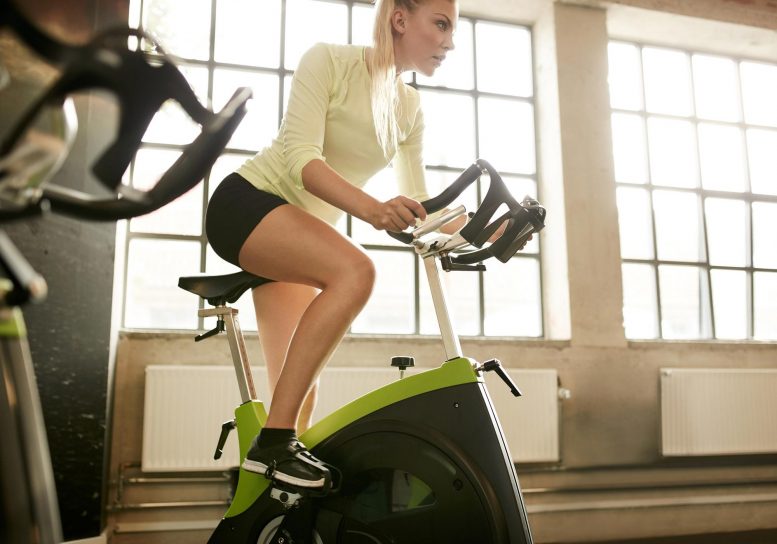
Analysis signifies that lively exercises suppress urge for food greater than reasonable workout, with girls appearing larger decreases in starvation hormones.
Analysis signifies that lively exercises suppress urge for food greater than reasonable workout, with girls appearing larger decreases in starvation hormones.
Top-intensity workout is simpler at suppressing starvation than reasonable ranges, particularly in ladies, in line with fresh analysis.
The find out about, that specialize in the “starvation hormone” ghrelin, means that such lively process could be a vital element of weight control methods.
Affect of Workout Depth on Urge for food
A brand new find out about printed as of late (October 24) within the Magazine of the Endocrine Society means that intense workout is simpler at lowering starvation in wholesome adults than reasonable workout, with girls appearing a specifically sturdy reaction.
The analysis excited by how other ranges of workout depth have an effect on ghrelin, a hormone referred to as the “starvation hormone” as it performs a key function in regulating urge for food.
“We discovered that high-intensity workout suppressed ghrelin ranges greater than moderate-intensity workout,” defined lead writer Kara Anderson, Ph.D., from the College of Virginia and the College of Virginia Well being Gadget in Charlottesville, Virginia. “As well as, we discovered that people felt ‘much less hungry’ after high-intensity workout in comparison to moderate-intensity workout.”
Gender Variations in Hormonal Responses
Ghrelin circulates in two bureaucracy—acylated (AG) and deacylated (DAG)—either one of which affect urge for food. Alternatively, knowledge on how workout depth affects those bureaucracy, specifically in terms of urge for food suppression, is proscribed and has most commonly excited by males.
To deal with this shortfall, the find out about tested 8 men and 6 ladies. Contributors fasted in a single day after which finished workouts of various depth ranges, made up our minds by means of measurements of blood lactate, adopted by means of self-reported measurements of urge for food.
Women had upper ranges of general ghrelin at baseline when compared with men, the find out about famous. Alternatively, simplest ladies demonstrated “considerably lowered AG” following the serious workout, in line with the findings.
Exploring the Physiological Results of Top-Depth Workout
“We discovered that reasonable depth both didn’t alternate ghrelin ranges or resulted in a internet build up,” the find out about famous. Those findings counsel that workout above the lactate threshold “could also be essential to elicit a suppression in ghrelin.”
Researchers additionally said that extra paintings is had to decide the level to which the results of workout vary by means of intercourse.
Ghrelin has been proven to have wide-ranging organic results in spaces together with power stability, urge for food, glucose homeostasis, immune serve as, sleep, and reminiscence.
Sensible Implications for Workout and Weight Control
“Workout will have to be regarded as a ‘drug,’ the place the ‘dose’ will have to be custom designed in accordance with a person’s private objectives,” Anderson stated. “Our analysis means that high-intensity workout could also be necessary for urge for food suppression, which may also be specifically helpful as a part of a weight reduction program.”
Reference: “The Affect of Workout Depth and Intercourse on Endogenous Ghrelin Ranges and Urge for food in Wholesome People” by means of Kara C Anderson, Tana Mardian, Benjamin Stephenson, Emily E Grammer, Macy E Stahl, Nathan R Weeldreyer, Zhenqi Liu, Kaitlin M Love, Sibylle Kranz, Jason D Allen and Arthur Weltman, 24 October 2024, Magazine of the Endocrine Society.
DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvae165
Different find out about authors come with Tana Mardian, Benjamin Stephenson, Emily Grammer, Macy Stahl, Nathan Weeldreyer, and Sibylle Kranz of the College of Virginia; Zhenqi Liu and Kaitlin Love of the College of Virginia Well being Gadget; and Jason Allen and Arthur Weltman of the College of Virginia and the College of Virginia Well being Gadget.
This analysis gained monetary make stronger from the Nationwide Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Sicknesses and the College of Virginia’s Faculty of Schooling and Human Construction.