A workforce of cave divers and scientists have exposed a brand new cache of extinct monkey fossils submerged deep throughout the underwater passages of a Caribbean cave.40 years in the past, just a few well-preserved stays of New International monkeys were discovered at the Caribbean islands of Hispaniola and Jamaica, but it surely was once sufficient to trace at a lacking patch of primate evolutionary historical past.
This sort of fossil species was once the Hispaniola monkey (Antillothrix bernensis), recognized best by way of an ankle bone and a couple of bits of damaged jaw.
However with enhancements in cave diving protection and era, researchers have probed deeper into the islands’ flooded cave programs since 2009, with the primary A. bernensis cranium present in 2011. Those submarine caverns, vital to the indigenous Taíno other people, are studded with “remarkably well-preserved” fossils that experience lain there for millennia, secure from the jostling of waves and animals.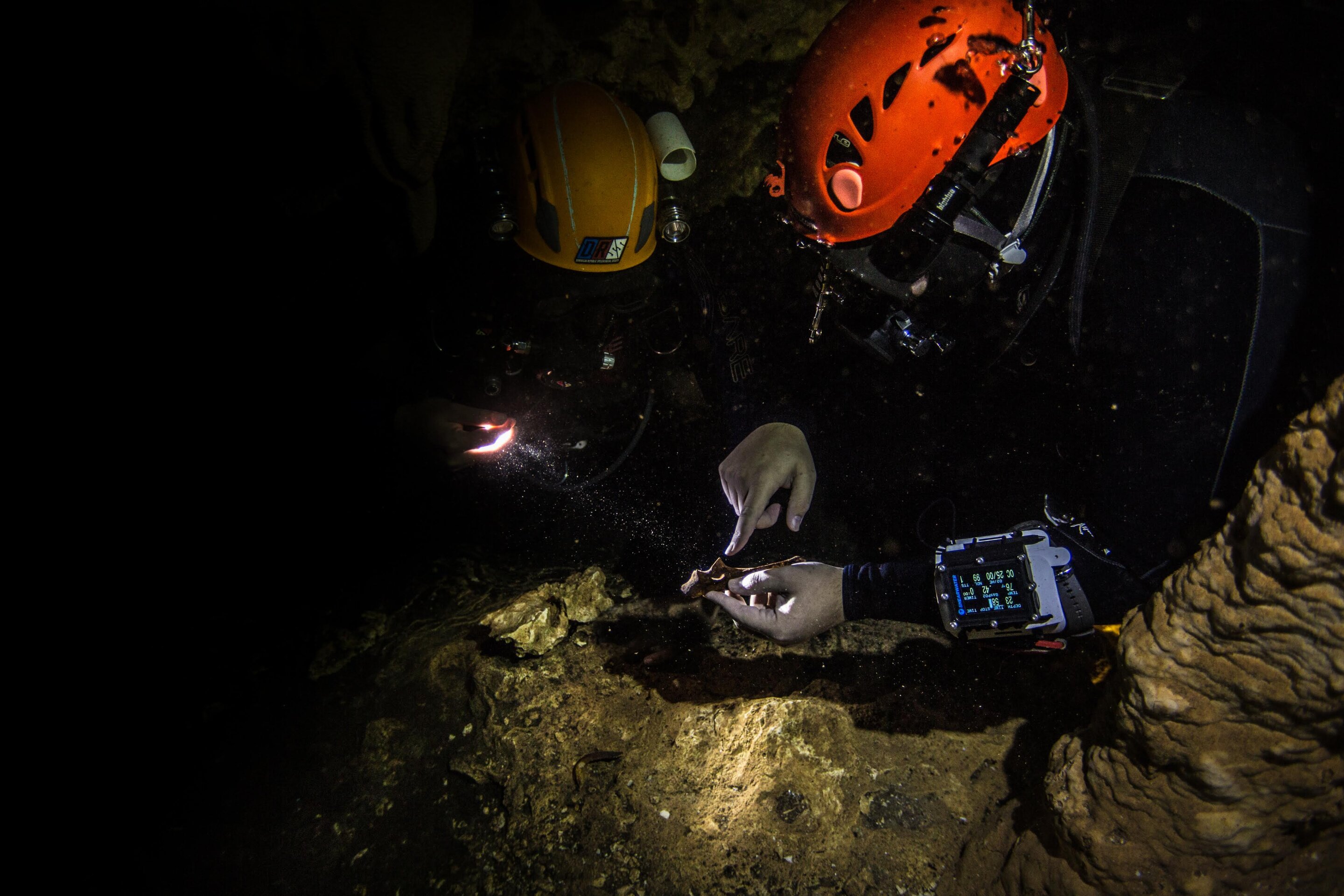 Divers from the Dominican Republic Speleological Society follow Antillothrix fossils underwater. (Zachary Klukkert)The most recent unearths, out of the Cueva Macho cave device, at the Dominican Republic facet of Hispaniola, upload new element to our figuring out of the extinct species.
Divers from the Dominican Republic Speleological Society follow Antillothrix fossils underwater. (Zachary Klukkert)The most recent unearths, out of the Cueva Macho cave device, at the Dominican Republic facet of Hispaniola, upload new element to our figuring out of the extinct species.
“The quantity and high quality of the Antillothrix crania defined on this paper permit us to explain the cranium totally and perceive variation between people,” says Johns Hopkins College paleobiologist Siobhán Cooke. “It will let us know in regards to the vitamin and social programs of those animals.”
4 new skulls had been discovered within the cave, at the side of 3 new mandibles. With those new items from the Cueva Macho device, in addition to an grownup mandible present in a an identical cave referred to as Padre Nuestro, all the Antillothrix bernensis species is now represented by means of seven near-complete crania, two maxillae fragments, an occipital fragment, 5 whole mandibles, and dozens of alternative non-skull bones.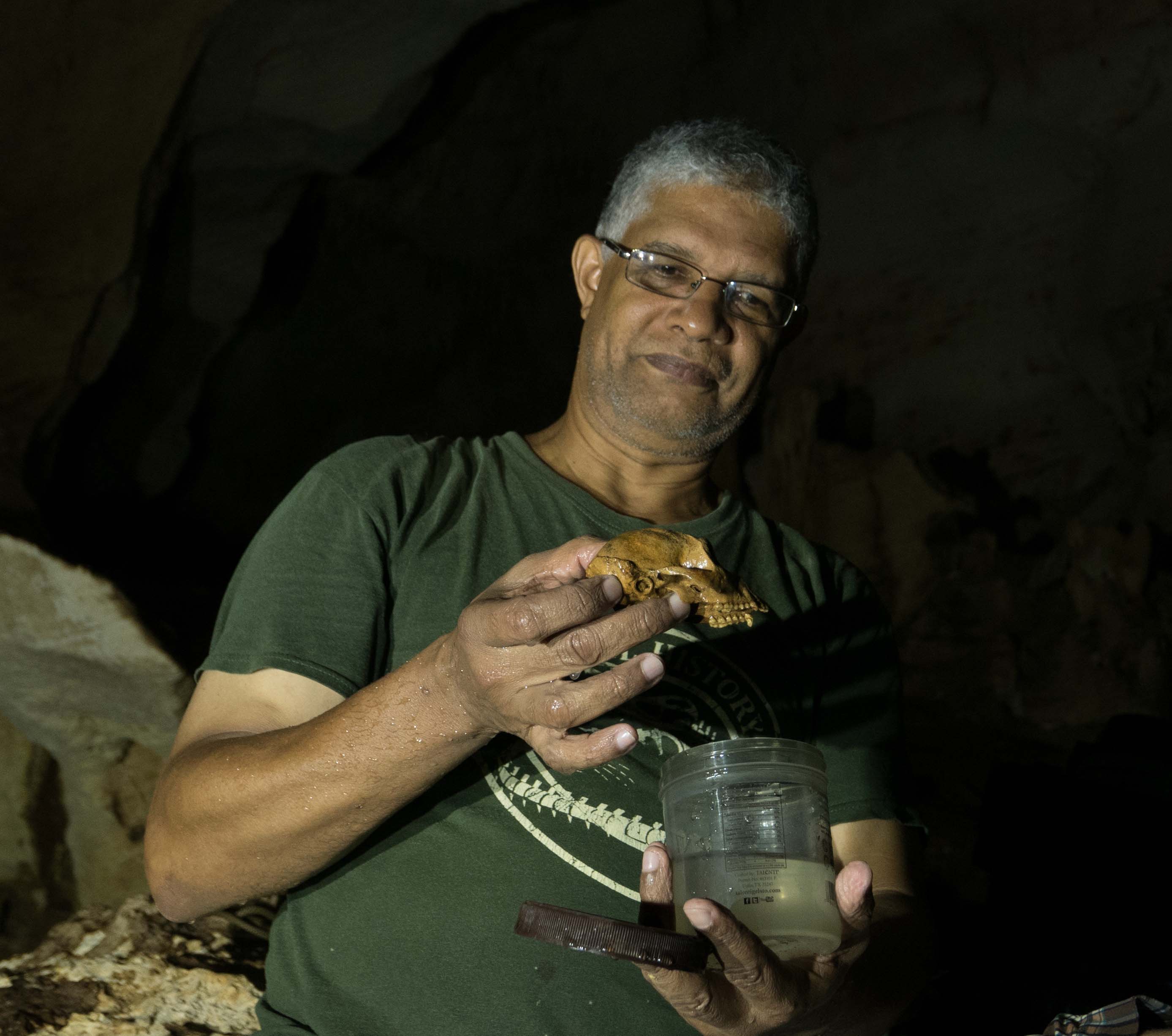  Juan Almonte-Milan inspects probably the most new crania discovered inside Cueva Macho. (Phillip Lehman)It does not sound like a lot to head off, however this assortment – particularly the skulls – is going a ways in describing the monkeys’ measurement, vitamin, intercourse variations, even social lives. And that’s the reason extra element than we’ve got for another Caribbean monkeys.
Juan Almonte-Milan inspects probably the most new crania discovered inside Cueva Macho. (Phillip Lehman)It does not sound like a lot to head off, however this assortment – particularly the skulls – is going a ways in describing the monkeys’ measurement, vitamin, intercourse variations, even social lives. And that’s the reason extra element than we’ve got for another Caribbean monkeys.
“Those new specimens, together with the ones in the past described, will permit for an in depth learn about of population- and species-level variation, an exceedingly uncommon alternative for any fossil primate,” the authors write of their paper.
By means of inspecting the fossils, the researchers estimate that men and women had been of a an identical measurement, as much as 3.4 kilograms (round 7 kilos), which means mating wasn’t overly aggressive, and that they will have lived in small monogamous circle of relatives teams with younger relying on their oldsters.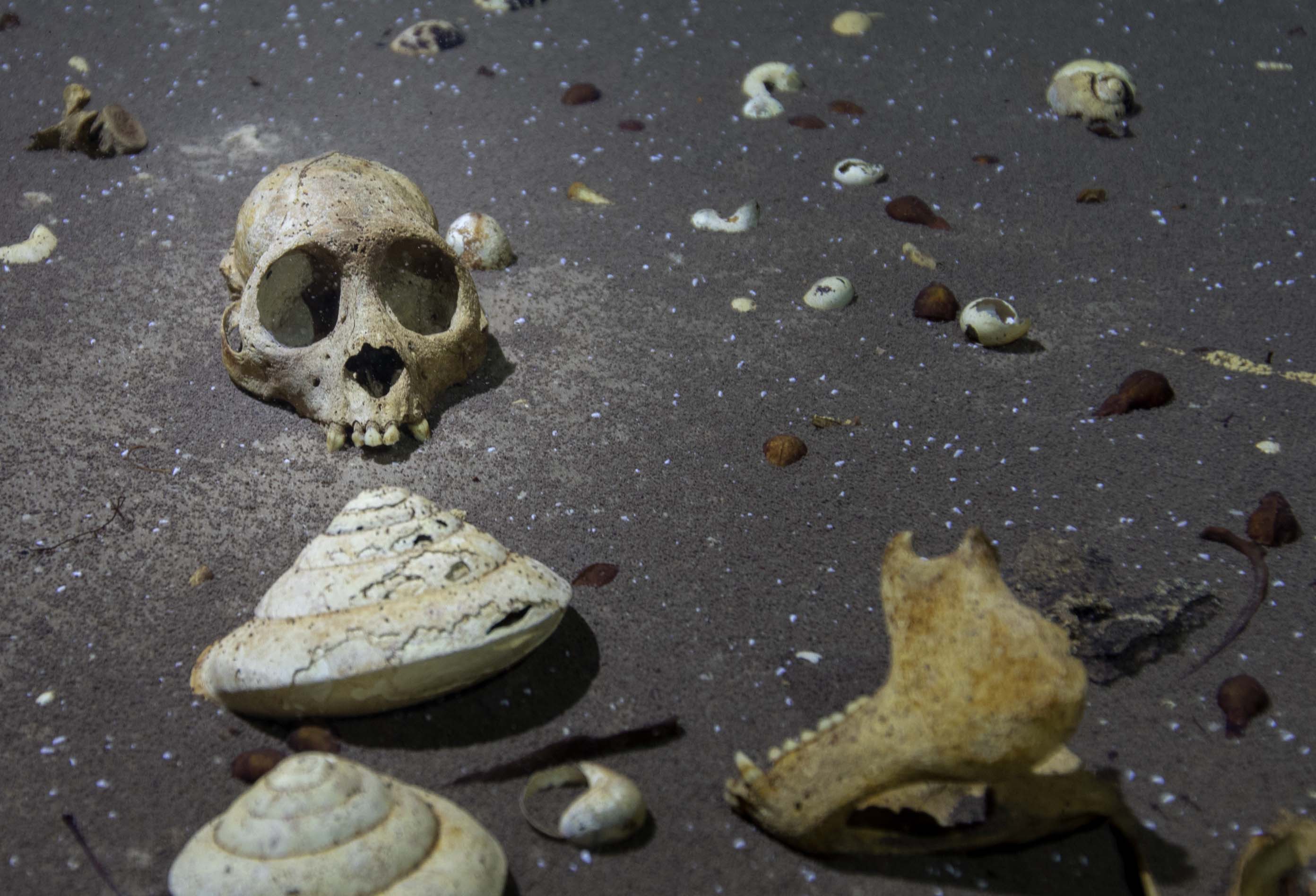 This cranium and mandible, photographed at the cave ground the place they had been discovered previous to assortment, could have been resting there for hundreds of years. (Phillip Lehman)Their rounded tooth, with small canine, would have suited a vitamin of fruit, very similar to the fashionable South American titi monkeys, that have an identical bodily options. They usually seem to have had no knowledge tooth, which is uncommon amongst primates.
This cranium and mandible, photographed at the cave ground the place they had been discovered previous to assortment, could have been resting there for hundreds of years. (Phillip Lehman)Their rounded tooth, with small canine, would have suited a vitamin of fruit, very similar to the fashionable South American titi monkeys, that have an identical bodily options. They usually seem to have had no knowledge tooth, which is uncommon amongst primates.
It is a thriller how those monkeys were given within the caves all the ones years in the past, however in line with injury to the jaw fossils, Cooke suspects it was once now not by means of selection.
“It might be imaginable {that a} now extinct owl, which might had been fairly huge, stuck those monkeys and taken them into the cave the place it was once residing –rather than the monkeys falling in at random,” she says. “Owl feeding deposits don’t seem to be unusual in Hispaniolan caves.”
The Hispaniola monkey was extinct throughout the ultimate 10,000 years, however it is unclear simply what drove this species below.
“Those fossils assist us to higher perceive the anatomy of Antillothrix, which is able to assist us establish ecological elements that may have predisposed it to extinction… [and] in the long run information coverage for holding the rest mammalian range at the Caribbean islands and somewhere else ” says Cooke.This analysis was once revealed in Magazine of Human Evolution.
Stunningly Preserved Bones of Extinct Caribbean Monkey Discovered by means of Divers