Abstract: Scientists have evolved a brand new brain-mapping instrument known as START, which mixes transcriptomics and viral tracing to map the connections between particular neuronal subtypes with extraordinary element. This era lets in researchers to spot distinct patterns of connectivity in inhibitory neurons inside the cerebral cortex, offering a blueprint of the mind’s circuits.Via focused on those neuronal subtypes, the instrument may just result in extra exact remedies for neurological stipulations like autism and schizophrenia. START’s insights into mind microcircuits be offering new avenues for growing therapeutics with fewer unintended effects than present approaches.Key Info:START maps particular neuronal subtypes’ connections, enabling detailed mind circuit mapping.It identifies distinct inhibitory neuron subtypes within the cortex and their roles.This instrument may just result in precision remedies for neurological and psychiatric issues.Supply: Salk InstituteScientists on the Salk Institute are unveiling a brand new brain-mapping neurotechnology known as Unmarried Transcriptome Assisted Rabies Tracing (START). The state of the art instrument combines two complicated applied sciences—monosynaptic rabies virus tracing and single-cell transcriptomics—to map the mind’s intricate neuronal connections with unprecedented precision. The usage of the method, the researchers changed into the primary to spot the patterns of connectivity made by way of transcriptomic subtypes of inhibitory neurons within the cerebral cortex.They are saying having this skill to map the connectivity of neuronal subtypes will power the improvement of novel therapeutics that may goal sure neurons and circuits with better specificity. 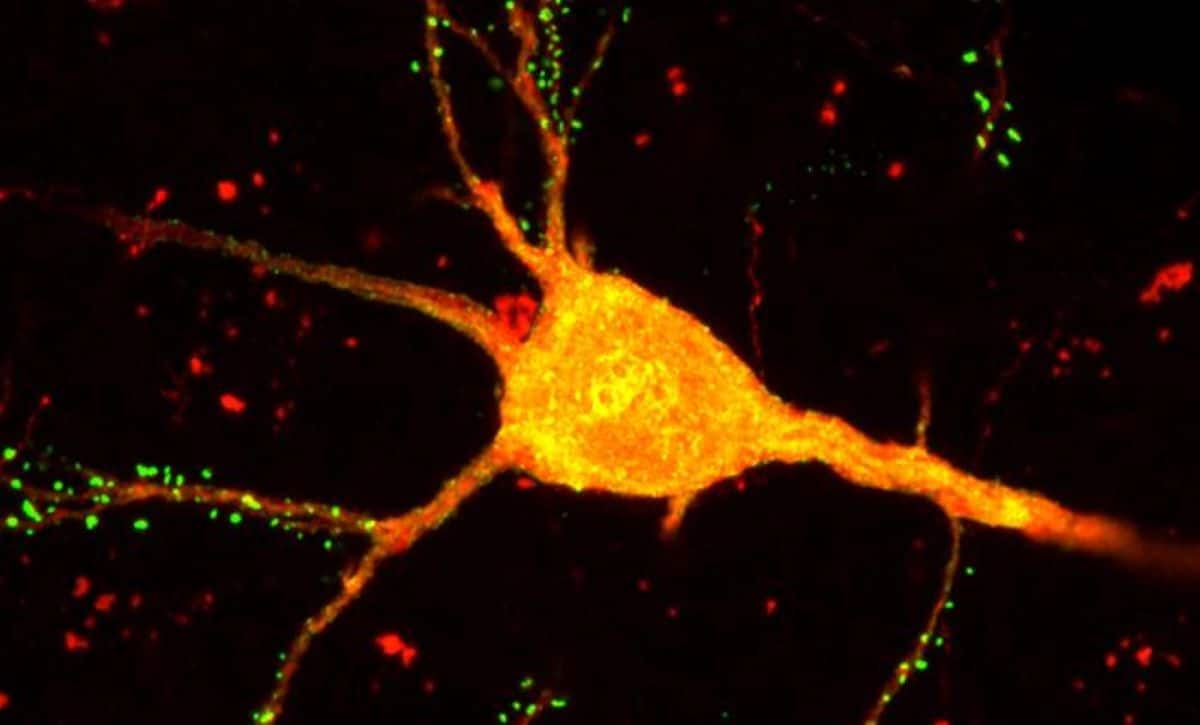 A cortical neuron classified with monosynaptic rabies virus (orange). Credit score: Salk InstituteSuch remedies may well be simpler and bring fewer unintended effects than present pharmacological approaches.The learn about, printed on September 30, 2024, in Neuron, is the primary to unravel cortical connectivity on the answer of transcriptomic cellular sorts.“In relation to treating neurological and neuropsychiatric issues, we’ve necessarily been seeking to repair a system with out absolutely figuring out its portions,” says senior writer Edward Callaway, professor and Vincent J. Coates Chair in Molecular Neurobiology at Salk.“START helps us create an in depth blueprint of the mind’s many portions and the way all of them attach.”It’s like seeking to restore a automobile with out realizing what an engine or an axle is, he says. However in case you had a diagram of the automobile’s portions, it is advisable begin to know how they could paintings in combination to make the wheels spin and the automobile transfer. That wisdom would then make it a lot more uncomplicated to identify an issue within the machine and work out which gear you’ll want to repair it.When describing a mind’s portions, neurons are to start with grouped into two huge categories: excitatory (those who stimulate mind task) and inhibitory (those who suppress task)—very similar to the accelerator and brake in a automobile.From there they may be able to be additional looked after into subclasses: Excitatory neurons are classified by way of the layer of the mind they’re in whilst inhibitory neurons are known by way of the marker proteins they categorical. Contemporary advances in transcriptomics now permit those subclasses to be damaged down even additional. The usage of single-cell RNA sequencing, scientists can now staff cells with identical gene expression patterns and outline each and every cluster as a selected neuronal subtype.“Defining a cellular variety is difficult as a result of it’s possible you’ll staff cells another way relying on which manner you’re the usage of to take a look at them,” Callaway says.“Two cells could have rather other gene expression patterns however carry out a identical serve as, or two cells with identical gene expression may well be additional separated in response to their anatomy, connectivity, or body structure.“For those who best believe a type of options, it is advisable finally end up over-splitting or under-splitting the teams. START is helping us perceive what degree of categorization could also be maximum significant to circuit serve as, and that may tell which cells to focus on with new therapeutics.”To create START, the Callaway lab engineered a solution to mix single-cell RNA sequencing with any other method that they had evolved in the past: monosynaptic rabies virus tracing.The way shall we a changed virus hop from one cellular form of pastime to simply the cells at once hooked up to it. Via detecting the place the virus finally ends up, the researchers can map which cells are hooked up to which.The researchers first used their new instrument to discover connectivity patterns within the mouse visible cortex. START used to be ready to unravel round 50 other subtypes of inhibitory neurons on this area and map their connections to excitatory neurons in each and every layer of the cortex.The researchers’ findings known distinct connectivity patterns throughout more than a few transcriptomic subtypes of inhibitory neurons that might now not were outstanding the usage of earlier strategies. “Other people ceaselessly deal with all inhibitory neurons as a unmarried uniform staff, however they’re in reality very numerous, and seeking to learn about or clinically goal them as one staff can difficult to understand essential variations which are essential to mind serve as and illness,” says first writer Maribel Patiño, a former graduate pupil in Callaway’s lab and present psychiatry resident at UC San Diego Faculty of Drugs.START published that each and every cortical layer of excitatory neurons won selective enter from particular transcriptomic subtypes of Sst, Pvalb, Vip, and Lamp5 inhibitory cells. Each and every subtype’s distinctive connectivity is helping identify subtle microcircuits that most probably give a contribution to specialised mind purposes.As an example, the researchers had been ready to unravel an inhibitory subtype known as Sst Chodl cells, which might be regarded as related to sleep law. The usage of START, they discovered that Chodl cells had been the cellular variety maximum densely hooked up to layer 6 excitatory neurons, which might be recognized to mission to the thalamus to coordinate sleep rhythms.This extraordinary answer will permit neuroscientists to proceed uncovering how particular neuronal subtypes form the mind’s circuitry to provide our ideas, perceptions, feelings, and behaviors.The researchers’ subsequent steps are to create viral vectors and gene-editing applied sciences that focus on each and every person cellular subtype. Sooner or later, those gear may well be tailored into novel therapeutics that selectively regulate the particular neuron populations contributing to stipulations comparable to autism, Rett syndrome, and schizophrenia. “We don’t know precisely how this data goes for use 10 or two decades from now, however what we do know is that applied sciences are converting hastily, and the best way the mind is handled nowadays with medication isn’t the best way the mind can be handled sooner or later,” says Callaway.“START can lend a hand power this innovation, so the viruses and assets are all freely to be had for all of the neuroscience group to make use of.”Different authors come with Marley A. Rossa, Willian Nuñez Lagos, and Neelakshi S. Patne of the Salk Institute.Investment: The paintings used to be supported by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R34 NS116885, T32 GM007198, P30 014195, S10 OD023689) and the Paul and Daisy Soros Fellowship for New American citizens.About this mind mapping and neurotech analysis newsAuthor: Salk Communications
A cortical neuron classified with monosynaptic rabies virus (orange). Credit score: Salk InstituteSuch remedies may well be simpler and bring fewer unintended effects than present pharmacological approaches.The learn about, printed on September 30, 2024, in Neuron, is the primary to unravel cortical connectivity on the answer of transcriptomic cellular sorts.“In relation to treating neurological and neuropsychiatric issues, we’ve necessarily been seeking to repair a system with out absolutely figuring out its portions,” says senior writer Edward Callaway, professor and Vincent J. Coates Chair in Molecular Neurobiology at Salk.“START helps us create an in depth blueprint of the mind’s many portions and the way all of them attach.”It’s like seeking to restore a automobile with out realizing what an engine or an axle is, he says. However in case you had a diagram of the automobile’s portions, it is advisable begin to know how they could paintings in combination to make the wheels spin and the automobile transfer. That wisdom would then make it a lot more uncomplicated to identify an issue within the machine and work out which gear you’ll want to repair it.When describing a mind’s portions, neurons are to start with grouped into two huge categories: excitatory (those who stimulate mind task) and inhibitory (those who suppress task)—very similar to the accelerator and brake in a automobile.From there they may be able to be additional looked after into subclasses: Excitatory neurons are classified by way of the layer of the mind they’re in whilst inhibitory neurons are known by way of the marker proteins they categorical. Contemporary advances in transcriptomics now permit those subclasses to be damaged down even additional. The usage of single-cell RNA sequencing, scientists can now staff cells with identical gene expression patterns and outline each and every cluster as a selected neuronal subtype.“Defining a cellular variety is difficult as a result of it’s possible you’ll staff cells another way relying on which manner you’re the usage of to take a look at them,” Callaway says.“Two cells could have rather other gene expression patterns however carry out a identical serve as, or two cells with identical gene expression may well be additional separated in response to their anatomy, connectivity, or body structure.“For those who best believe a type of options, it is advisable finally end up over-splitting or under-splitting the teams. START is helping us perceive what degree of categorization could also be maximum significant to circuit serve as, and that may tell which cells to focus on with new therapeutics.”To create START, the Callaway lab engineered a solution to mix single-cell RNA sequencing with any other method that they had evolved in the past: monosynaptic rabies virus tracing.The way shall we a changed virus hop from one cellular form of pastime to simply the cells at once hooked up to it. Via detecting the place the virus finally ends up, the researchers can map which cells are hooked up to which.The researchers first used their new instrument to discover connectivity patterns within the mouse visible cortex. START used to be ready to unravel round 50 other subtypes of inhibitory neurons on this area and map their connections to excitatory neurons in each and every layer of the cortex.The researchers’ findings known distinct connectivity patterns throughout more than a few transcriptomic subtypes of inhibitory neurons that might now not were outstanding the usage of earlier strategies. “Other people ceaselessly deal with all inhibitory neurons as a unmarried uniform staff, however they’re in reality very numerous, and seeking to learn about or clinically goal them as one staff can difficult to understand essential variations which are essential to mind serve as and illness,” says first writer Maribel Patiño, a former graduate pupil in Callaway’s lab and present psychiatry resident at UC San Diego Faculty of Drugs.START published that each and every cortical layer of excitatory neurons won selective enter from particular transcriptomic subtypes of Sst, Pvalb, Vip, and Lamp5 inhibitory cells. Each and every subtype’s distinctive connectivity is helping identify subtle microcircuits that most probably give a contribution to specialised mind purposes.As an example, the researchers had been ready to unravel an inhibitory subtype known as Sst Chodl cells, which might be regarded as related to sleep law. The usage of START, they discovered that Chodl cells had been the cellular variety maximum densely hooked up to layer 6 excitatory neurons, which might be recognized to mission to the thalamus to coordinate sleep rhythms.This extraordinary answer will permit neuroscientists to proceed uncovering how particular neuronal subtypes form the mind’s circuitry to provide our ideas, perceptions, feelings, and behaviors.The researchers’ subsequent steps are to create viral vectors and gene-editing applied sciences that focus on each and every person cellular subtype. Sooner or later, those gear may well be tailored into novel therapeutics that selectively regulate the particular neuron populations contributing to stipulations comparable to autism, Rett syndrome, and schizophrenia. “We don’t know precisely how this data goes for use 10 or two decades from now, however what we do know is that applied sciences are converting hastily, and the best way the mind is handled nowadays with medication isn’t the best way the mind can be handled sooner or later,” says Callaway.“START can lend a hand power this innovation, so the viruses and assets are all freely to be had for all of the neuroscience group to make use of.”Different authors come with Marley A. Rossa, Willian Nuñez Lagos, and Neelakshi S. Patne of the Salk Institute.Investment: The paintings used to be supported by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R34 NS116885, T32 GM007198, P30 014195, S10 OD023689) and the Paul and Daisy Soros Fellowship for New American citizens.About this mind mapping and neurotech analysis newsAuthor: Salk Communications
Supply: Salk Institute
Touch: Salk Communications – Salk Institute
Symbol: The picture is credited to Salk InstituteOriginal Analysis: Open get admission to.
“Transcriptomic cell-type specificity of native cortical circuits” by way of Edward Callaway et al. NeuronAbstractTranscriptomic cell-type specificity of native cortical circuitsComplex neocortical purposes depend on networks of various excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Whilst native connectivity regulations between primary neuronal subclasses were established, the specificity of connections on the degree of transcriptomic subtypes stays unclear.We introduce unmarried transcriptome assisted rabies tracing (START), one way combining monosynaptic rabies tracing and single-nuclei RNA sequencing to spot transcriptomic cellular sorts, offering inputs to outlined neuron populations. We make use of START to transcriptomically symbolize inhibitory neurons offering monosynaptic enter to five other layer-specific excitatory cortical neuron populations in mouse number one visible cortex (V1).On the subclass degree, we follow effects in line with findings from prior research that unravel neuronal subclasses the usage of antibody staining, transgenic mouse strains, and morphological reconstruction.With progressed neuronal subtype granularity completed with START, we exhibit transcriptomic subtype specificity of inhibitory inputs to more than a few excitatory neuron subclasses. Those effects identify native connectivity regulations on the answer of transcriptomic inhibitory cellular sorts.
New Mind Mapping Instrument Unearths Detailed Neuronal Connections – Neuroscience Information













