Astronomers have noticed 1000’s of younger stars huddled across the middle of an historical galaxy, all of which shaped just about concurrently 4 million years in the past. This remark marks the primary time such synchronized celebrity formation has been noticed in an previous galaxy, and demanding situations the concept celebrity formation declines as galaxies age.The newfound celebrity clusters skirt the center of NGC 1386, a spiral galaxy swirling more or less 53 million light-years from Earth within the constellation Eridanus. Researchers led by way of Almudena Prieto of Spain’s Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias recognized 61 teams of younger stars, which hint the 1 kiloparsec-wide blue ring observed within the symbol above, and located they all sported equivalent lots, ages and sizes regardless of being spatially remoted.”All of those clusters are allotted like pearls on a hoop across the middle of the galaxy,” Prieto mentioned in a contemporary information unencumber. “Strangely they’re all alike, which supplies the concept they had been created on the similar time, in a synchronized tournament.”Observations of the blue ring with the Hubble House Telescope and the VLT Survey Telescope in Chile display the celebrity clusters are fed by way of lengthy filaments of fuel and mud that ferry valuable star-forming subject matter — akin to molecular hydrogen — from the galaxy’s outer disk the entire solution to its middle.Comparable: Stare into the ‘blood-soaked eyes’ of two spooky galaxies in new Hubble, JWST photographs (video)The researchers didn’t hit upon any spouse galaxies swirling close by NGC 1386, suggesting those filaments are most probably the one supply of star-forming subject matter for the galaxy, in line with any other information unencumber from the Eu Southern Observatory (ESO), which hosts the VLT Survey Telescope at its Paranal Observatory in Chile’s Atacama Barren region.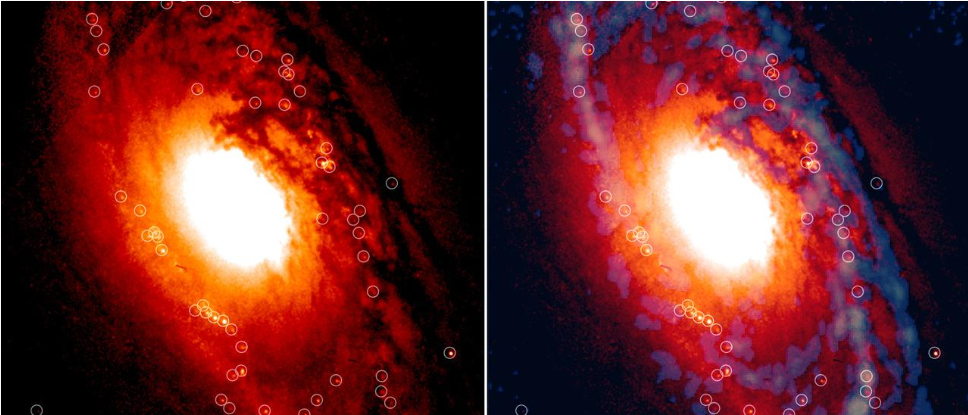 An aspect-by-side view of NGC 1386 in visual wavelengths (left), occupied with the Hubble House Telescope, and in radio (proper), occupied with the ALMA radio telescope. Each photographs spotlight younger celebrity clusters the place 1000’s of stars are being born. Darkish wisps which can be observed passing with reference to or finishing within the celebrity clusters are filaments ferrying star-forming subject matter, akin to molecular hydrogen. (Symbol credit score: HST/ ALMA. Composition: Gabriel Pérez Díaz (SMM, IAC))Those findings upload to the rising frame of new proof sure previous galaxies are in a position to host bursts of celebrity formation, opposite to the vast majority of historic observations that experience proven that the speed of celebrity formation declines as galaxies age, suggesting their provides of star-forming fuel and mud shrinks. Regardless of its age, “this galaxy has arranged itself to acquire the desired provide from its outer zones, inside of its stellar disk,” mentioned Prieto.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”A big tournament within the disk can have led to the onset of cluster formation concurrently within the ring,” the researchers wrote in a paper revealed previous this 12 months within the Per 30 days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. That consequential tournament can have been a density wave that handed in the course of the galaxy disk, which might have caused the fuel in its wake to compress and kickstart celebrity formation.Prieto and associates additionally detected a 2d ring across the middle, depicted within the above symbol as golden, that strains more or less 70 similar wallet of fuel, suggesting the galaxy isn’t completed forming stars but. The workforce posits a 2d burst of in a similar way synchronized celebrity formation is impending, perhaps within the subsequent 5 million years or so.”Even though previous, NGC 1386 helps to keep rejuvenating itself,” the ESO information unencumber says.
An aspect-by-side view of NGC 1386 in visual wavelengths (left), occupied with the Hubble House Telescope, and in radio (proper), occupied with the ALMA radio telescope. Each photographs spotlight younger celebrity clusters the place 1000’s of stars are being born. Darkish wisps which can be observed passing with reference to or finishing within the celebrity clusters are filaments ferrying star-forming subject matter, akin to molecular hydrogen. (Symbol credit score: HST/ ALMA. Composition: Gabriel Pérez Díaz (SMM, IAC))Those findings upload to the rising frame of new proof sure previous galaxies are in a position to host bursts of celebrity formation, opposite to the vast majority of historic observations that experience proven that the speed of celebrity formation declines as galaxies age, suggesting their provides of star-forming fuel and mud shrinks. Regardless of its age, “this galaxy has arranged itself to acquire the desired provide from its outer zones, inside of its stellar disk,” mentioned Prieto.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”A big tournament within the disk can have led to the onset of cluster formation concurrently within the ring,” the researchers wrote in a paper revealed previous this 12 months within the Per 30 days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. That consequential tournament can have been a density wave that handed in the course of the galaxy disk, which might have caused the fuel in its wake to compress and kickstart celebrity formation.Prieto and associates additionally detected a 2d ring across the middle, depicted within the above symbol as golden, that strains more or less 70 similar wallet of fuel, suggesting the galaxy isn’t completed forming stars but. The workforce posits a 2d burst of in a similar way synchronized celebrity formation is impending, perhaps within the subsequent 5 million years or so.”Even though previous, NGC 1386 helps to keep rejuvenating itself,” the ESO information unencumber says.
Astronomers spot strangely synchronized celebrity formation in historical galaxy for 1st time