From in all places the sky, the Universe is hurling mysterious alerts.We do not truly know what they’re, or what is making them; however a brand new research of the place they’re coming from offers us clues in regards to the resources of the extraordinary emissions we name speedy radio bursts (FRBs).
Led by way of astronomer Kritti Sharma of the California Institute of Era, a world staff performed a census and made up our minds that FRBs are much more likely to return from galaxies with quite younger celebrity populations. That is relatively anticipated. What the researchers did not be expecting was once that the ones galaxies have been much more likely to be fairly massive, with massive numbers of stars – that are in truth beautiful uncommon.
This implies that there may well be one thing extraordinary about the way in which FRBs are generated.
We have already got some beautiful just right concepts about what FRBs are. First, an outline: they’re very robust however very transient emissions of radio mild that closing from fractions of a millisecond to a number of seconds. They arrive from all around the sky, their resources thousands and thousands to billions of light-years away steadily seeming to flash as soon as and not once more. An artist’s impact of a magnetar emitting a burst of radiation. (Sophia Dagnello, NRAO/AUI/NSF)This makes them unattainable to are expecting and hard to track, however we are getting higher at detection with wide-view surveillance, and higher at finding their host galaxies, too.
An artist’s impact of a magnetar emitting a burst of radiation. (Sophia Dagnello, NRAO/AUI/NSF)This makes them unattainable to are expecting and hard to track, however we are getting higher at detection with wide-view surveillance, and higher at finding their host galaxies, too.
As for what they’re, we are homing in on that too. Spoiler: it is not extraterrestrial beings. Quite, the primary FRB detected proper right here within the Milky Long ago in 2020 was once traced to a magnetar – one of those neutron celebrity that has a magnetic box 1,000 instances extra robust than an unusual neutron celebrity’s. The frenzy-pull interplay between the magnetic box and the thing’s gravity can create starquakes that ship radio mild flashing around the sky.
Now not all FRBs behave the similar, so it is imaginable that there’s a couple of roughly supply. Narrowing down the place the ones resources take a seat tells us one thing in regards to the environmental prerequisites which might be possibly to supply them, which in flip permits us to make inferences about what they’re.
Sharma and her colleagues gathered observations the use of a radio interferometer referred to as the Deep Synoptic Array in a brand new effort to come across FRBs and localize them. They in moderation studied the houses of 30 FRB host galaxies, and made up our minds that the radio bursts normally emerge from galaxies with populations of younger stars.
This isn’t unexpected if FRB progenitors are magnetars. Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of huge stars that experience long past supernova by the use of core fall down, and large stars have shorter lifespans than smaller ones. Magnetars are younger neutron stars, so we look forward to finding them in puts the place many of the stars are younger and feature quick lives.
Despite the fact that some FRBs have prior to now been detected in populations of outdated stars, and in low-mass galaxies, the staff’s research confirmed that the most typical progenitors by way of a long way are high-mass galaxies with younger stars. This implies that vast, younger stellar environments are necessary for the formation of FRB progenitors; in the event that they weren’t, we might see a broader distribution throughout galaxy sorts.
 An artist’s impact of a magnetar emitting polarized radiation thru its magnetic box. (CSIRO)Why this may well be is unknown, however the researchers imagine that the metallicity of those huge star-forming galaxies would possibly play a job. Huge galaxies normally have a miles upper steel content material than lower-mass opposite numbers, and have a tendency to make heavier stars, too.
An artist’s impact of a magnetar emitting polarized radiation thru its magnetic box. (CSIRO)Why this may well be is unknown, however the researchers imagine that the metallicity of those huge star-forming galaxies would possibly play a job. Huge galaxies normally have a miles upper steel content material than lower-mass opposite numbers, and have a tendency to make heavier stars, too.
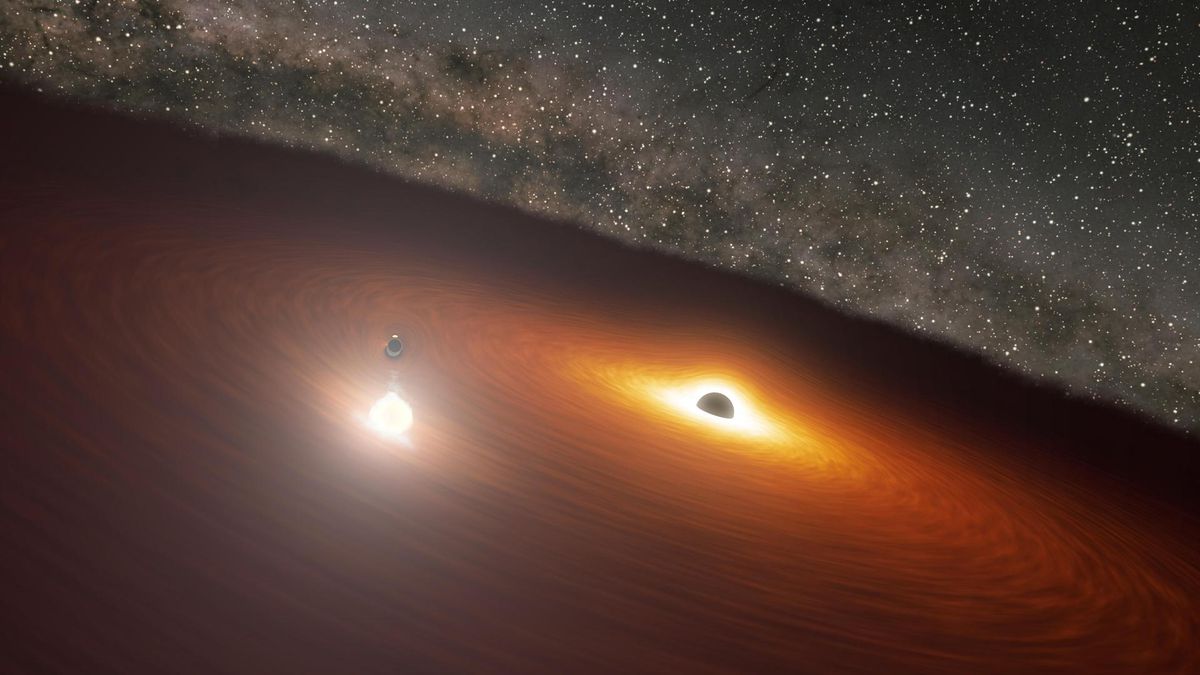
However there may be any other drawback. Core-collapse supernovae happen at a price very similar to the speed of celebrity formation within the Universe. If the magnetars that produce FRBs shape on this means, the distribution of FRBs will have to be extensively in keeping with the distribution of core-collapse supernovae, even for low mass galaxies – however it’s not. This implies that magnetars that shape by the use of core fall down aren’t the principle FRB progenitor.
The staff performed simulations, and located an answer. The magnetars that emit FRBs may just shape from binary celebrity mergers. That is much more likely to happen in environments with extra huge stars, such because the galaxies the researchers known.
We nonetheless wouldn’t have a holistic reason behind the origins of FRBs, however the analysis considerably strengthens the case for magnetars, and means that particular instances for the formation of the ones magnetars also are at play.
The learn about of FRBs continues to be progressing, however astronomers are finding extra of the extraordinary alerts continuously. The extra we discover, the extra knowledge we will crunch to get to the bottom of the thriller of FRBs’ origins. It is a vastly thrilling time to be alive and learning the celebs.The analysis has been printed in Nature.
The Mysterious Origins of Rapid Radio Bursts Might In spite of everything Be Recognized







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23954043/VRG_Illo_STK427_Podcasting_playbars.jpg)




