The usage of the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), astronomers have noticed the earliest tough “galaxy-size” wind blowing from a feeding supermassive black hole-powered quasar. The tough wind is pushing fuel and dirt from its galaxy at unbelievable speeds, killing famous person delivery in its host galaxy. This quasar, designated J1007+2115, is so remote that it’s noticed because it was once simply 700 million years after the Giant Bang — when the 13.8 billion-year-old universe was once simply round 5% of its present age. Although this makes J1007+2115 simply the third-earliest quasar ever noticed, it’s the earliest ever seen with a formidable, galaxy-size wind flowing from it.The outflows from this quasar are not simply exceptional for his or her antiquity, regardless that. The winds from J1007+2115 stretch out from the black gap at their supply for a staggering 7,500 light-years, which is an identical to round 25 sun methods coated up side-by-side. The fabric they shunt every 12 months is an identical to 300 suns at speeds an identical to six,000 instances the velocity of sunshine, researchers mentioned.”It’s the third-earliest and third-most-distant quasar powered by way of an accreting supermassive black gap identified these days,” discovery workforce chief and College of Arizona researcher Weizhe Liu advised House.com. “To our wisdom, this galaxy-scale quasar-driven wind is lately the earliest one identified.”Similar: How black-hole-powered quasars killed off neighboring galaxies within the early universeThe winds from this feeding central supermassive black gap will even be tough sufficient to “kill” the host galaxy they rip via at 6,000 instances the velocity of sound, by way of depriving it of the subject had to delivery new stars.How supermassive black holes get windAll huge galaxies are believed to have at their hearts a supermassive black gap, carrying a mass between thousands and thousands and billions of instances that of the solar. However no longer all of those black holes energy quasars, the brightest resources of sunshine within the cosmos. Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!That is as a result of some supermassive black holes are not surrounded by way of huge quantities of fuel and dirt that they are able to feed on. For example, the supermassive black gap on the middle of our personal galaxy, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), is quiet and dim.Different supermassive black holes are surrounded by way of a wealth of subject material swirling round them in a flattened cloud known as an accretion disk that steadily feeds them. The immense gravitational affect of the central black gap reasons tough friction in accretion disks, heating this subject material and inflicting it to glow brightly.Those areas, known as energetic galactic nuclei (AGNs) are so brilliant they are able to outshine the blended mild of each and every famous person within the galaxy round them. When noticed at nice distances, those areas are known as “quasars.”The tough radiation emitted by way of accretion disks has any other impact, too: It pushes away subject like fuel and dirt from across the AGN. Those quasar winds too can push fuel and dirt clear of the broader quasar-hosting galaxy.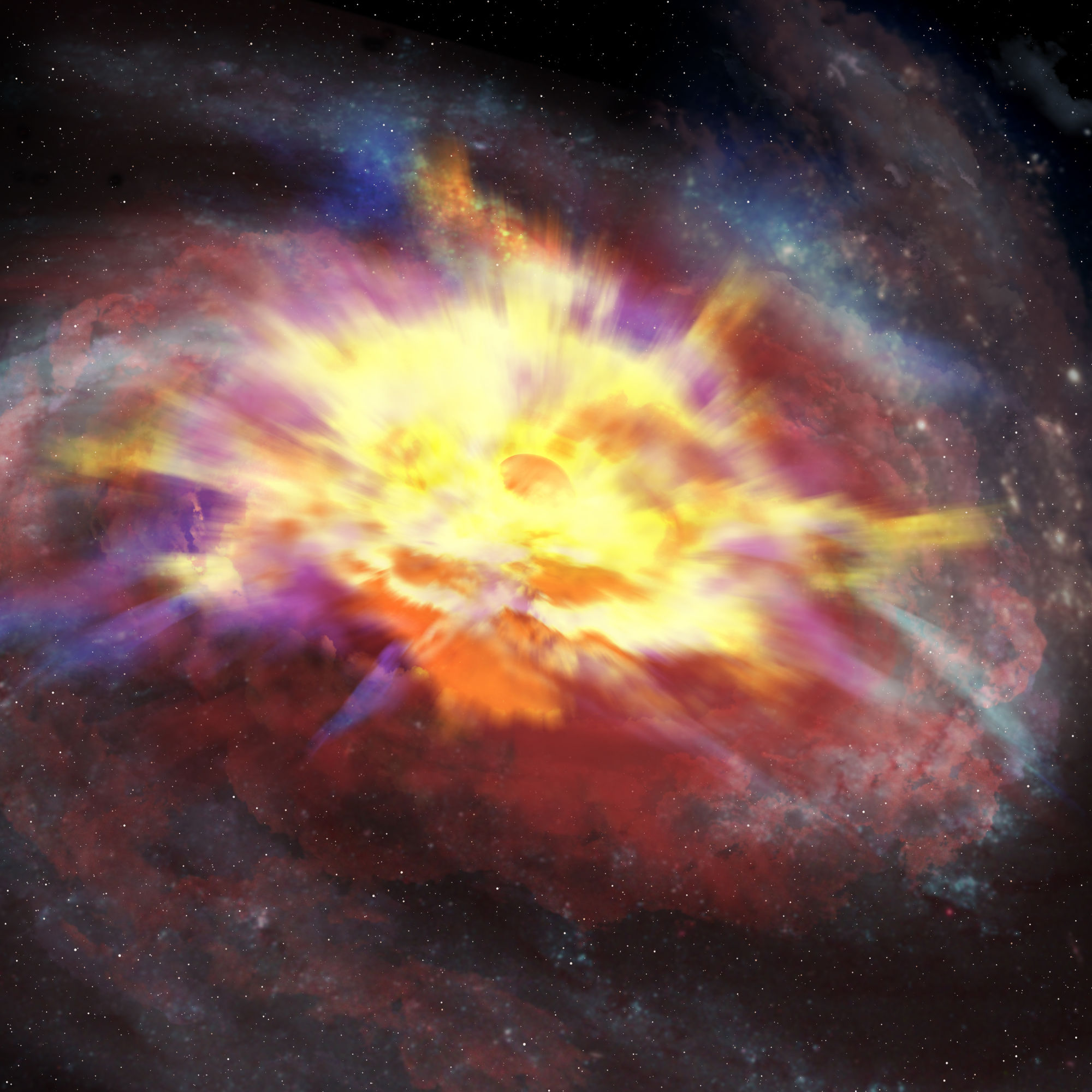 An artist’s depiction, in infrared mild, of a quasar-driven wind emanating from the core of galaxy. (Symbol credit score: Global Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/P. Marenfeld)With assistance from the JWST, the researchers had been ready to peer that the fabric within the quasar winds from J1007+2115 is touring at an improbable 4.7 million mph (7.6 million kph). As it’s possible you’ll consider, such tough and far-reaching winds raise a limiteless quantity of subject. Liu mentioned that the quasar winds from J1007+2115 are wearing subject material with a mass an identical to 300 suns every 12 months.The galaxy that properties J1007+2115 is wealthy in dense molecular fuel and dirt, the development blocks of stars, as noticed by way of the JWST. The galaxy paperwork stars at a fee of round 80 to 250 sun plenty once a year. However the mild from that galaxy has been touring to us for 13.1 billion years, which means it’s most likely reasonably other now. Specifically, thank you to those quasar winds, starburst task won’t have endured for lengthy.
An artist’s depiction, in infrared mild, of a quasar-driven wind emanating from the core of galaxy. (Symbol credit score: Global Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/P. Marenfeld)With assistance from the JWST, the researchers had been ready to peer that the fabric within the quasar winds from J1007+2115 is touring at an improbable 4.7 million mph (7.6 million kph). As it’s possible you’ll consider, such tough and far-reaching winds raise a limiteless quantity of subject. Liu mentioned that the quasar winds from J1007+2115 are wearing subject material with a mass an identical to 300 suns every 12 months.The galaxy that properties J1007+2115 is wealthy in dense molecular fuel and dirt, the development blocks of stars, as noticed by way of the JWST. The galaxy paperwork stars at a fee of round 80 to 250 sun plenty once a year. However the mild from that galaxy has been touring to us for 13.1 billion years, which means it’s most likely reasonably other now. Specifically, thank you to those quasar winds, starburst task won’t have endured for lengthy.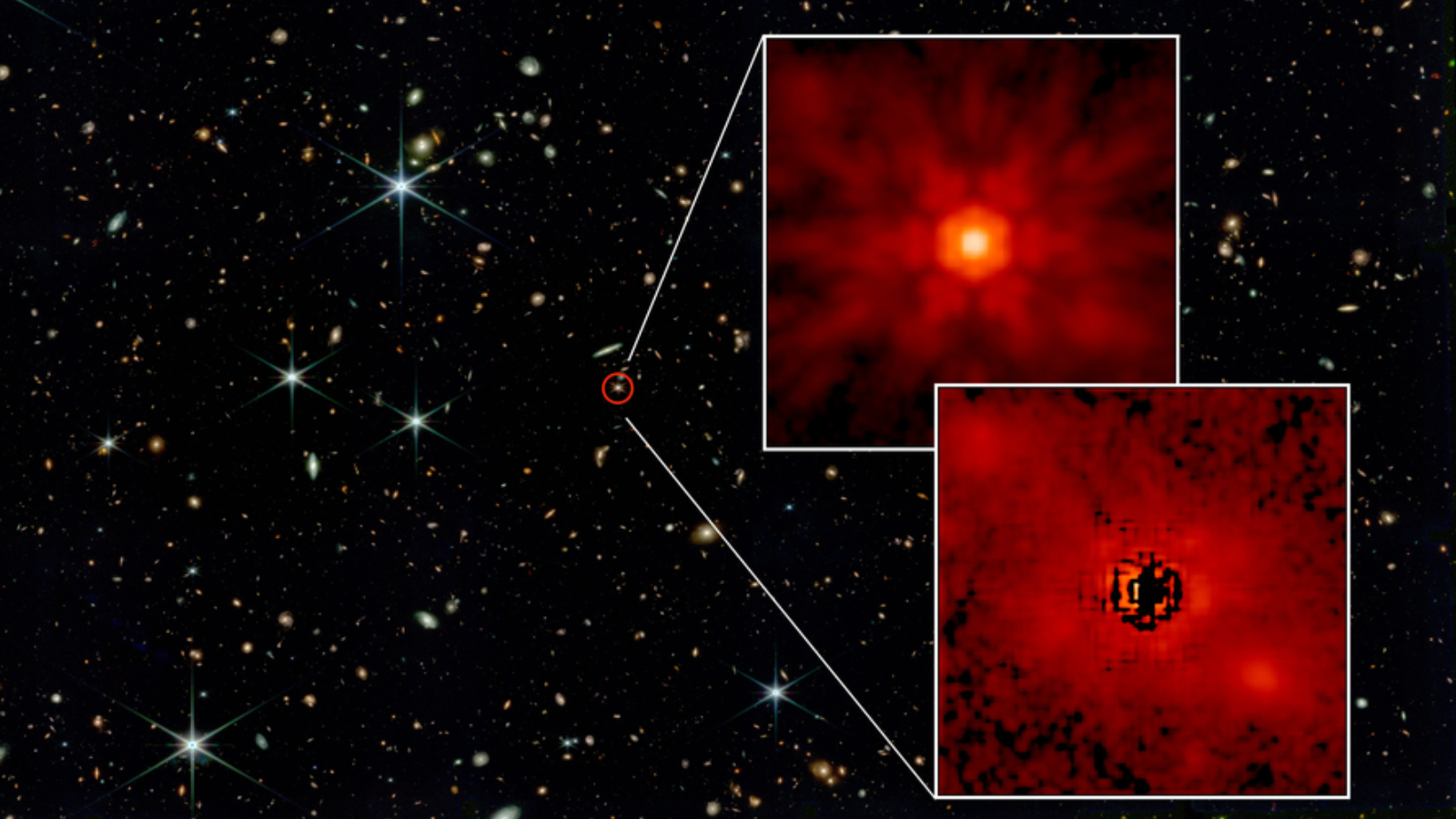 A James Webb House Telescope symbol of the quasar J0148. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Yue, et al)The purging of fuel and dirt by means of those quasar winds can even bring to an end the meals provide for the supermassive black gap using them. Which means that the expansion of the supermassive black gap, with a mass estimated to be equivalent to that of one billion suns, could have additionally been halted.”The wind is pushing a considerable amount of fuel outwards,” Liu mentioned. “This may occasionally suppress the famous person formation task of the galaxy, which wishes fuel to shape stars, and likewise the expansion of the supermassive black gap itself, which additionally wishes the accretion of fuel.”This might imply that this early galaxy is now a lifeless galaxy and is not rising a lot on account of its star-forming subject material being purged and its famous person delivery being curtailed.Similar: Brightest quasar ever noticed is powered by way of black gap that eats a ‘solar an afternoon’The workforce is not performed with quasar winds and investigating their affect on their host galaxies. They’re going to proceed to seek them and will even discover extra that existed lower than one thousand million years after the Giant Bang.”We now intention to search for extra such galaxy-scale, quasar-driven winds within the
A James Webb House Telescope symbol of the quasar J0148. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Yue, et al)The purging of fuel and dirt by means of those quasar winds can even bring to an end the meals provide for the supermassive black gap using them. Which means that the expansion of the supermassive black gap, with a mass estimated to be equivalent to that of one billion suns, could have additionally been halted.”The wind is pushing a considerable amount of fuel outwards,” Liu mentioned. “This may occasionally suppress the famous person formation task of the galaxy, which wishes fuel to shape stars, and likewise the expansion of the supermassive black gap itself, which additionally wishes the accretion of fuel.”This might imply that this early galaxy is now a lifeless galaxy and is not rising a lot on account of its star-forming subject material being purged and its famous person delivery being curtailed.Similar: Brightest quasar ever noticed is powered by way of black gap that eats a ‘solar an afternoon’The workforce is not performed with quasar winds and investigating their affect on their host galaxies. They’re going to proceed to seek them and will even discover extra that existed lower than one thousand million years after the Giant Bang.”We now intention to search for extra such galaxy-scale, quasar-driven winds within the
very early universe and get to understand their homes as a inhabitants,” Liu concluded.A pre-print model of the workforce’s analysis is featured at the paper repository arXiv.
Historic supermassive black gap is blowing galaxy-killing wind, James Webb House Telescope reveals