The arena is grappling with a big disaster of plastic air pollution. Each and every yr, numerous lots of plastic waste finally end up in Earth’s oceans, rivers, and landfills.
Researchers at Northwestern College have offered a herbal resolution that would assist battle the rising factor of plastic air pollution. They have got known a wastewater micro organism this is able to breaking down PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastic.
Amongst all plastic waste, PET is especially problematic because of its sturdiness and resistance to degradation.
It’s broadly utilized in meals packaging and beverage bottles. As soon as discarded, it might stay within the surroundings for many years, harming natural world and contaminating water assets.
“We’ve got systematically proven, for the primary time, {that a} wastewater bacterium can take a beginning plastic subject material, go to pot it, fragment it, destroy it down and use it as a supply of carbon,” stated Ludmilla Aristilde, who led the find out about.
“It’s superb that this bacterium can carry out that complete procedure, and we known a key enzyme answerable for breaking down the plastic fabrics. This might be optimized and exploited to assist do away with plastics within the surroundings,” Aristilde added.
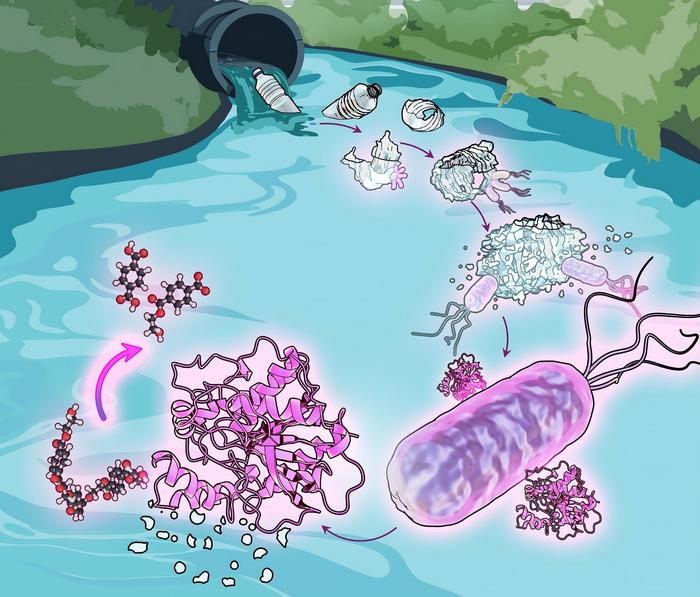 Comamonas micro organism reside in wastewater, the place they destroy down plastic waste for meals. Ludmilla Aristilde/Northwestern College
Comamonas micro organism reside in wastewater, the place they destroy down plastic waste for meals. Ludmilla Aristilde/Northwestern College
The breakdown procedure
Researchers have known the hidden energy of Comamonas testosteri bacterium: it feeds on plastic waste. It’s an environmental microorganism present in city waterways and wastewater.
Despite the fact that the bacterium has been actively degrading plastic for a very long time, its position on this procedure remained unrecognized till now.
The micro organism’s skill to degrade plastic is mediated via a mix of bodily and biochemical processes.
The bacterium works via first chewing the plastic into tiny items. The organisms then free up an enzyme into motion that additional degrades the plastic, permitting the micro organism to soak up the carbon atoms as vitamins.
Those underlying processes had been elucidated thru a mix of theoretical and experimental strategies. For this, the staff remoted bacterium from wastewater. They had been then grown in laboratory prerequisites on PET substrates, simulating their herbal surroundings.
The use of complicated microscopy ways, the researchers carefully tested the adjustments at the floor of the plastic subject material. The encompassing water used to be moderately analyzed to search for proof of plastic degradation in addition to the presence of nanoplastics.
Concurrently, they tested the inner construction of the micro organism to spot the mechanisms fascinated with plastic breakdown.
“Within the presence of the bacterium, the microplastics had been damaged down into tiny nanoparticles of plastics,” Aristilde defined. “We discovered that the wastewater bacterium has an innate skill to degrade plastic all of the approach all the way down to monomers, small development blocks which sign up for in combination to shape polymers. Those small gadgets are a bioavailable supply of carbon that micro organism can use for enlargement.”
Function of enzyme
Aristilde’s staff additional known a selected enzyme utilized by the micro organism to damage down PET. To substantiate the enzyme’s position in plastic degradation, they created bacterial cells with out this enzyme and located that their skill to degrade plastic used to be considerably lowered or misplaced.
The authors spotlight that nanoplastics may also be created in wastewater remedy crops via micro organism.
“That’s one thing we’d like to concentrate on as our society tries to grasp the conduct of plastics all over its adventure from wastewater to receiving rivers and lakes,” Aristilde famous.
As in step with the clicking free up, PET makes up 12% of all plastic in use and 50% of microplastics in wastewater. Therefore, its protected disposal is a big fear.
This discovery may just result in new bacteria-based tactics to wash up plastic waste from water our bodies.
The findings had been printed within the magazine Environmental Science & Generation.












/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25656820/All_New_202025_20Ford_20Expedition_Platinum_20Ultimate_04.jpg)