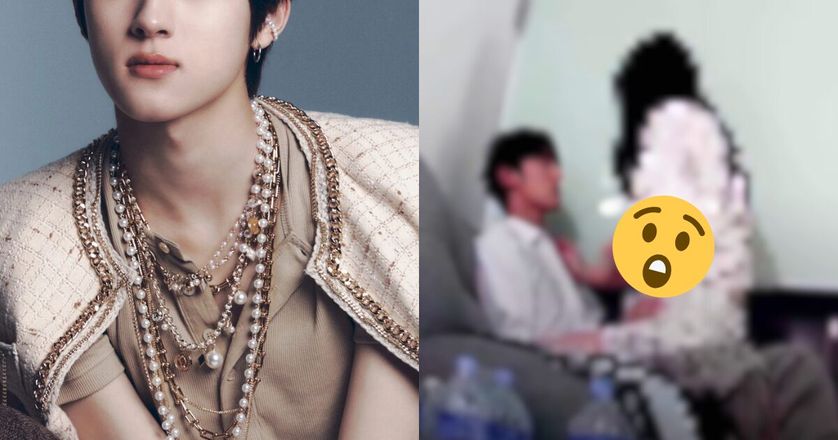
Merchandise 1 of two An artist’s representation displays a impulsively feeding black hollow this is emitting tough gasoline outflows. The usage of knowledge from NASA’s JWST and Chandra X-ray Observatory, a workforce of U.S. Nationwide Science Basis NOIRLab astronomers have found out this low-mass black hollow on the heart of a galaxy simply 1.5 billion years after the Large Bang. It’s accreting subject at a wonderful charge — over 40 occasions the theoretical restrict. Whilst quick lived, this black hollow’s ‘ceremonial dinner’ may lend a hand astronomers provide an explanation for how supermassive black holes grew so temporarily within the early Universe. NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/M. Zamani/Handout by way of REUTERS [1/2]An artist’s representation displays a impulsively feeding black hollow this is emitting tough gasoline outflows. The usage of knowledge from NASA’s JWST and Chandra X-ray Observatory, a workforce of U.S. Nationwide Science Basis NOIRLab astronomers have found out this low-mass black hollow on the heart of a galaxy simply 1.5… Acquire Licensing Rights, opens new tab Learn moreBlack hollow existed 1.5 billion years after Large BangObject exceeded theoretical limits on expansion rateWASHINGTON, Nov 5 (Reuters) – On the center of our Milky Approach galaxy lurks a supermassive black hollow about 4 million occasions the mass of the solar, referred to as Sagittarius A*. In truth, those items, which building up in mass through the years through consuming subject matter that wanders too shut, live on the heart of maximum galaxies.However since NASA’s James Webb House Telescope got here on-line in 2022, astronomers had been shocked to search out supermassive black holes inhabiting the early universe – previous than they’d idea imaginable making an allowance for the time had to accumulate such nice mass. New observations of 1 such primordial black hollow is providing perception into how this may increasingly have took place – thru episodes of supercharged expansion.Black holes are extraordinarily dense items with gravity so robust that now not even gentle can break out. With their immense gravitational pull, they develop in mass through sucking in subject matter comparable to gasoline, mud and stars unlucky sufficient to stray within reach.”The lifestyles of supermassive black holes within the early universe demanding situations our present fashions of black hollow formation and expansion,” stated astronomer Hyewon Suh of the World Gemini Observatory in Hawaii and the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis’s NOIRLab, lead writer of the find out about revealed within the magazine Nature Astronomy, opens new tab.The brand new Webb observations contain a supermassive black hollow referred to as LID-568 that existed when the cosmos used to be about 11% its present age – about 1.5 billion years after the Large Bang match 13.8 billion years in the past that initiated the universe. LID-568 has a mass about 10 million occasions more than the solar, so 2-1/2 occasions that of Sagittarius A*. The researchers have now not but made up our minds the mass of its house galaxy.LID-568 used to be noticed gaining mass at a tempo quicker than prior to now idea imaginable. Webb confirmed that, according to its noticed vigorous output, LID-568 gave the look to be eating infalling subject matter – referred to as accretion – at greater than 40 occasions the hypothesized most, referred to as the Eddington restrict, for such job.”The Eddington restrict is a theoretical restrict for the utmost calories output the black hollow can produce during the accretion procedure. This theoretical restrict assumes that the outward pressure from the radiation produced all over the accretion procedure balances the gravity of the infalling subject matter,” stated astronomer and find out about co-author Julia Scharwächter of the Gemini Observatory and NOIRLab.Those primordial black holes are idea to have originated in one in all two techniques, both following the explosive dying of the universe’s first era of stars or during the cave in of enormous clouds of gasoline provide within the early universe.”The invention of LID-568 means that a good portion of mass expansion can happen all over a unmarried episode of speedy accretion. This is able to lend a hand provide an explanation for how supermassive black holes shaped so early within the universe, without reference to how they originated,” Suh stated.”Till now, we now have lacked observational affirmation of ways those black holes may develop so temporarily within the early universe,” Suh added.A key signal of a rising supermassive black hollow is emission of X-rays, high-energy electromagnetic radiation with very quick wavelengths. Subject material swirling round a supermassive black hollow earlier than it’s ate up is superheated and glows strongly in X-ray wavelengths. The researchers first noticed LID-568 the use of NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory after which studied it extra intently the use of Webb’s infrared observational functions.The Webb observations counsel the lifestyles of a few type of mechanism in which a black hollow can gobble up subject matter at a quicker tempo than prior to now believed imaginable.”LID-568 is exceptional because of its excessive expansion charge and the truth that it exists so early within the universe,” Suh stated. “We do not know but how LID-568 is in a position to exceed the Eddington restrict. To analyze additional, we want extra knowledge, so we’re making plans to habits follow-up observations with Webb.” Join right here.Reporting through Will Dunham, Modifying through Rosalba O’BrienOur Requirements: The Thomson Reuters Believe Ideas., opens new tabPurchase Licensing Rights
Webb telescope finds speedy expansion of primordial black hollow