The Moon, our nearest celestial frame, is shrouded in a fancy previous.
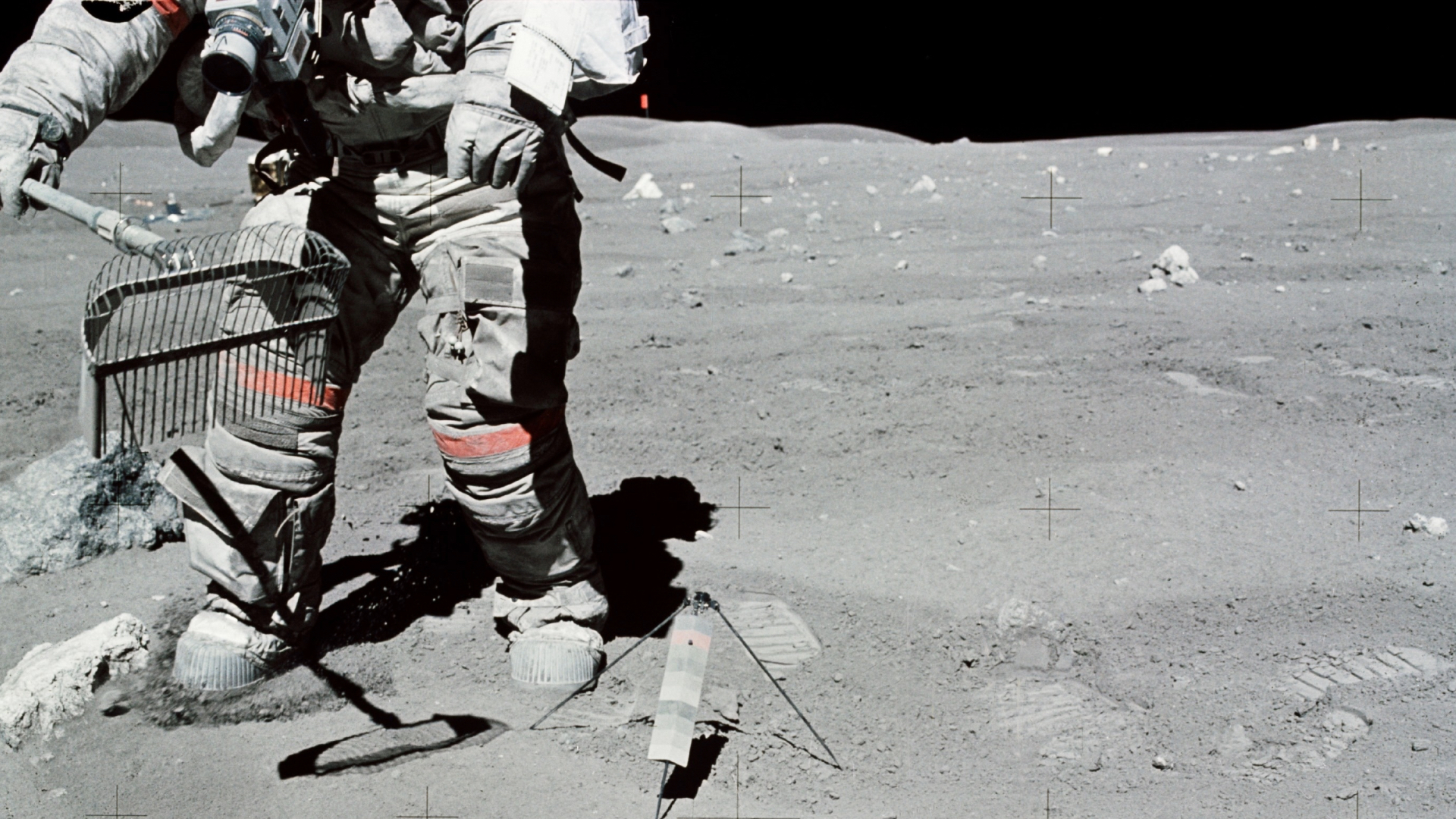
Over fifty years in the past, the Apollo 16 challenge introduced again a treasure trove from the Moon. Those samples have supplied the distance neighborhood with a substantial amount of data at the Moon’s historical previous.
Within the new learn about, the researchers involved in a particular form of pattern: regolith breccias. Those rocks shaped when lunar mud was once fused via asteroid affects.
“The Moon’s historical past is the Earth’s historical past too – the file of asteroid bombardments etched on its face and below its floor can assist us perceive the stipulations of the early sun machine which shaped our planet in addition to its closest neighbour,” mentioned Mark Nottingham, the paper’s lead writer from the College of Glasgow.
Moon samples accrued in 1972
The Moon‘s floor has been formed via numerous collisions over billions of years. Those affects have left their mark at the lunar regolith.
The samples have been accrued from the Moon’s Descartes highlands and have been introduced again to Earth in 1972
The researchers applied cutting-edge mass spectrometry to check the gases contained inside of smaller soil-like breccia samples.
“Mass spectrometry, which identifies molecules in samples and quantifies their relative abundance, can assist us resolve how a lot time the samples spent uncovered on or close to the Moon’s floor. That is helping give us a clearer concept of the historical past of affects in this explicit space of the Moon,” mentioned Nottingham.
Exam of noble gases
The learn about supplied insights into the processes that experience formed the Moon’s floor over the last two billion years, together with the affect of asteroids and the affect of the sun wind.
“Over the process the samples’ time at the floor of the Moon as regolith, they have been uncovered to various quantities of sun wind – charged debris flowing from the solar which additionally raise strains of noble gases like argon and xenon – which constructed up at the outer layers in their mineral grains for tens of millions of years ahead of they have been struck via an asteroid,” defined Nottingham.
Earlier research on Apollo 16 breccia samples analyzed noble fuel strains to categorize them into two age teams: historical (3.8-2.4 billion years) and younger (2.5-1.7 billion years). Noble gases gather at the floor of the Moon over the years because of publicity to the sun wind.
On this new research, some samples printed a various vary of publicity ages, suggesting that the area has skilled more than a few affects.
As well as, the learn about confirmed that some samples have been uncovered to the sun wind for a protracted duration, whilst others have been delivered to the outside via newer occasions.
The findings recommend that two of the lunar samples have been shaped a lot more just lately than the others. That is according to the considerably decrease concentrations of noble gases present in those samples.
The researchers suggest that the affect that created the within reach South Ray crater might be the supply of those more youthful samples.
Dr Nottingham mentioned: “This learn about establishes for the primary time that soil-like breccias are their very own distinct class, with their very own histories to proportion. Mixed with research of the traditional and younger rocks recovered via Apollo 16, we will construct a a lot more entire image of the historical past of this a part of the Moon right through the early sun machine, the place heavier affects at the lunar floor in its first billion years or so gave solution to much less intense sessions from two billion years in the past or so.”
The analysis may just give a contribution to long run lunar missions, similar to NASA’s Artemis program, via offering treasured details about the Moon’s herbal assets.
The findings have been revealed within the magazine Meteoritics & Planetary Science.