Abstract: Researchers have found out two new mind pathways that adjust motion and emotional choices by way of controlling dopamine free up. Those pathways, discovered within the striatum, both stimulate or inhibit dopamine-producing neurons, influencing the cross and no-go pathways that regulate motion.By means of regulating dopamine, those pathways is also particularly interested in choices tied to robust feelings or nervousness. The findings be offering new insights into how motivation and motion are related, with possible implications for problems like Parkinson’s illness.Key Details:Two newly known mind pathways regulate dopamine free up and affect motion.Those pathways modify choices involving robust feelings or nervousness.Findings would possibly assist in figuring out movement-related problems like Parkinson’s illness.Supply: MITWithin the human mind, motion is coordinated by way of a mind area referred to as the striatum, which sends directions to motor neurons within the mind. The ones directions are conveyed by way of two pathways, one who initiates motion (“cross”) and one who suppresses it (“no-go”).In a brand new find out about, MIT researchers have found out an extra two pathways that get up within the striatum and seem to modulate the consequences of the cross and no-go pathways. Those newly found out pathways connect with dopamine-producing neurons within the mind — one stimulates dopamine free up and the opposite inhibits it. 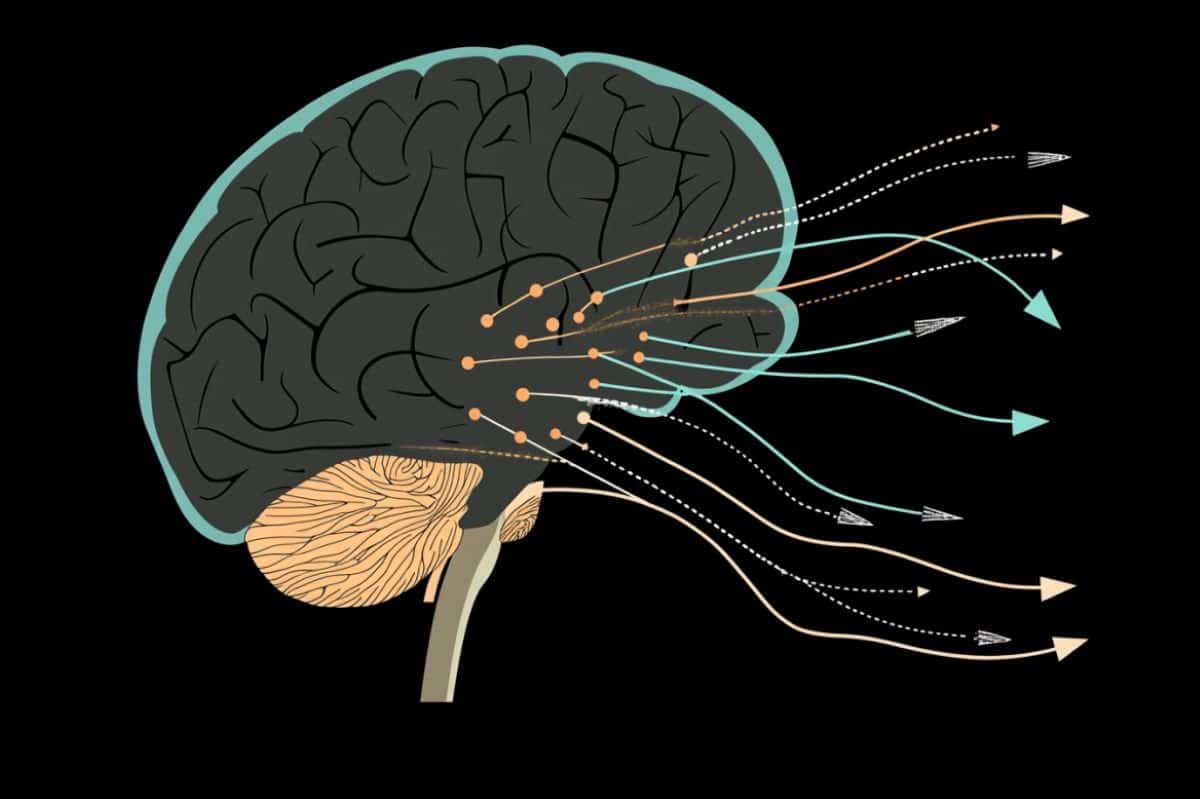 Every other risk the researchers plan to discover is whether or not striosomes and matrix cells are organized in modules that impact motor regulate of explicit portions of the frame. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsBy controlling the quantity of dopamine within the mind by the use of clusters of neurons referred to as striosomes, those pathways seem to change the directions given by way of the cross and no-go pathways. They is also particularly interested in influencing choices that experience a robust emotional element, the researchers say.“Amongst all of the areas of the striatum, the striosomes on my own became out so as to undertaking to the dopamine-containing neurons, which we predict has one thing to do with motivation, temper, and controlling motion,” says Ann Graybiel, an MIT Institute Professor, a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis, and the senior writer of the brand new find out about.Iakovos Lazaridis, a analysis scientist on the McGovern Institute, is the lead writer of the paper, which seems these days within the magazine Present Biology.New pathwaysGraybiel has spent a lot of her profession finding out the striatum, a construction situated deep inside the mind this is interested in finding out and decision-making, in addition to regulate of motion.Throughout the striatum, neurons are organized in a labyrinth-like construction that comes with striosomes, which Graybiel found out within the Seventies. The classical cross and no-go pathways get up from neurons that encompass the striosomes, which can be recognized jointly because the matrix.The matrix cells that give upward push to those pathways obtain enter from sensory processing areas such because the visible cortex and auditory cortex. Then, they ship cross or no-go instructions to neurons within the motor cortex.Alternatively, the serve as of the striosomes, which aren’t a part of the ones pathways, remained unknown. For a few years, researchers in Graybiel’s lab were seeking to resolve that thriller.Their earlier paintings published that striosomes obtain a lot in their enter from portions of the mind that procedure emotion. Inside striosomes, there are two main varieties of neurons, categorised as D1 and D2. In a 2015 find out about, Graybiel discovered that this kind of cellular sorts, D1, sends enter to the substantia nigra, which is the mind’s main dopamine-producing middle.It took for much longer to track the output of the opposite set, D2 neurons. Within the new Present Biology find out about, the researchers found out that the ones neurons additionally sooner or later undertaking to the substantia nigra, however first they connect with a collection of neurons within the globus palladus, which inhibits dopamine output. This pathway, an oblique connection to the substantia nigra, reduces the mind’s dopamine output and inhibits motion.The researchers additionally showed their previous discovering that the pathway coming up from D1 striosomes connects at once to the substantia nigra, stimulating dopamine free up and beginning motion.“Within the striosomes, we’ve discovered what’s most certainly a mimic of the classical cross/no-go pathways,” Graybiel says.“They’re like vintage motor cross/no-go pathways, however they don’t cross to the motor output neurons of the basal ganglia. As an alternative, they cross to the dopamine cells, which can be so necessary to motion and motivation.”Emotional decisionsThe findings counsel that the classical type of ways the striatum controls motion must be changed to incorporate the position of those newly known pathways. The researchers now hope to check their speculation that enter associated with motivation and emotion, which enters the striosomes from the cortex and the limbic device, influences dopamine ranges in some way that may inspire or discourage motion.That dopamine free up is also particularly related for movements that induce nervousness or pressure. Of their 2015 find out about, Graybiel’s lab discovered that striosomes play a key position in making choices that galvanize prime ranges of tension; particularly, the ones which are prime chance however might also have a large payoff.“Ann Graybiel and associates have previous discovered that the striosome is all for inhibiting dopamine neurons. Now they display all of a sudden that any other form of striosomal neuron exerts the other impact and will sign praise. The striosomes can thus each up- or down-regulate dopamine task, an important discovery.“Obviously, the law of dopamine task is important in our on a regular basis lifestyles in regards to each actions and temper, to which the striosomes give a contribution,” says Sten Grillner, a professor of neuroscience on the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, who was once no longer concerned within the analysis.Every other risk the researchers plan to discover is whether or not striosomes and matrix cells are organized in modules that impact motor regulate of explicit portions of the frame.“The next move is attempting to isolate a few of these modules, and by way of concurrently operating with cells that belong to the similar module, whether or not they’re within the matrix or striosomes, attempt to pinpoint how the striosomes modulate the underlying serve as of each and every of those modules,” Lazaridis says.Additionally they hope to discover how the striosomal circuits, which undertaking to the similar area of the mind this is ravaged by way of Parkinson’s illness, would possibly affect that dysfunction.Investment: The analysis was once funded by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, the Saks-Kavanaugh Basis, the William N. and Bernice E. Bumpus Basis, Jim and Joan Schattinger, the Hock E. Tan and Okay. Lisa Yang Heart for Autism Analysis, Robert Buxton, the Simons Basis, the CHDI Basis, and an Ellen Schapiro and Gerald Axelbaum Investigator BBRF Younger Investigator Grant.About this dopamine and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Anne Trafton
Every other risk the researchers plan to discover is whether or not striosomes and matrix cells are organized in modules that impact motor regulate of explicit portions of the frame. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsBy controlling the quantity of dopamine within the mind by the use of clusters of neurons referred to as striosomes, those pathways seem to change the directions given by way of the cross and no-go pathways. They is also particularly interested in influencing choices that experience a robust emotional element, the researchers say.“Amongst all of the areas of the striatum, the striosomes on my own became out so as to undertaking to the dopamine-containing neurons, which we predict has one thing to do with motivation, temper, and controlling motion,” says Ann Graybiel, an MIT Institute Professor, a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis, and the senior writer of the brand new find out about.Iakovos Lazaridis, a analysis scientist on the McGovern Institute, is the lead writer of the paper, which seems these days within the magazine Present Biology.New pathwaysGraybiel has spent a lot of her profession finding out the striatum, a construction situated deep inside the mind this is interested in finding out and decision-making, in addition to regulate of motion.Throughout the striatum, neurons are organized in a labyrinth-like construction that comes with striosomes, which Graybiel found out within the Seventies. The classical cross and no-go pathways get up from neurons that encompass the striosomes, which can be recognized jointly because the matrix.The matrix cells that give upward push to those pathways obtain enter from sensory processing areas such because the visible cortex and auditory cortex. Then, they ship cross or no-go instructions to neurons within the motor cortex.Alternatively, the serve as of the striosomes, which aren’t a part of the ones pathways, remained unknown. For a few years, researchers in Graybiel’s lab were seeking to resolve that thriller.Their earlier paintings published that striosomes obtain a lot in their enter from portions of the mind that procedure emotion. Inside striosomes, there are two main varieties of neurons, categorised as D1 and D2. In a 2015 find out about, Graybiel discovered that this kind of cellular sorts, D1, sends enter to the substantia nigra, which is the mind’s main dopamine-producing middle.It took for much longer to track the output of the opposite set, D2 neurons. Within the new Present Biology find out about, the researchers found out that the ones neurons additionally sooner or later undertaking to the substantia nigra, however first they connect with a collection of neurons within the globus palladus, which inhibits dopamine output. This pathway, an oblique connection to the substantia nigra, reduces the mind’s dopamine output and inhibits motion.The researchers additionally showed their previous discovering that the pathway coming up from D1 striosomes connects at once to the substantia nigra, stimulating dopamine free up and beginning motion.“Within the striosomes, we’ve discovered what’s most certainly a mimic of the classical cross/no-go pathways,” Graybiel says.“They’re like vintage motor cross/no-go pathways, however they don’t cross to the motor output neurons of the basal ganglia. As an alternative, they cross to the dopamine cells, which can be so necessary to motion and motivation.”Emotional decisionsThe findings counsel that the classical type of ways the striatum controls motion must be changed to incorporate the position of those newly known pathways. The researchers now hope to check their speculation that enter associated with motivation and emotion, which enters the striosomes from the cortex and the limbic device, influences dopamine ranges in some way that may inspire or discourage motion.That dopamine free up is also particularly related for movements that induce nervousness or pressure. Of their 2015 find out about, Graybiel’s lab discovered that striosomes play a key position in making choices that galvanize prime ranges of tension; particularly, the ones which are prime chance however might also have a large payoff.“Ann Graybiel and associates have previous discovered that the striosome is all for inhibiting dopamine neurons. Now they display all of a sudden that any other form of striosomal neuron exerts the other impact and will sign praise. The striosomes can thus each up- or down-regulate dopamine task, an important discovery.“Obviously, the law of dopamine task is important in our on a regular basis lifestyles in regards to each actions and temper, to which the striosomes give a contribution,” says Sten Grillner, a professor of neuroscience on the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, who was once no longer concerned within the analysis.Every other risk the researchers plan to discover is whether or not striosomes and matrix cells are organized in modules that impact motor regulate of explicit portions of the frame.“The next move is attempting to isolate a few of these modules, and by way of concurrently operating with cells that belong to the similar module, whether or not they’re within the matrix or striosomes, attempt to pinpoint how the striosomes modulate the underlying serve as of each and every of those modules,” Lazaridis says.Additionally they hope to discover how the striosomal circuits, which undertaking to the similar area of the mind this is ravaged by way of Parkinson’s illness, would possibly affect that dysfunction.Investment: The analysis was once funded by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, the Saks-Kavanaugh Basis, the William N. and Bernice E. Bumpus Basis, Jim and Joan Schattinger, the Hock E. Tan and Okay. Lisa Yang Heart for Autism Analysis, Robert Buxton, the Simons Basis, the CHDI Basis, and an Ellen Schapiro and Gerald Axelbaum Investigator BBRF Younger Investigator Grant.About this dopamine and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Anne Trafton
Supply: MIT
Touch: Anne Trafton – MIT
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Striosomes regulate dopamine by the use of twin pathways paralleling canonical basal ganglia circuits” by way of Iakovos Lazaridis et al. Present BiologyAbstractStriosomes regulate dopamine by the use of twin pathways paralleling canonical basal ganglia circuitsBalanced task of canonical direct D1 and oblique D2 basal ganglia pathways is regarded as a core requirement for traditional motion, and their imbalance is an etiologic think about motion and neuropsychiatric problems.We provide proof for a conceptually an identical pair of direct D1 and oblique D2 pathways that get up from striatal projection neurons (SPNs) of the striosome compartment slightly than from SPNs of the matrix, as do the canonical pathways.Those striosomal D1 (S-D1) and D2 (S-D2) pathways goal substantia nigra dopamine-containing neurons as an alternative of basal ganglia motor output nuclei. They modulate motion with web results reverse to these exerted by way of the canonical pathways: S-D1 is web inhibitory and S-D2 is web excitatory.The S-D1 and S-D2 circuits most probably affect motivation for finding out and motion, complementing and reorienting canonical pathway modulation.A significant conceptual reformulation of the vintage direct-indirect pathway type of basal ganglia serve as is wanted, in addition to reconsideration of the consequences of D2-targeting healing medication.
Neural Pathways Hyperlink Dopamine to Motion and Motivation – Neuroscience Information