Ruled through carbon-rich swamps and forests proliferating throughout Earth’s rocky floor, the Carboniferous duration noticed a spice up in atmospheric oxygen and huge amounts of carbon dioxide trapped in what in the end turned into Earth’s coal deposits. Terrestrial plant and animal lifestyles flourished amid those adjustments.
However now we have lengthy been lacking the earliest a part of that image, with maximum of our wisdom in this important level of Earth’s evolutionary previous coming from layers of coal-bearing swamp deposits shaped between 315 and 307 million years in the past, representing the Heart Pennsylvanian duration.
Now, a global workforce has found out a complete ecosystem preserved in sedimentary stone from the Early Pennsylvanian (a duration from round 320 to 318 million years in the past), containing greater than 100 other organisms.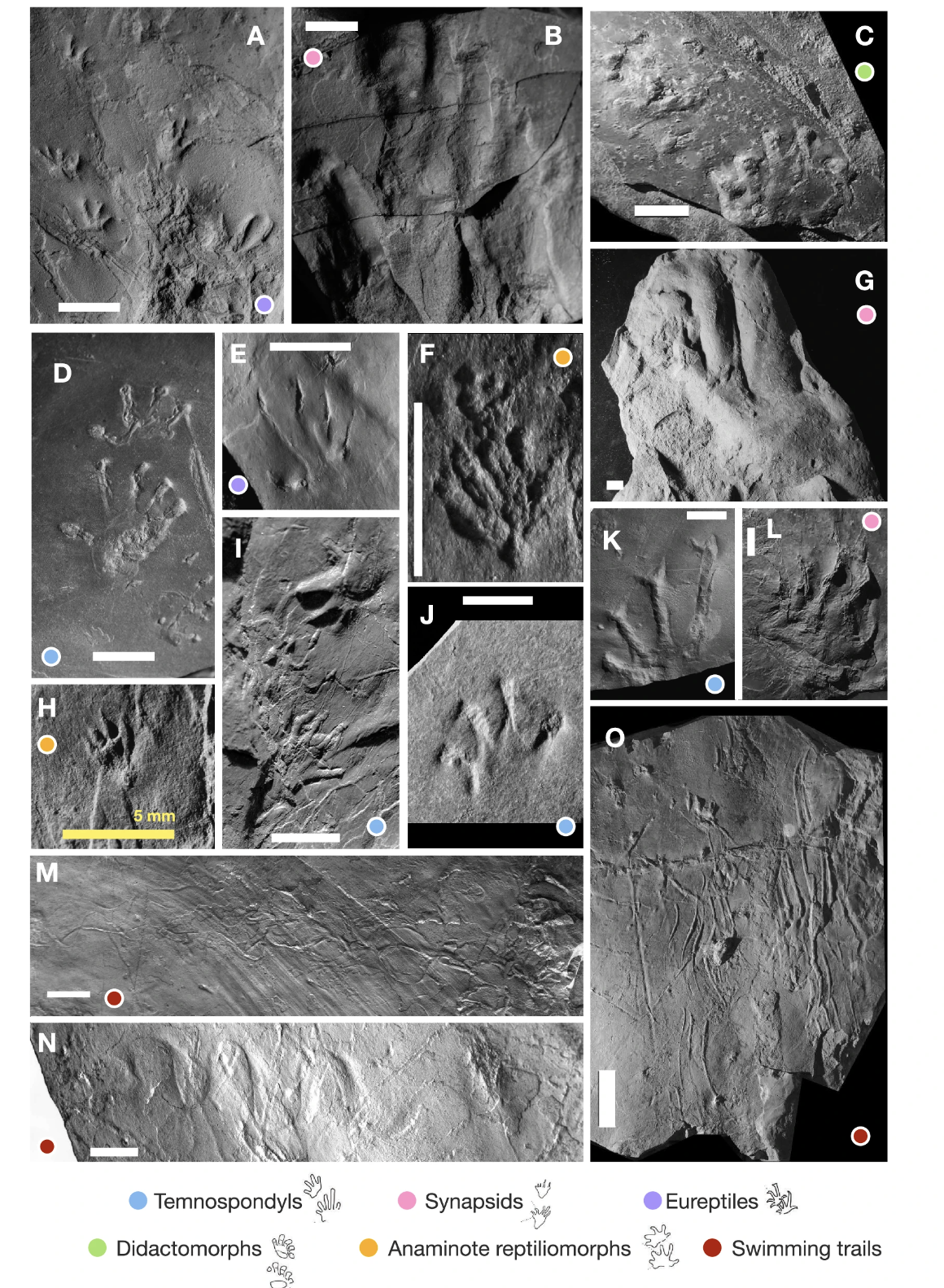 Vertebrate fossil teams from the Wamsutta Formation. Scale bars are 1 cm until differently said. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)The fossil website online, dubbed Lantern North, was once found out in jap North The us inside the Wamsutta Formation.
Vertebrate fossil teams from the Wamsutta Formation. Scale bars are 1 cm until differently said. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)The fossil website online, dubbed Lantern North, was once found out in jap North The us inside the Wamsutta Formation.
Its geological profile is distinct from different Pennsylvanian-era websites, being shaped from broken-up items of older rocks. Lantern North could also be a time pill of a drier, upland atmosphere that accommodates information of the day-to-day lives of tetrapod, arthropod, and seed plant teams at a time when terrestrial environments – and the creatures that had not too long ago expanded into them – had been converting all of a sudden.
Coarse layers of sedimentary rock interspersed with fossil-rich, oxidized-red wafers of sandstone shale shape a basin which were laid earlier than the duration’s signature carbonaceous deposits crammed in a swampy middle.
“The phenomenal preservation of refined impressions and strains lets in us to reconstruct behaviors and ecology in techniques now not in most cases conceivable with physique fossils on my own,” says College of Tennessee paleoecologist Jacob Benner, who led the learn about at the side of Harvard College paleobiologist Richard Knecht.
“We will see how those early terrestrial communities functioned as built-in ecosystems.” Invertebrate full-body impressions, physique fossils, tracks and trails. Scale bars = 1 cm, until said differently. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)”The fossiliferous pink shale facies might, due to this fact, constitute deposition in shallow depressions close to the bottom of a fan complicated that hosted ephemeral or seasonal ponds and swimming pools wherein suspended sediment may settle after a flood,” the authors write.
Invertebrate full-body impressions, physique fossils, tracks and trails. Scale bars = 1 cm, until said differently. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)”The fossiliferous pink shale facies might, due to this fact, constitute deposition in shallow depressions close to the bottom of a fan complicated that hosted ephemeral or seasonal ponds and swimming pools wherein suspended sediment may settle after a flood,” the authors write.
Most of these years, the ones layers have held the our bodies and imprints of historical vertebrates, invertebrates, and crops like carefully-pressed vegetation stored within the pages of a e book.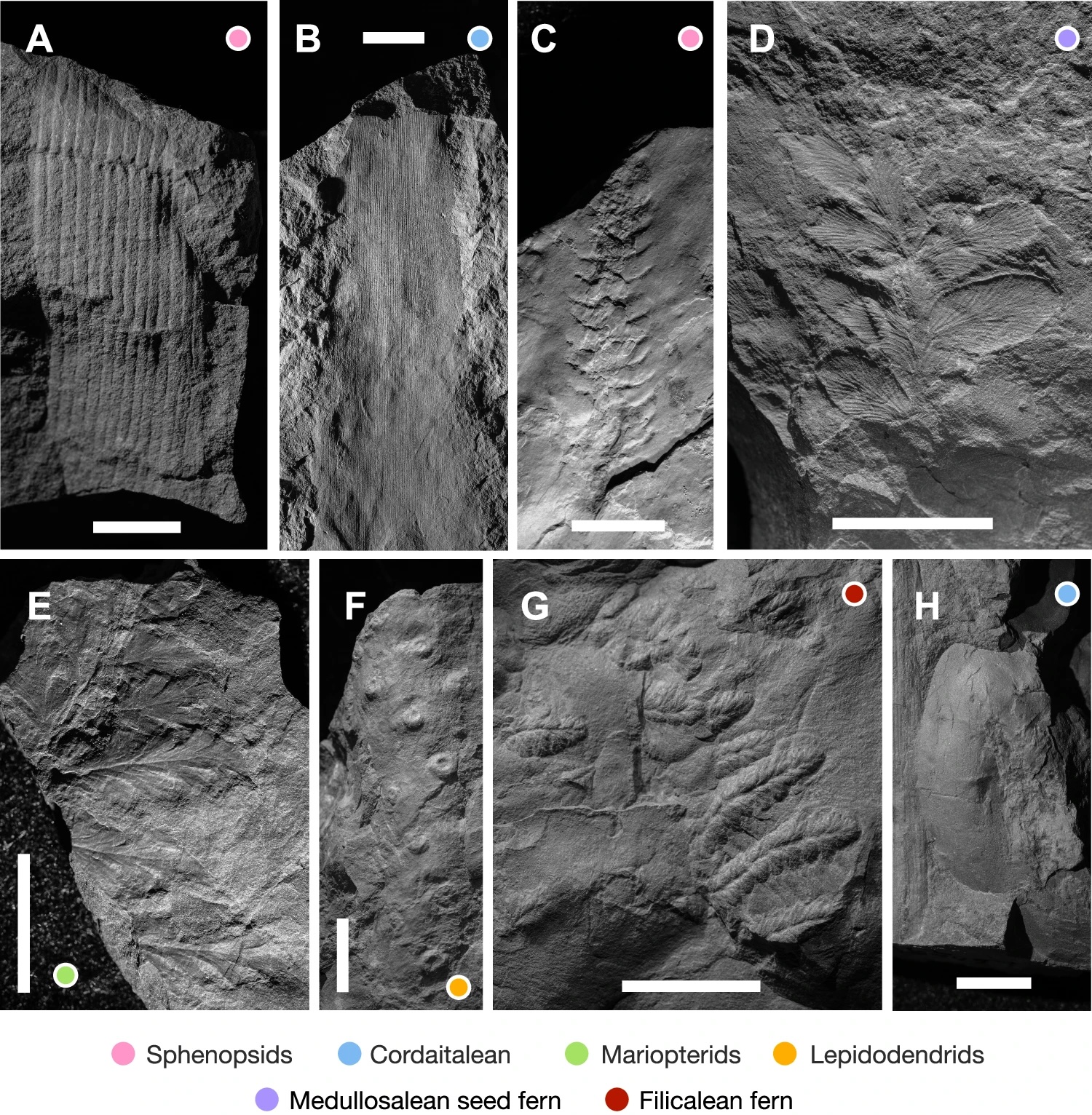 Macrofloral fossils from the Wamsutta Formation. Scale bars = 1 cm. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)The researchers known 131 other plant taxa, together with 83 distinctive types of plant foliage.
Macrofloral fossils from the Wamsutta Formation. Scale bars = 1 cm. (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)The researchers known 131 other plant taxa, together with 83 distinctive types of plant foliage.
This beautiful in finding additionally contains the earliest proof but of insect oviposition, wherein eggs are laid from an ovipositor into or onto a floor.
The scientists discovered lesions on a species of Cordaites, bushes that grew as much as round 30 meters (100 toes) and that could be the earliest conifers. Those lesions shape when bugs lay their eggs at the floor of a plant, and the newfound fossils counsel bugs could have begun depositing their eggs on this manner a minimum of 14 million years previous than we concept.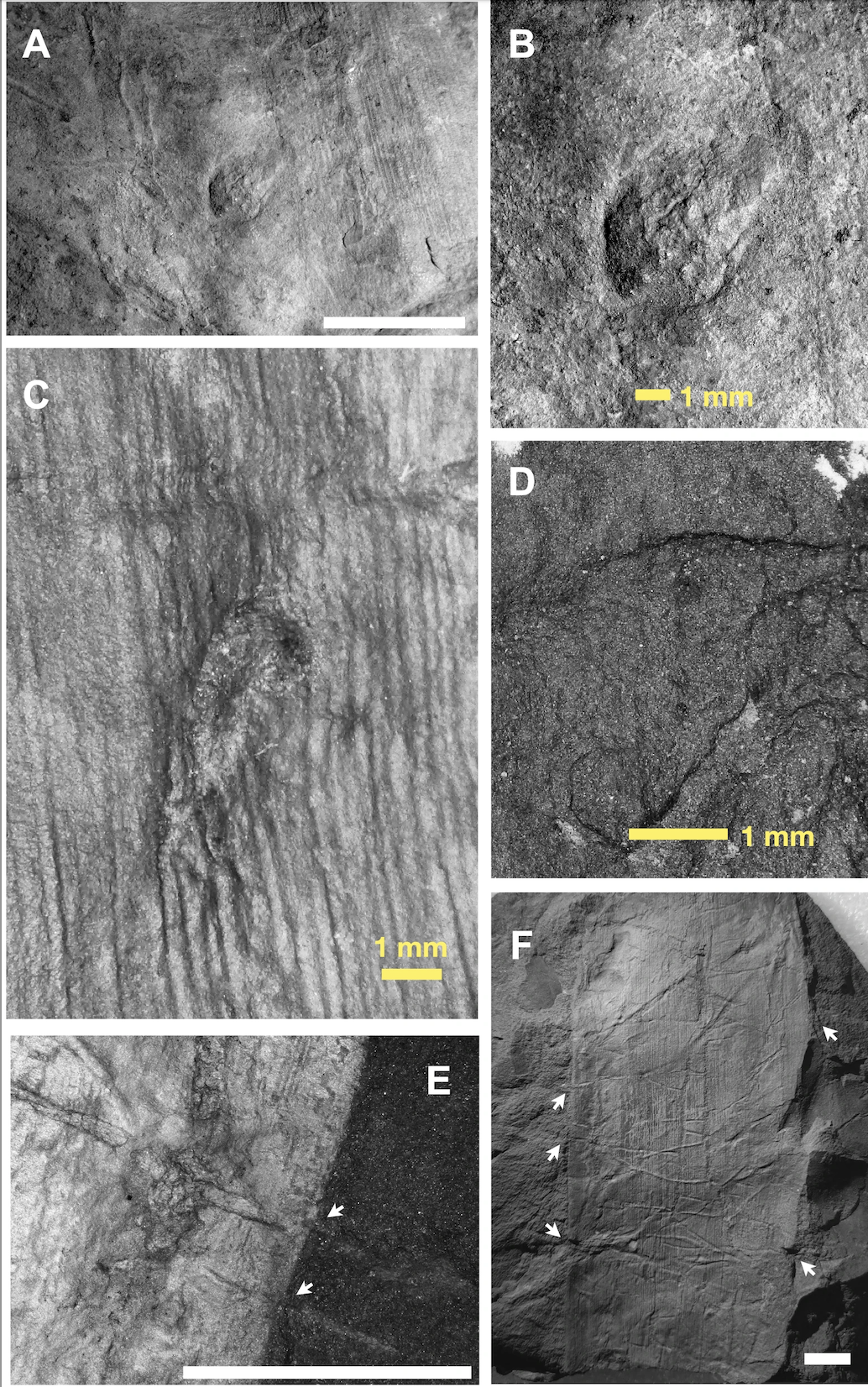 A) A gall preserved on Sigillaria species; B) Shut up of gall noticed in (A); C) An oviposition lesion preserved on Cordaites species; D) Piercing and sucking punctures on a Cordaites species; E) and F) Rhizomorphs on Cordaites species. (Scale bars = 1 cm, until said differently) (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)They have additionally exposed one of the vital earliest proof of insect gall formation, wherein the insect or its larvae burrow into the residing tissue of a plant to shape refuge and a meals supply. The insect modifies the plant’s enlargement chemically, forming unique shapes and bumps at the plant floor referred to as galls.
A) A gall preserved on Sigillaria species; B) Shut up of gall noticed in (A); C) An oviposition lesion preserved on Cordaites species; D) Piercing and sucking punctures on a Cordaites species; E) and F) Rhizomorphs on Cordaites species. (Scale bars = 1 cm, until said differently) (Knecht et al., Nature Communications, 2024)They have additionally exposed one of the vital earliest proof of insect gall formation, wherein the insect or its larvae burrow into the residing tissue of a plant to shape refuge and a meals supply. The insect modifies the plant’s enlargement chemically, forming unique shapes and bumps at the plant floor referred to as galls.
This, the researchers say, is among the oldest documented occurrences of insect-inflicted gall injury in our information.
“We are seeing proof of complicated plant-insect interactions and one of the vital earliest appearances of primary animal teams that went directly to dominate terrestrial habitats,” says Knecht.
“This website online offers us an extraordinary have a look at a terrestrial ecosystem from a a very powerful time within the evolution of lifestyles on land.”
One of these detailed document of this little-known time frame is certain to proceed revealing secrets and techniques of the early Carboniferous in long term research.This analysis is printed in Nature Communications.
Complete Fossilized Ecosystem Finds Over 100 Carboniferous Organisms















