Say hi to the ionocaloric sit back. This can be a new option to scale back warmth and has the power to exchange current cooling strategies with some way this is more secure and higher for the planet. Refrigerants shipping warmth clear of the ambience via a liquid that absorbs warmth because it evaporates into air, which is then absorbed via a closed tube and re-inflated into liquid. As helpful as this procedure is, one of the crucial fabrics we use corresponding to fridges are very unfriendly to the surroundings. Then again, there are a number of techniques during which a substance is compelled to soak up and fritter away warmth power. The process that was once unveiled closing yr, advanced through researchers from the Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory and the College of California, Berkeley, takes good thing about the best way that power is saved or launched when a substance adjustments segment, corresponding to when forged ice turns to liquid water, as an example. Lift the warmth at the ice block, it is going to soften. What we will’t simply see is that melting takes warmth from the environment, and cools it down. One option to pressure ice to soften with out heating is so as to add extra debris, or ions. Striking salt on roads to forestall ice from forming is a not unusual instance of this. The ionocaloric cycle additionally makes use of salt to exchange the liquid segment and funky the encompassing space.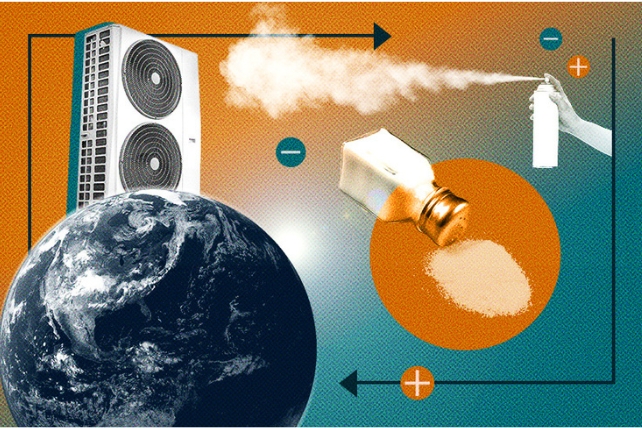 Diagram of the ionocaloric cycle thought. (Jenny Nuss/Berkeley Lab) “The design of fridges is an unsolved drawback,” stated engineer Drew Lilley from Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory in California in January 2023. “Nobody has effectively advanced a technique that makes issues cool, that works. neatly, it is secure, and it does not hurt the surroundings. The researchers followed the idea of the ionocaloric cycle to turn how it might compete with, or toughen, the potency of the fridges used as of late. The glide of present during the gadget strikes the ions in it, shifting the melting level of the fabric to switch the temperature. The group additionally attempted the use of salts made from iodine and sodium to dissolve ethylene carbonate. Those natural solvents also are utilized in lithium-ion batteries and are made the use of oxygen as a catalyst [global warming potential] 0 however damaging GWP. A temperature exchange of 25 levels Celsius (45 levels Fahrenheit) was once measured the use of lower than one volt within the experiment, which exceeds what different caloric applied sciences were in a position to succeed in to this point.
Diagram of the ionocaloric cycle thought. (Jenny Nuss/Berkeley Lab) “The design of fridges is an unsolved drawback,” stated engineer Drew Lilley from Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory in California in January 2023. “Nobody has effectively advanced a technique that makes issues cool, that works. neatly, it is secure, and it does not hurt the surroundings. The researchers followed the idea of the ionocaloric cycle to turn how it might compete with, or toughen, the potency of the fridges used as of late. The glide of present during the gadget strikes the ions in it, shifting the melting level of the fabric to switch the temperature. The group additionally attempted the use of salts made from iodine and sodium to dissolve ethylene carbonate. Those natural solvents also are utilized in lithium-ion batteries and are made the use of oxygen as a catalyst [global warming potential] 0 however damaging GWP. A temperature exchange of 25 levels Celsius (45 levels Fahrenheit) was once measured the use of lower than one volt within the experiment, which exceeds what different caloric applied sciences were in a position to succeed in to this point.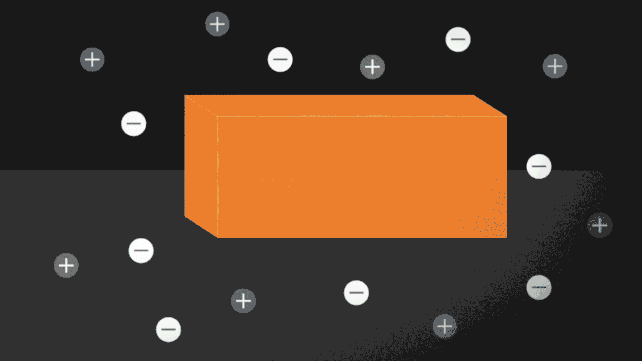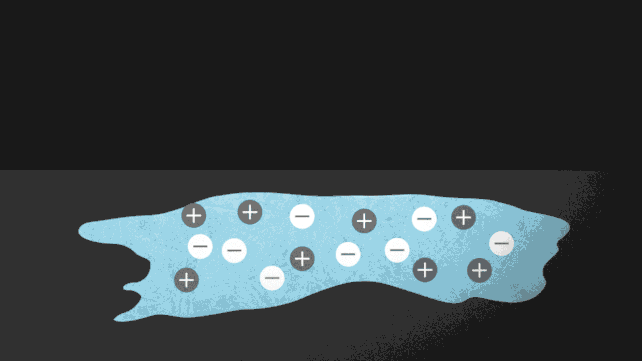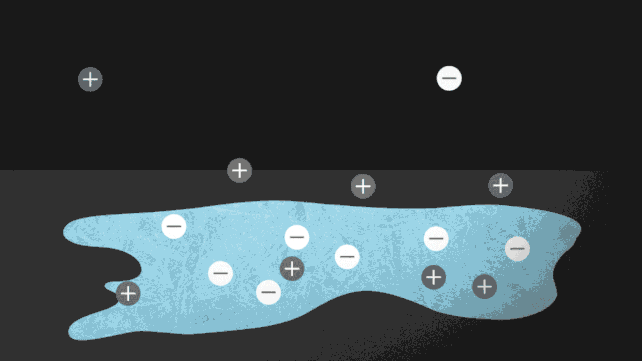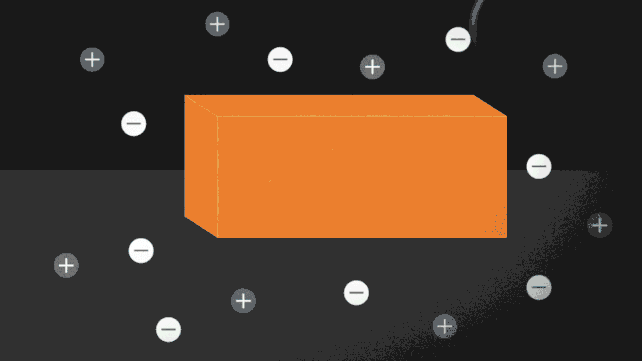 The ionocaloric cycle is lively. (Jenny Nuss/Berkeley Lab) “There are 3 issues we are seeking to steadiness: the GWP of the fridge, the power potency, and the price of the similar apparatus,” stated engineer Ravi Prasher from Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory. “From the primary check, our information seems to be dependable for all 3 components.” The air compressors lately utilized in refrigeration depend on gases with top GWP, corresponding to more than a few hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). Nations that experience signed the Kigali Modification have dedicated to lowering the manufacturing and use of HFCs through no less than 80 % over the following 25 years – and ionocaloric cooling can lend a hand so much. Now, the researchers want to take the era out of the lab and put it into apply that can be utilized commercially and scaled up with out issues. In spite of everything, the gadget can be utilized for each heating and cooling. “We’ve got this new thermodynamic style that mixes other houses, and we’ve got proven that it could actually paintings,” Prasher stated. “Now, it is time to experiment with several types of gear and strategies to unravel technical issues.” The analysis was once printed in Science. An previous model of this text was once printed in January 2023.
The ionocaloric cycle is lively. (Jenny Nuss/Berkeley Lab) “There are 3 issues we are seeking to steadiness: the GWP of the fridge, the power potency, and the price of the similar apparatus,” stated engineer Ravi Prasher from Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory. “From the primary check, our information seems to be dependable for all 3 components.” The air compressors lately utilized in refrigeration depend on gases with top GWP, corresponding to more than a few hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). Nations that experience signed the Kigali Modification have dedicated to lowering the manufacturing and use of HFCs through no less than 80 % over the following 25 years – and ionocaloric cooling can lend a hand so much. Now, the researchers want to take the era out of the lab and put it into apply that can be utilized commercially and scaled up with out issues. In spite of everything, the gadget can be utilized for each heating and cooling. “We’ve got this new thermodynamic style that mixes other houses, and we’ve got proven that it could actually paintings,” Prasher stated. “Now, it is time to experiment with several types of gear and strategies to unravel technical issues.” The analysis was once printed in Science. An previous model of this text was once printed in January 2023.
Scientists Invented an Solely New Technique to Refrigerate Issues