out.
Credit score: Kevin Hainline for the JADES Collaboration, AAS242
We’ve to begin with the variation between a galaxy candidate and a showed galaxy. Whilst you have a look at an object within the Universe, and this is applicable to any object in any respect, it’s important to believe the trade-off between:
the period of time you’ll be able to dedicate to anyone specific commentary,
and the quantity of medical wisdom you’ll be able to acquire with the commentary(s) that you just’re undertaking.
In astronomy, the function is to collect sufficiently huge quantities of sunshine in order that we will be able to establish exactly what a person object of passion is and what its essential homes are.That implies, first, we want to in truth to find those items and “tag” them as fascinating, by some means. This typically proceeds during the underappreciated science of photometry. We did it with Hubble, we’re doing it now with JWST, and we’re going to proceed to do it with no matter ground-based and space-based telescopes are at our disposal one day. It’s simple to look {that a} telescope is a big “light-bucket,” the place we open a large eye at the Universe and gather the entire mild that is available in for so long as we practice with it. However we don’t wish to gather the entire mild that spans the entire other wavelengths directly; we wish to be delicate to mild of various wavelengths and energies.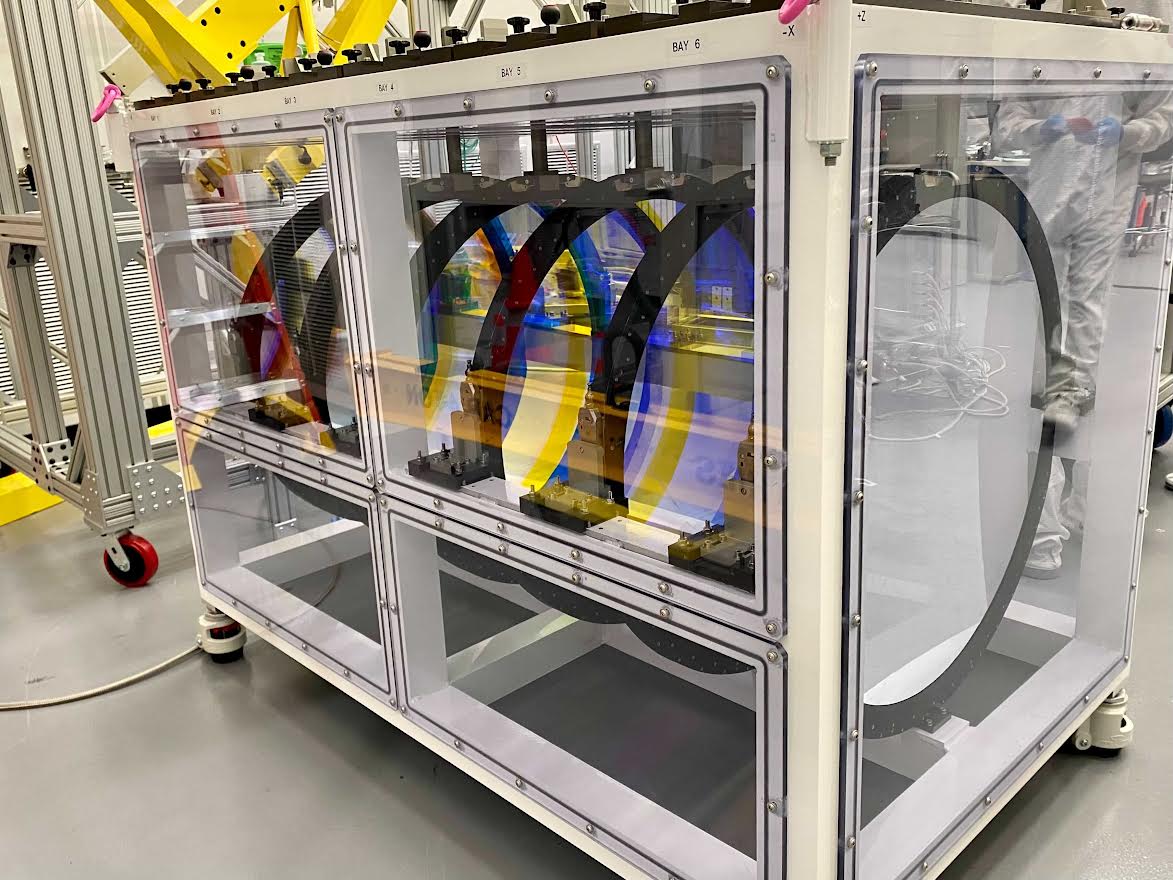 This {photograph} presentations all six photometric filters, pre-installation, designed for the LSST digicam on the Vera Rubin Observatory. They span the gamut of wavelengths from ultraviolet during the optical and into the infrared. For comparability, JWST has greater than 20 other clear out choices aboard its NIRCam and MIRI tools.
This {photograph} presentations all six photometric filters, pre-installation, designed for the LSST digicam on the Vera Rubin Observatory. They span the gamut of wavelengths from ultraviolet during the optical and into the infrared. For comparability, JWST has greater than 20 other clear out choices aboard its NIRCam and MIRI tools.
Credit score: Travis Lange/SLAC Nationwide Accelerator Laboratory
The best way we do this is by means of putting what we name a photometric clear out over our tools. As an alternative of accumulating all the mild emitted by means of items inside our field-of-view, we gather most effective the sunshine that falls inside a selected wavelength vary: each and every particular person clear out lets in mild inside a undeniable vary of colours (and wavelengths) to move via it, the place it reaches the tools, whilst filtering out all different wavelengths of sunshine.Via then looking at the similar field-of-view with a couple of other photometric filters for a undeniable long-enough length of time, we will be able to begin to see what this area of area — in addition to each and every object that’s vivid adequate to look inside that area, given the boundaries of our looking at time — seems like in a undeniable stage of element.It’s similar to the truth that (maximum) people have 3 various kinds of cone receptors in our retina: basically receptive to blue, inexperienced/yellow, and crimson wavelengths of sunshine, respectively. When the sunshine supply is vivid adequate to turn on our cones (as an alternative of most effective our rods, which don’t clear out mild by means of wavelength), the quantity of process in each and every cone kind determines the sign energy in our optic nerve, which then will get interpreted by means of our brains as a full-color symbol.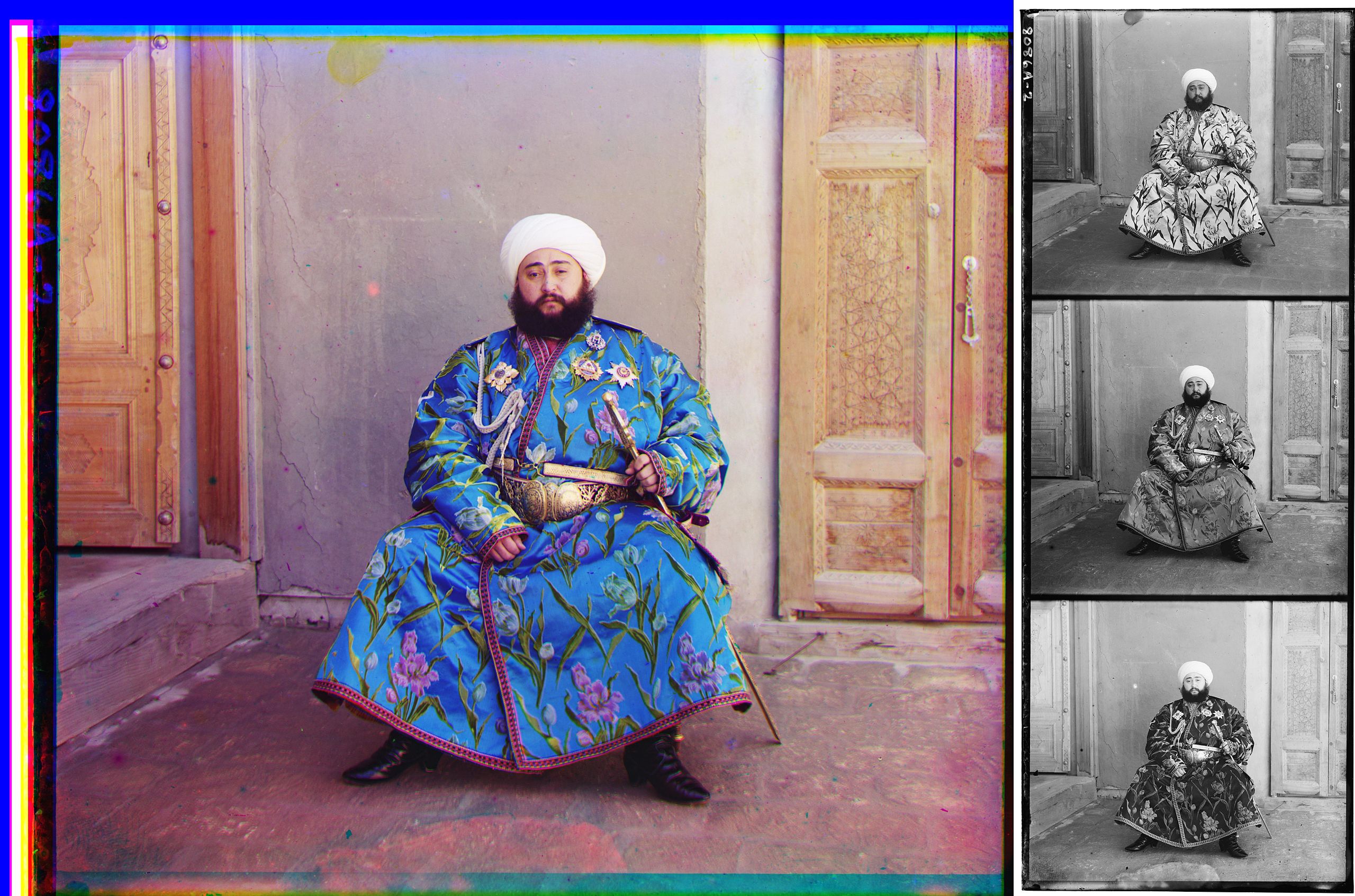 This {photograph}, from 1911, demonstrates the methodology of additive coloration blending as implemented to images. 3 coloration filters, blue, yellow, and crimson, have been implemented to the topic, generating the 3 images at proper. When the information from the 3 are added in combination in the right kind proportions, a colour symbol is produced. Our brains, with 3 various kinds of cones sending indicators from our eyes, do that mechanically.
This {photograph}, from 1911, demonstrates the methodology of additive coloration blending as implemented to images. 3 coloration filters, blue, yellow, and crimson, have been implemented to the topic, generating the 3 images at proper. When the information from the 3 are added in combination in the right kind proportions, a colour symbol is produced. Our brains, with 3 various kinds of cones sending indicators from our eyes, do that mechanically.
Credit score: Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii
With regards to astronomy, alternatively, if we’re at the hunt for ultra-distant galaxies, we don’t wish to merely upload that mild in combination and assign a colour to it; that could be the suitable approach for human brains, however no longer for figuring out record-breakingly remote galaxies. As an alternative, we wish to search for a undeniable magnificence of sign from an object that shows the next homes.
In brief wavelengths of sunshine, it’s utterly invisible, emitting no detectable mild in any respect.
Then, previous some positive wavelength threshold, it no longer most effective turns into visual, however persistently vivid.
That’s principally it. Even though there are no doubt extra main points that one can cross into, those two homes, in combination, are steadily adequate to spot an object as a candidate object for being an ultra-distant galaxy.The explanation why is easy. Galaxies are large collections of stars, fuel, mud, plasma, and (usually) a central, supermassive black hollow. They emit mild throughout all kinds of wavelengths, however the most powerful mild sign typically — this is, for non-active galaxies — comes from stars. The higher your inhabitants of younger, sizzling, huge, recently-formed stars, the bluer a galaxy’s mild will probably be. Specifically, there’s going to be a considerable amount of visual and ultraviolet mild emitted, with the brightest items emitting a huge quantity of ultraviolet mild. On the other hand, from an overly remote galaxy, that mild is then going to get redshifted, or stretched to longer wavelengths, because it travels during the increasing Universe sooner than achieving our telescope’s eyes. This simplified animation presentations how mild redshifts and the way distances between unbound items trade through the years within the increasing Universe. Observe that the items get started off nearer than the period of time it takes mild to journey between them, the sunshine redshifts because of the growth of area, and the 2 galaxies finally end up a lot farther aside than the light-travel trail taken by means of the photon exchanged between them.
This simplified animation presentations how mild redshifts and the way distances between unbound items trade through the years within the increasing Universe. Observe that the items get started off nearer than the period of time it takes mild to journey between them, the sunshine redshifts because of the growth of area, and the 2 galaxies finally end up a lot farther aside than the light-travel trail taken by means of the photon exchanged between them.
Credit score: Rob Knop
By the point that mild arrives at our telescope, if it’s from an overly remote galaxy, there gained’t be any ultraviolet mild left. If truth be told, if the galaxy is remote adequate, there gained’t also be any visual mild left in any respect. Even mild that used to be emitted within the ultraviolet a part of the spectrum, assuming the galaxy is remote adequate, could have its wavelength stretched by means of any such large amount that it arrives in infrared wavelengths.Astronomers have a phrase for this “stretch issue” that will get imprinted on all kinds of mild from the increasing Universe: redshift, denoted by means of the letter z. If you know the way atoms paintings, for instance, you’ll know that there are a couple of essential transitions in hydrogen atoms — the most typical species of atom within the Universe by means of a ways — that at all times create mild of a selected wavelength. As an example:
when a hydrogen atom de-excites from the n=3 stage to the n=2 stage, it emits a (visual mild) photon of exactly 656.3 nanometers, or what astronomers name H-alpha,
and when a hydrogen atom de-excites from the n=2 stage to the (lowest calories) n=1 stage, it emits a photon (at ultraviolet wavelengths) of 121.5 nanometers, or what astronomers name Lyman-alpha.
If you wish to practice the ones photons that come to us from galaxy, alternatively, you’ll be able to’t merely have a look at the ones wavelengths and be expecting to look an emission sign. As an alternative, it’s important to account for the growth of the Universe, and multiply the ones rest-frame wavelengths by means of the right stretch issue, an element of (1 + z), in an effort to to find essentially the most remote items of all. The farther away we glance, the nearer in time we’re seeing to the primary moments of the Large Bang. After we see items from the primary ~1 billion years of cosmic historical past, there are nonetheless impartial, light-blocking atoms within the intergalactic medium, fighting us from seeing the shorter emitted wavelengths of sunshine from our vantage level these days.
The farther away we glance, the nearer in time we’re seeing to the primary moments of the Large Bang. After we see items from the primary ~1 billion years of cosmic historical past, there are nonetheless impartial, light-blocking atoms within the intergalactic medium, fighting us from seeing the shorter emitted wavelengths of sunshine from our vantage level these days.
Credit score: Robin Dienel/Carnegie Establishment for Science
There’s additionally the truth that even supposing our Universe these days is most commonly clear to mild, again at early occasions in cosmic historical past — all over the primary billion years and particularly all over the primary few hundred million years — lots of the atoms in intergalactic area have been nonetheless impartial, and succesful (and environment friendly) at blocking off and soaking up starlight. Since hydrogen is essentially the most plentiful atom within the Universe, and maximum impartial atoms exist within the floor (n=1) state, that implies that if an energetic-enough quantum of sunshine (i.e., a photon) comes alongside and moves that impartial atom, the atom can soak up that mild and get excited to a higher-energy state.Due to this fact, when galaxy emits mild, a portion of that mild goes to strike the intervening atoms and get absorbed. For items that we’re viewing from inside the first a thousand million years of cosmic historical past — akin to a redshift of z = 6 or past — as a result of there’s such a lot impartial hydrogen that the sunshine should move via, the ones ground-state atoms will soak up that initially-ultraviolet mild anywhere they come upon it. This creates a lot of options:At wavelengths shorter than the redshifted Lyman-alpha characteristic [i.e., 121.5 nm multiplied by (1 + z)], that Lyman-break guarantees that no mild will get via, while at longer wavelengths, a number of mild comes via.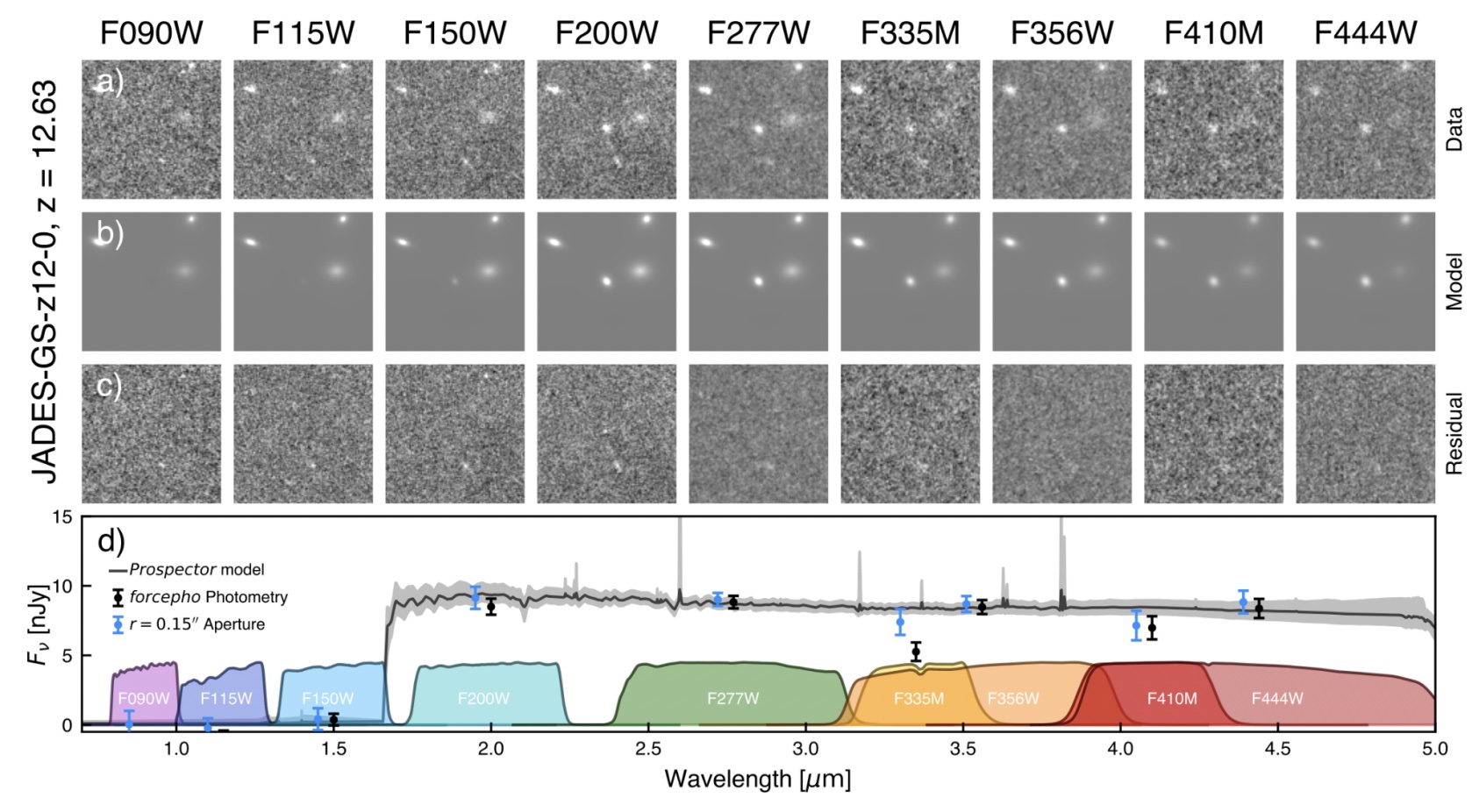 This diagram presentations the photometric reaction of a candidate ultra-distant galaxy from the JWST Deep Complex Extragalactic Survey: JADES. The shortage of sunshine at brief wavelengths and the abundance at lengthy wavelengths trace at the potential of it being ultra-distant, however spectroscopic affirmation is needed to make sure.
This diagram presentations the photometric reaction of a candidate ultra-distant galaxy from the JWST Deep Complex Extragalactic Survey: JADES. The shortage of sunshine at brief wavelengths and the abundance at lengthy wavelengths trace at the potential of it being ultra-distant, however spectroscopic affirmation is needed to make sure.
Credit score: B. E. Robertson et al., arXiv:2212.04480, 2022
That’s a huge quantity of science that we will be able to behavior the use of photometry on my own, which is why virtually each and every ultra-distant galaxy candidate has been recognized with observatories that may succeed in into the infrared: Hubble, which is able to cross a little bit bit into the infrared (out to round 2.0 microns), and JWST, which is able to cross a lot, a lot deeper into the infrared (as much as 28-30 microns at its prohibit). With many alternative wavelength filters, we will be able to establish the ones galaxies that seem to emit no mild underneath a undeniable wavelength threshold, after which huge quantities of it past that threshold. In line with the sunshine we see, we will be able to assign what we name a photometric redshift to that object: the place, in line with the sunshine we practice, how remote we predict that object to actually be.However this is most effective enough to spot one thing as a candidate ultra-distant galaxy. To be able to ensure our photometric redshift estimate is correct — that the item actually is on the distance we assign to it — we’d like spectroscopic affirmation. Spectroscopy comes to:
amassing a considerable amount of mild about one specific object (even supposing it’s imaginable to do multiple object directly),
breaking that illuminate into its particular person part wavelengths and recording all of them,
and revealing the imprint of particular person atoms, ions, and (now and again) molecules which might be emitting and/or soaking up that object’s mild.
In comparison to photometry, spectroscopy is costly: it calls for for much longer classes of looking at time. However not like with photometry, the place there are a couple of imaginable explanations for an object’s distance, spectroscopy can spoil the anomaly, appearing which units of traces at which wavelengths, together with figuring out the presence or absence of the essential Lyman-break characteristic, correspond to the item in query.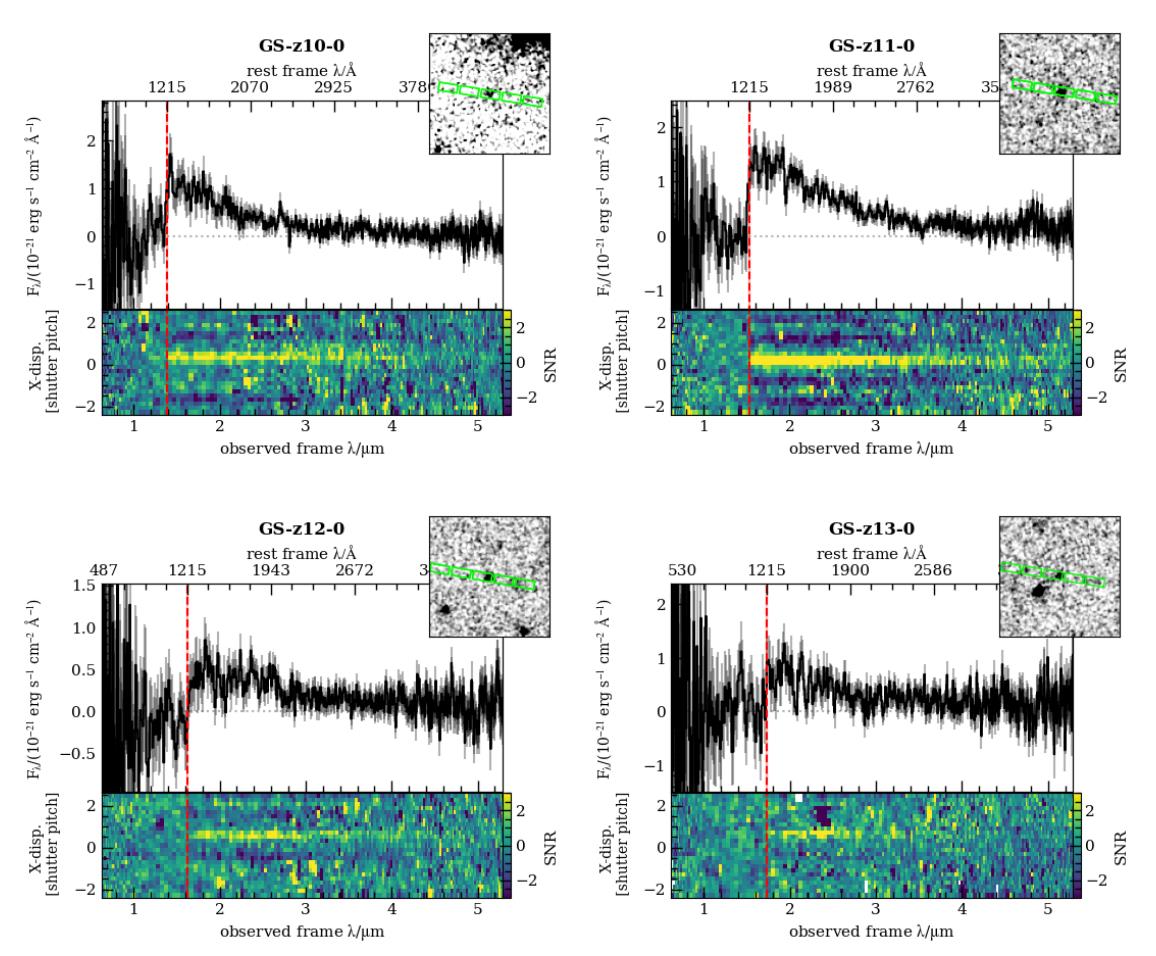 The spectra acquired by means of JADES and the JWST NIRSpec device for the 4 maximum remote galaxies discovered inside JADES survey as of December, 2022. The Lyman spoil characteristic, robustly recognized right here for each and every of the 4 galaxies, determines the gap and redshift past an inexpensive doubt, which made JADES-GS-z13-0 the cosmic record-holder for many remote galaxy till Would possibly of 2024.
The spectra acquired by means of JADES and the JWST NIRSpec device for the 4 maximum remote galaxies discovered inside JADES survey as of December, 2022. The Lyman spoil characteristic, robustly recognized right here for each and every of the 4 galaxies, determines the gap and redshift past an inexpensive doubt, which made JADES-GS-z13-0 the cosmic record-holder for many remote galaxy till Would possibly of 2024.
Credit score: JADES Collaboration, E. Curtis-Lake et al., preprint, 2022
The search for essentially the most remote galaxy of all has led to a few nice successes and a few nice near-misses, and whilst photometry has been key for figuring out all of those galaxies again once they have been simply candidate galaxies, spectroscopy has been the essential device in confirming — or, now and again, refuting — the purported ultra-distant nature of those items. As an example:GN-z11 were recognized as an object of passion, photometrically, years sooner than spectroscopy used to be first carried out on it in 2015. Its announcement in 2016 corresponded to the e-newsletter of its spectroscopic information, which printed the important thing Lyman-break characteristic. At a redshift of z = 11 (akin to a cosmic age of ~420 million years), it used to be certainly the one-time record-holder.HD1, introduced in 2022 however with photometric information most effective, had its photometric redshift interpreted to be an excellent z = 13.3, which might have positioned it simply ~320 million years after the Large Bang. On the other hand, that wasn’t the one imaginable interpretation of the photometric information. As an example:
it might showcase no short-wavelength mild as it’s intrinsically dusty, and that mud blocks the shorter-wavelengths of sunshine,
it might showcase huge, even quantities of long-wavelength mild as it’s sizzling and shows robust emission traces: traces that may “spice up” longer wavelengths once they fall into a selected set of photometric filters,
and most effective looking at emission traces, spectroscopically and with the proper component/line-origin id, would be capable of inform the a couple of doable answers aside.
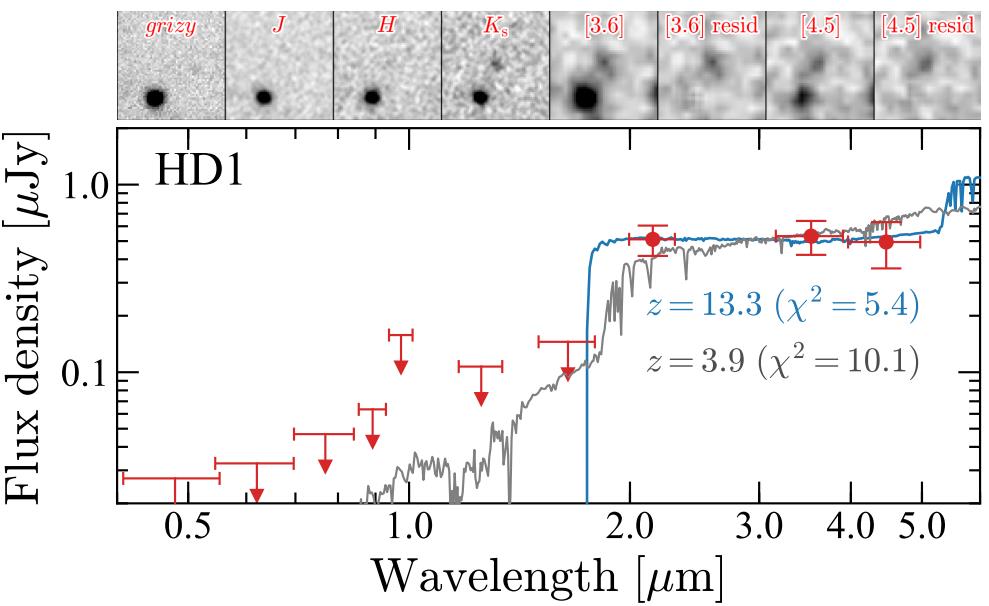 This determine presentations quite a lot of photometric filters (best) and the pictures of HD1 that they do or don’t disclose, in addition to two other suits to the photometric information. Observe that despite the fact that the high-redshift are compatible is awesome, spectroscopic affirmation is needed to understand which resolution (if both) is right kind. NIRSpec information puts this galaxy at a redshift of round z = 4, in keeping with the less-favored (secondary) photometric redshift.
This determine presentations quite a lot of photometric filters (best) and the pictures of HD1 that they do or don’t disclose, in addition to two other suits to the photometric information. Observe that despite the fact that the high-redshift are compatible is awesome, spectroscopic affirmation is needed to understand which resolution (if both) is right kind. NIRSpec information puts this galaxy at a redshift of round z = 4, in keeping with the less-favored (secondary) photometric redshift.
Credit score: Y. Harikane et al., ApJ, 2022
Because it grew to become out, HD1 has now been spectroscopically noticed with JWST’s NIRSpec device, and it’s, in truth, crimson, dusty, and reasonably shut by means of. The spectrum, in the event you have a look at it intimately, presentations a “spike” at 3.3 microns: a spike that’s a redshifted H-alpha line, akin to a redshift of kind of z = 4. This used to be no high-redshift galaxy in the end, and — regardless of what Wikipedia and Guinness could have stated — used to be by no means the cosmic record-holder. For the highest-redshift galaxies of all, photometric redshifts nonetheless require spectroscopic affirmation sooner than they may be able to be depended on. Many examples of photometric redshifts that shouldn’t be depended on till that affirmation arrives have abounded.
F200DB-045, these days indexed on Wikipedia as essentially the most remote candidate object, may well be at a redshift of 20 as one paper indicated, however others want a more in-depth (z = 4.4, and even z = 0.70) resolution. With out spectroscopy, we can not know.
Callum’s galaxy (CEERS-93316), inferred by means of astronomer Callum Donnan to have a photometric redshift of z = 16.4 within the CEERS information, had its spectrum taken, and used to be decided to be a crimson, dusty, nearer galaxy (at a modest redshift of z = 4.9) with emission traces boosting its long-wavelength mild sign as a result of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen indicators.
CEERS-DSFG-1, which looked as if it would showcase no mild at wavelengths as much as 1.5 microns, additionally grew to become out to be a dusty, a lot nearer starburst galaxy.
As of these days, there are nonetheless a minimum of a dozen recognized candidate galaxies that might spoil the present cosmic distance checklist if the spectroscopic information have been to be had. On the other hand, with most effective photometric redshifts to head off of, none of those will have to be depended on.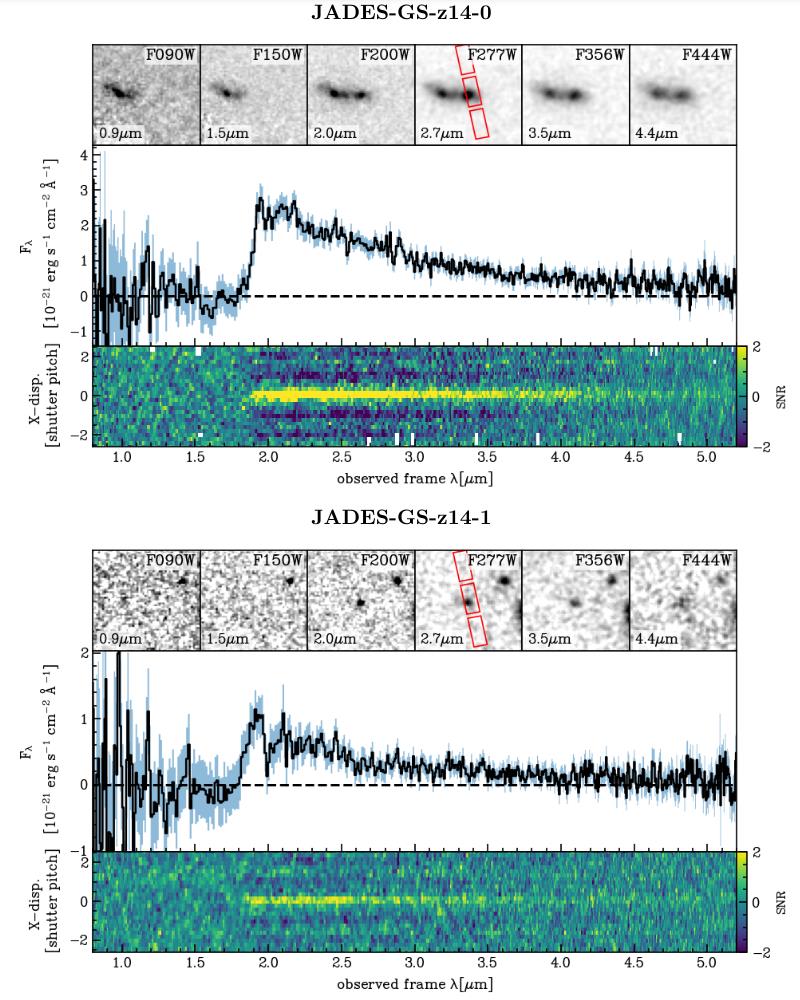 The extremely complicated NIRSpec device aboard JWST can take the sunshine from an overly tiny area of area. Via pointing the telescope accurately, the required assets, JADES-GS-z14-0 and JADES-GS-z14-1 on this case, can also be received one after the other from even extraordinarily close by, in part overlapping assets. The important thing “Lyman-break” characteristic is definitely observable within the spectrum of each galaxies, while photometric information presentations not anything at filters of one.5 microns or much less, however lots in filters of two.0 microns or higher.
The extremely complicated NIRSpec device aboard JWST can take the sunshine from an overly tiny area of area. Via pointing the telescope accurately, the required assets, JADES-GS-z14-0 and JADES-GS-z14-1 on this case, can also be received one after the other from even extraordinarily close by, in part overlapping assets. The important thing “Lyman-break” characteristic is definitely observable within the spectrum of each galaxies, while photometric information presentations not anything at filters of one.5 microns or much less, however lots in filters of two.0 microns or higher.
Credit score: S. Carniani et al. (JADES collaboration), arXiv:2405.18485, 2024
In September of 2024, greater than two years into the JWST technology, we at the moment know of ten galaxies, with tough spectroscopic affirmation, that surpass GN-z11 relating to distance.
Two of them have been discovered by means of the CEERS collaboration,
one used to be discovered by means of the GLASS collaboration,
two have been discovered by means of the UNCOVER collaboration,
one used to be recognized by means of Hubble however didn’t get spectroscopic information till the JADES collaboration measured it,
and 4 have been discovered and measured by means of the JADES collaboration.
It’s most effective by accident that the JADES collaboration were given there first in 2022, and once they did, essentially the most remote amongst their recognized galaxies used to be JADES-GS-z13-0: these days the 3rd maximum remote galaxy recognized. That first JWST checklist has most effective been damaged as soon as: when the JADES collaboration introduced in 2024 the invention of JADES-GS-z14-0 and JADES-GS-z14-1, these days the primary and 2d maximum remote galaxies recognized.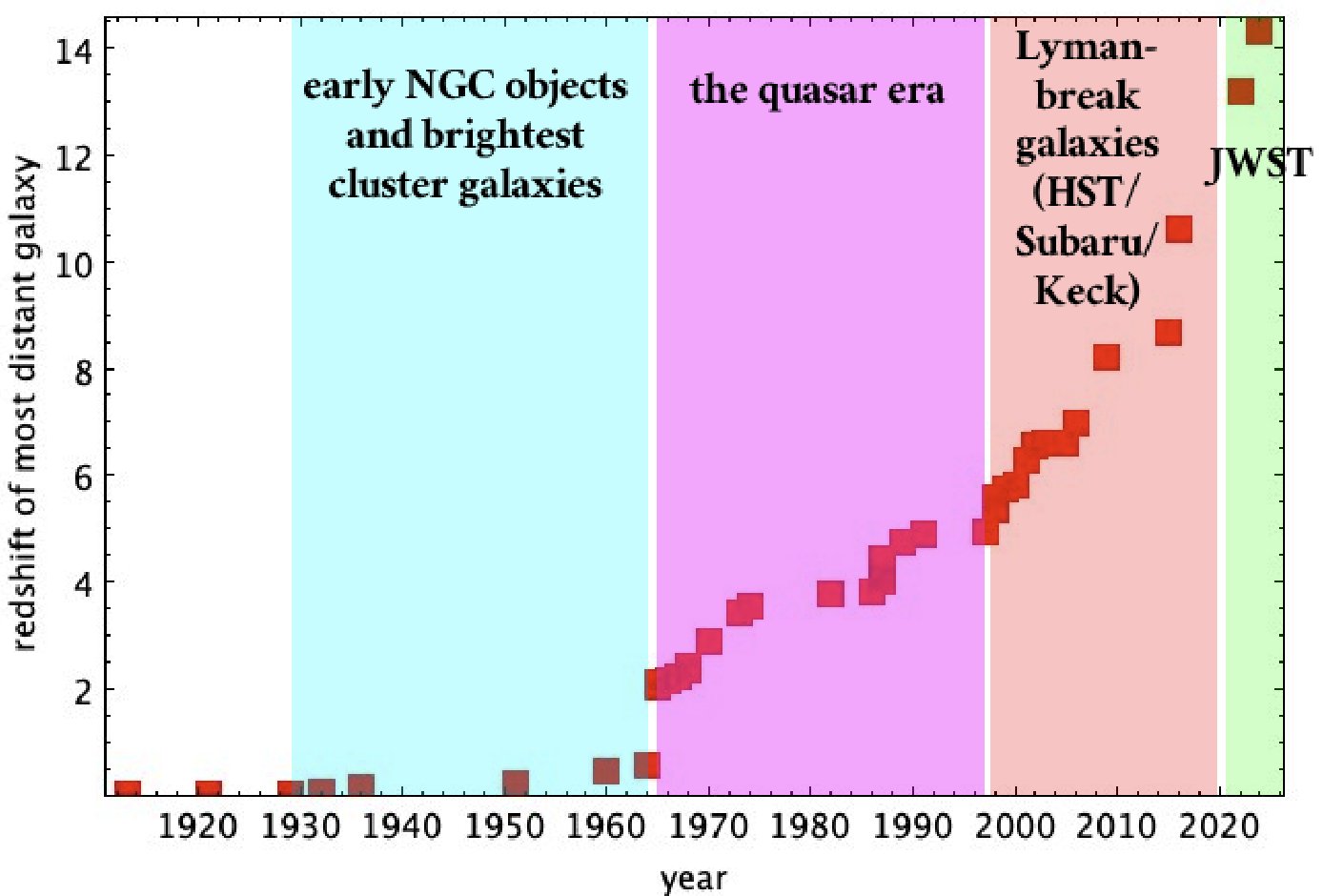 When you plot the cosmic distance checklist through the years, it’s transparent that there have been many huge jumps: within the Sixties, within the past due Nineties, and now once more within the 2020s within the JWST technology. Even though there are nonetheless uncertainties in cosmology, this new record-breaking galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, should seem between 270 and 305 million years after the Large Bang, akin to a redshift of z = 14.3.
When you plot the cosmic distance checklist through the years, it’s transparent that there have been many huge jumps: within the Sixties, within the past due Nineties, and now once more within the 2020s within the JWST technology. Even though there are nonetheless uncertainties in cosmology, this new record-breaking galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, should seem between 270 and 305 million years after the Large Bang, akin to a redshift of z = 14.3.
Credit score: Stefano Carniani/Kevin Hainline/Twitter
If the order of discovery were other, the checklist may have been set as much as as many as 5 and even six occasions by means of now; if some dusty, starbursting interlopers had grew to become out to be true ultra-distant galaxies, most likely that quantity could be even higher. It’s additionally imaginable that, when longer-period observations are undertaken by means of JWST, some even fainter, extra remote photometric galaxy applicants will probably be printed, and that the ones would possibly but surpass all present cosmic data. It’s essential to take into account that we’re most effective two years into JWST’s lifetime, with about two complete many years left to head. With each and every new galaxy and each and every new checklist, we’re gaining data-driven wisdom about sides of the early Universe that, simply two years in the past, have been only an issue of theoretical hypothesis.
Join the Begins With a Bang publication
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all











/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25640359/STK450_STK093_STK095_GOOGLE_EU_MICROSOFTD.jpg)

